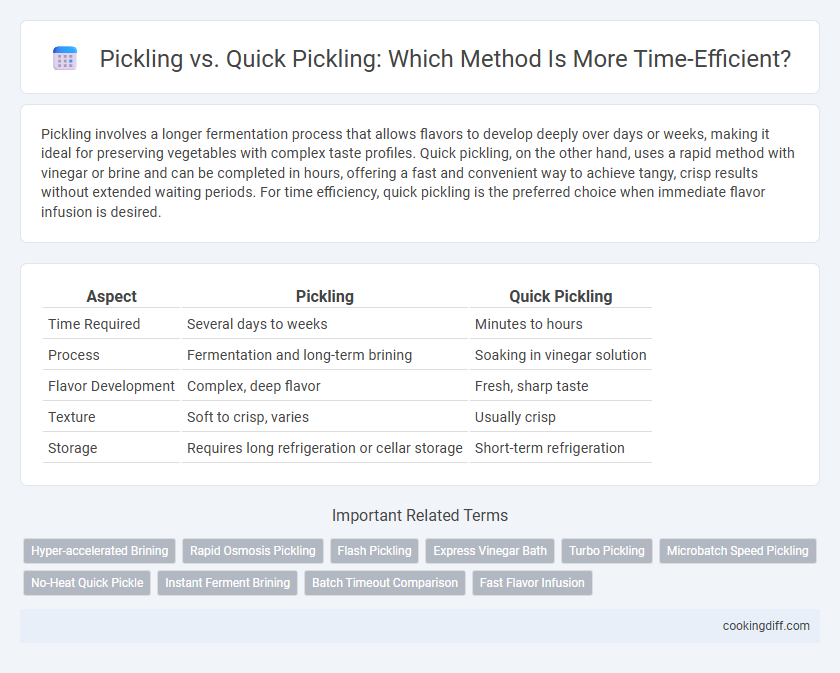
Pickling involves a longer fermentation process that allows flavors to develop deeply over days or weeks, making it ideal for preserving vegetables with complex taste profiles. Quick pickling, on the other hand, uses a rapid method with vinegar or brine and can be completed in hours, offering a fast and convenient way to achieve tangy, crisp results without extended waiting periods. For time efficiency, quick pickling is the preferred choice when immediate flavor infusion is desired.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pickling | Quick Pickling |
|---|---|---|
| Time Required | Several days to weeks | Minutes to hours |
| Process | Fermentation and long-term brining | Soaking in vinegar solution |
| Flavor Development | Complex, deep flavor | Fresh, sharp taste |
| Texture | Soft to crisp, varies | Usually crisp |
| Storage | Requires long refrigeration or cellar storage | Short-term refrigeration |
Understanding Traditional Pickling vs Quick Pickling
Traditional pickling involves fermenting vegetables in a brine solution over several weeks, allowing natural bacteria to develop complex flavors. Quick pickling shortcuts this process by soaking produce in vinegar and spices, achieving edible results within hours or days.
Understanding traditional pickling versus quick pickling highlights the trade-off between flavor depth and time investment. Traditional pickling relies on lacto-fermentation, which enhances probiotics and imparts tangy, robust tastes but requires patience. Quick pickling is ideal for immediate consumption, offering crisp texture and tang without the lengthy fermentation period.
Time Commitment: Traditional Pickling Compared to Quick Pickling
Traditional pickling requires a time commitment ranging from several days to weeks to develop full flavors as the brine ferments vegetables slowly. This process allows for deeper flavor complexity but demands extended refrigeration or cool storage periods.
Quick pickling reduces the time needed to just a few hours to a couple of days by using a hot vinegar-based brine, making it ideal for immediate consumption. This method sacrifices some depth of flavor complexity yet maximizes convenience and speed for busy cooks.
Preparation Steps: Which Method Is Faster?
Pickling involves a thorough preparation process including washing, slicing, brining, and a long fermentation period that can last from days to weeks, making it time-intensive. This method requires more detailed steps to ensure proper preservation and flavor development.
Quick pickling drastically reduces preparation time by using a hot vinegar brine poured directly over vegetables, skipping lengthy fermentation periods. This approach allows for consumption within hours to days, making it significantly faster for immediate use.
Ingredient Differences in Pickling Methods
Traditional pickling uses a fermentation process that relies on salt, water, and time to develop complex flavors, while quick pickling involves soaking ingredients in vinegar-based brine for a short period. Ingredients like cucumbers and cabbage in traditional pickling undergo natural microbial fermentation, whereas quick pickling often incorporates a variety of fresh herbs, spices, and sugar to enhance immediate flavor. The choice between these methods impacts the texture and taste, with quick pickling favoring crispness and sharpness, and traditional pickling offering deeper, tangier profiles due to extended fermentation.
Time-Saving Tips for Quick Pickling
| Quick pickling reduces processing time by using preheated vinegar brine and thinly sliced vegetables, speeding up flavor absorption to as little as 30 minutes. Traditional pickling involves a fermentation or longer soaking period, often taking days to weeks for optimal taste development. Time-saving tips include using warm brine, thin cuts, and immediate refrigeration to maximize freshness and rapid flavor infusion. |
Flavor Development: Speed vs Depth
Pickling allows flavors to mature and deepen over several days to weeks, resulting in a more complex taste profile. Quick pickling accelerates the process by using vinegar and a shorter soaking time, providing immediate but less nuanced flavors.
- Flavor Complexity - Traditional pickling develops richer, more layered flavors due to extended fermentation.
- Time Efficiency - Quick pickling reduces preparation time drastically, ideal for immediate consumption.
- Flavor Profile - Quick pickling offers a brighter, sharper taste while slower pickling yields mellow, well-rounded flavors.
Ideal Foods for Quick Pickling and Traditional Pickling
Quick pickling significantly reduces the preservation time compared to traditional pickling methods by using vinegar-based brines and refrigeration. Traditional pickling involves fermenting vegetables for weeks, enhancing flavors over time but requiring patience and specific conditions.
- Quick pickling is ideal for cucumbers, radishes, and carrots - These vegetables absorb flavors rapidly, making them perfect for short-term pickling.
- Traditional pickling suits cabbage, cucumbers, and green beans - These foods develop complex, tangy flavors through a lengthy fermentation process.
- Time efficiency varies significantly - Quick pickling takes hours to days, while traditional pickling can take several weeks to achieve desired taste.
Choosing between quick and traditional pickling depends on desired flavor complexity and available preparation time.
Storage and Shelf Life: Quick Pickles vs Fully Pickled
How do storage requirements and shelf life compare between quick pickling and traditional pickling methods? Quick pickles, typically stored in the refrigerator, have a shorter shelf life of up to a few weeks. Fully pickled items undergo fermentation or complete brining, allowing them to be stored at room temperature for several months while developing deeper flavors.
Equipment Needed: Quick Pickling vs Traditional Techniques
Quick pickling requires minimal equipment, often just jars and vinegar solutions, enabling faster preparation and consumption. Traditional pickling involves specialized tools like fermentation crocks and airlocks, which extend processing time but enhance flavor complexity.
- Quick Pickling Equipment - Typically involves clean jars, vinegar, spices, and refrigeration for immediate use.
- Traditional Pickling Equipment - Utilizes fermentation crocks, weights, and airlocks to maintain anaerobic environments over weeks or months.
- Time Efficiency Impact - Minimal equipment in quick pickling reduces setup and waiting times compared to the elaborate setup needed for traditional methods.
Related Important Terms
Hyper-accelerated Brining
Hyper-accelerated brining significantly reduces the time required for traditional pickling by rapidly infusing flavors and preserving agents into vegetables, achieving similar taste and texture outcomes in hours instead of days. Quick pickling, while faster than standard methods, typically relies on vinegar-based solutions and shorter soaking periods, but hyper-accelerated brining optimizes osmotic pressure and temperature control to enhance time efficiency without compromising quality.
Rapid Osmosis Pickling
Rapid osmosis pickling significantly reduces processing time compared to traditional pickling methods by accelerating salt and flavor infusion through enhanced osmosis. This technique enables vegetables to achieve optimal taste and texture within hours rather than days, making it ideal for efficient food preservation.
Flash Pickling
Flash pickling significantly reduces processing time compared to traditional pickling by using shorter marination periods and higher acidity levels to quickly preserve vegetables. This method enhances time efficiency while maintaining flavor and texture, making it ideal for rapid preparation and immediate consumption.
Express Vinegar Bath
Express vinegar bath in quick pickling reduces preservation time to under 24 hours compared to traditional pickling methods that require weeks for fermentation. This rapid acid bath not only accelerates flavor infusion and texture softening but also maintains safety by preventing microbial growth efficiently.
Turbo Pickling
Turbo pickling accelerates the fermentation process by using higher temperatures and specific microbial starters, reducing the pickling time from weeks to just a few days compared to traditional pickling methods. Quick pickling, typically involving vinegar and shorter marination, is faster but lacks the depth of flavor and probiotic benefits found in turbo pickled products.
Microbatch Speed Pickling
Microbatch Speed Pickling significantly reduces fermentation time by utilizing smaller batches and optimized brine concentrations, allowing rapid flavor development within hours instead of days. This method outperforms traditional pickling by enhancing time efficiency without compromising texture or taste, making it ideal for fast-paced production environments.
No-Heat Quick Pickle
No-Heat Quick Pickling drastically reduces preparation time by eliminating the cooking step, allowing vegetables to be ready in as little as 30 minutes compared to traditional pickling methods that require days or weeks for fermentation. This time-efficient technique preserves texture and bright flavors while ensuring rapid infusion of vinegar and spices.
Instant Ferment Brining
Pickling typically requires several days to develop flavors through traditional fermentation, while quick pickling drastically reduces this time by using vinegar-based solutions for immediate preservation. Instant ferment brining enhances time efficiency by combining the benefits of fermentation with rapid brine absorption, allowing for faster flavor development compared to conventional pickling methods.
Batch Timeout Comparison
Traditional pickling typically requires several days to weeks for full flavor development, whereas quick pickling accelerates this process to just a few hours or overnight. Batch timeout for quick pickling methods ranges from 30 minutes to 24 hours, significantly improving time efficiency compared to the extended fermentation periods in conventional pickling.
Pickling vs Quick Pickling for time efficiency. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com