Pickling involves preserving fruits or vegetables in a vinegar-based solution, creating a sour flavor that enhances their shelf life and taste, while shrubs specifically refer to concentrated drinking vinegars blended with fruit, sugar, and vinegar for cocktails and refreshing beverages. Shrubs offer a more balanced sweetness and acidity, making them ideal for versatile drink mixers, whereas pickled products are primarily consumed as snacks or condiments. Choosing between pickling and shrubs depends on whether the goal is long-term preservation or creating flavorful drinking vinegars for mixology.
Table of Comparison
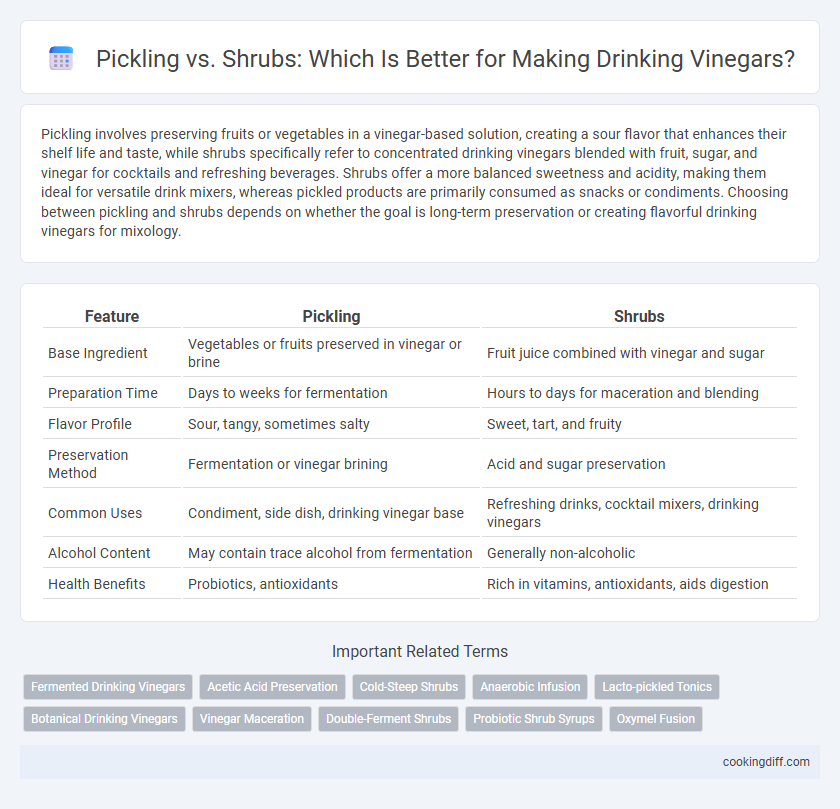
| Feature | Pickling | Shrubs |
|---|---|---|
| Base Ingredient | Vegetables or fruits preserved in vinegar or brine | Fruit juice combined with vinegar and sugar |
| Preparation Time | Days to weeks for fermentation | Hours to days for maceration and blending |
| Flavor Profile | Sour, tangy, sometimes salty | Sweet, tart, and fruity |
| Preservation Method | Fermentation or vinegar brining | Acid and sugar preservation |
| Common Uses | Condiment, side dish, drinking vinegar base | Refreshing drinks, cocktail mixers, drinking vinegars |
| Alcohol Content | May contain trace alcohol from fermentation | Generally non-alcoholic |
| Health Benefits | Probiotics, antioxidants | Rich in vitamins, antioxidants, aids digestion |
Introduction to Drinking Vinegars
Drinking vinegars, also known as shrub syrups, are tart, flavorful beverages made by infusing vinegar with fruits, herbs, and sugar. Unlike traditional pickling, which preserves vegetables, drinking vinegars focus on creating a refreshing, healthful tonic rich in acetic acid and antioxidants.
Pickling uses a fermentation or brining process to transform vegetables and sometimes fruits, emphasizing preservation and shelf life. Shrubs, or drinking vinegars, emphasize balance between acidity and sweetness, often consumed diluted with water or alcohol for a tangy drink. These vinegars harness natural acids and flavorful infusions to provide digestive benefits and unique taste experiences distinct from classic pickled foods.
What is Pickling in Beverage Making?
What is pickling in beverage making? Pickling in beverage making involves fermenting fruits, vegetables, or herbs in vinegar or brine to create flavorful drinking vinegar bases. This method preserves ingredients while developing tart, complex flavors ideal for crafting artisanal shrubs, which are sweetened vinegar concentrates used in cocktails and sodas.
What are Shrubs?
Shrubs are concentrated vinegar-based syrups made from fruit, sugar, and vinegar, traditionally used as a refreshing beverage base. Unlike pickling, which preserves whole or sliced produce in vinegar and spices, shrubs focus on creating a balanced sweet and tart liquid for drinks.
- Shrubs are drinking vinegars - They blend fruit juice, sugar, and vinegar to create a flavorful syrup.
- Shrubs offer versatility - Used in cocktails, mocktails, or diluted with water as a refreshing drink.
- Shrubs differ from pickling - Pickling preserves texture and flavor of fruits or vegetables, while shrubs emphasize a concentrated liquid form.
Shrubs provide a unique tangy flavor profile ideal for beverage applications, making them distinct from traditional pickled products.
Key Differences: Pickling vs Shrubs
Pickling transforms vegetables through fermentation or vinegar preservation to enhance shelf life and flavor, while shrubs are concentrated vinegar-based syrups infused with fruit, sugar, and spices for drinking. Shrubs focus on creating balanced sweet and tart profiles for cocktails, contrasting with pickling's preservation purpose.
- Purpose - Pickling preserves and flavors vegetables; shrubs create drinkable vinegar syrups.
- Ingredients - Pickling mainly uses vegetables, salt, and vinegar; shrubs combine fruit, sugar, and vinegar.
- Usage - Pickled items serve as condiments or snacks; shrubs function as cocktail mixers or refreshing beverages.
Ingredients Used in Pickling vs Shrubs
Pickling typically uses vegetables, salt, water, and vinegar as core ingredients to preserve and ferment foods, enhancing their flavor and shelf life. Shrubs, in contrast, combine fruit, sugar, and vinegar to create a concentrated syrup that balances sweetness and acidity for drinking vinegars. The primary distinction lies in pickling's preservation focus versus shrubs' flavor infusion through sweetened vinegar blends.
Flavor Profiles: Pickling vs Shrub Drinks
Pickling imparts a robust, savory flavor to drinking vinegars, often characterized by tangy and salty notes from vinegar and spices during fermentation. Shrubs, on the other hand, offer a balanced combination of sweetness, acidity, and fruitiness due to the use of fresh fruit, sugar, and vinegar in their preparation.
The flavor profile of pickled vinegars tends to be more intense and complex, ideal for savory cocktails and culinary applications. Shrub drinks provide a refreshing, bright taste that enhances a variety of beverages with a layered and nuanced sweetness.
Health Benefits of Pickling vs Shrubs
| Health Benefit Aspect | Pickling | Shrubs (Drinking Vinegars) |
| Probiotic Content | Rich in live beneficial bacteria promoting gut health through natural fermentation. | Typically vinegar-based, contains acetic acid but lacks live probiotics due to pasteurization. |
| Antioxidants and Nutrients | Retains vitamins and antioxidants from vegetables, supporting immune function and reducing inflammation. | Infused with fruits and herbs, delivering antioxidants but often in lower concentrations than fresh or fermented produce. |
| Blood Sugar Regulation | May improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar through fermented acids. | Acetic acid in shrubs has been shown to moderate blood glucose spikes after meals. |
Methods and Techniques: Pickling vs Shrubs
Pickling involves fermenting or preserving fruits and vegetables in vinegar or brine to develop complex flavors, while shrubs use a quick infusion method combining vinegar, sugar, and fruit for tangy drinking vinegars. Techniques for pickling focus on controlled fermentation over days or weeks, whereas shrubs require minimal time, balancing acidity and sweetness for immediate use.
- Pickling Fermentation - Uses natural bacteria to ferment vegetables or fruits, creating a unique, sour flavor profile over time.
- Shrub Infusion - Combines vinegar, sugar, and fresh fruit, often macerated for hours to impart a bright, tangy taste quickly.
- Preservation Methods - Pickling relies on brine or vinegar to preserve and develop flavors, while shrubs focus on blending and sweetening for versatile drinking vinegars.
Serving and Usage Ideas
Pickling vinegars are typically served chilled and used as a tangy accompaniment in salads, marinades, and cold dishes, enhancing flavors with a sharp, acidic bite. Shrubs, on the other hand, combine vinegar with fruit and sugar, making them ideal for cocktail mixers, sparkling water infusions, or drizzled over desserts for a balanced sweet-tart profile. Both vinegars offer versatile serving options, but shrubs excel in beverage applications due to their natural sweetness and fruit-forward taste.
Related Important Terms
Fermented Drinking Vinegars
Fermented drinking vinegars created through pickling involve a natural fermentation process using raw fruits, sugar, and beneficial bacteria, resulting in a tangy, probiotic-rich beverage. Shrubs, in contrast, are vinegar-based syrups combining vinegar, fruit, and sweetener without fermentation, offering a quicker, non-probiotic alternative for drinking vinegars.
Acetic Acid Preservation
Pickling utilizes acetic acid concentrations typically between 4-8%, effectively preserving vegetables by creating an acidic environment that inhibits microbial growth, whereas shrubs combine fruit, sugar, and vinegar with varying acetic acid levels, resulting in a sweeter, less acidic profile suited for drinking vinegars. The higher acetic acid concentration in traditional pickling ensures longer preservation and stronger antimicrobial effects compared to the milder acidity and flavor complexity found in shrub-based drinking vinegars.
Cold-Steep Shrubs
Cold-steep shrubs enhance drinking vinegars by infusing fruit, sugar, and vinegar slowly at low temperatures, preserving vibrant flavors and bright acidity compared to traditional pickling methods that involve heat and fermentation. This technique offers a balanced and refreshing profile ideal for cocktails, emphasizing aromatic complexity and a smoother taste.
Anaerobic Infusion
Pickling and shrubs differ primarily in their fermentation environments, with pickling relying on anaerobic infusion to preserve vegetables through lactic acid fermentation, while shrubs use acidic infusions of fruit, sugar, and vinegar without strict anaerobic conditions. The anaerobic infusion in pickling promotes beneficial bacterial growth for sour flavor development, whereas shrubs emphasize sweet-tart balance without fermentation.
Lacto-pickled Tonics
Lacto-pickled tonics leverage natural fermentation with lactic acid bacteria to produce complex, probiotic-rich drinking vinegars distinct from shrubs, which typically combine vinegar, fruit, and sugar without active fermentation. This method enhances gut health benefits and introduces deeper umami flavors that develop over extended fermentation periods, setting lacto-pickled tonics apart in functional beverage crafting.
Botanical Drinking Vinegars
Botanical drinking vinegars made from shrubs offer a complex flavor profile and richer phytochemical composition compared to traditional pickling methods, which primarily focus on preserving without enhancing botanical diversity. Shrubs incorporate natural fruit acids, herbs, and spices, resulting in probiotic-rich vinegars that provide both health benefits and versatile culinary uses beyond the acidic tang of pickled foods.
Vinegar Maceration
Vinegar maceration in pickling leverages the natural fermentation process to infuse vegetables directly with acetic acid, creating a complex flavor profile rich in probiotics and preserving nutrients. In contrast, shrubs use a vinegar maceration method where fruit, sugar, and vinegar are combined and steeped to develop a balanced sweet-tart drinking vinegar, emphasizing fruit essence over vegetable preservation.
Double-Ferment Shrubs
Double-ferment shrubs utilize an initial fermentation to develop complex flavors by converting sugars into alcohol, followed by a secondary fermentation with vinegar-producing bacteria that enhances acidity and preserves the beverage naturally. Compared to traditional pickling methods, double-ferment shrubs offer a balanced tartness and depth, making them ideal for creating nuanced, probiotic-rich drinking vinegars.
Probiotic Shrub Syrups
Probiotic shrub syrups offer a vibrant alternative to traditional pickling by combining fermented fruit vinegar with live cultures that enhance gut health and flavor complexity. Unlike pickled produce, shrub syrups provide a balanced tartness and natural effervescence, making them an ideal base for nutritious drinking vinegars rich in antioxidants and beneficial probiotics.
Pickling vs Shrubs for making drinking vinegars. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com