Pickling preserves food through an acidic brine that inhibits harmful bacteria, while probiotic pickling promotes beneficial bacteria growth essential for gut health. Probiotic pickling involves lacto-fermentation, producing live cultures that enhance digestion and boost the immune system. Regular consumption of probiotic pickled foods supports a balanced gut microbiome, unlike traditional pickles that may lack live probiotics due to vinegar use.
Table of Comparison
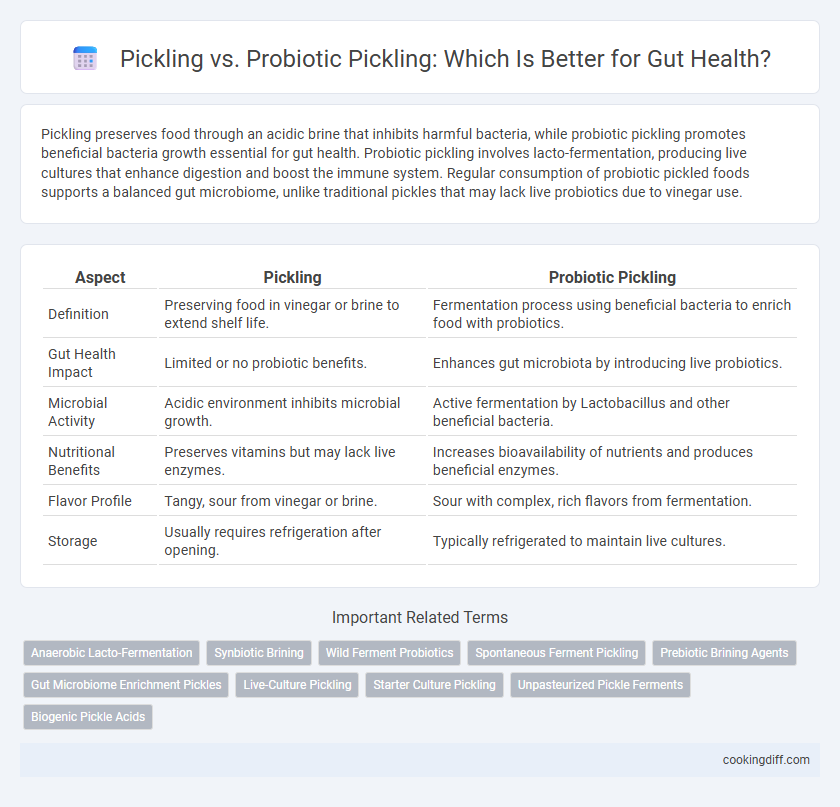
| Aspect | Pickling | Probiotic Pickling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preserving food in vinegar or brine to extend shelf life. | Fermentation process using beneficial bacteria to enrich food with probiotics. |
| Gut Health Impact | Limited or no probiotic benefits. | Enhances gut microbiota by introducing live probiotics. |
| Microbial Activity | Acidic environment inhibits microbial growth. | Active fermentation by Lactobacillus and other beneficial bacteria. |
| Nutritional Benefits | Preserves vitamins but may lack live enzymes. | Increases bioavailability of nutrients and produces beneficial enzymes. |
| Flavor Profile | Tangy, sour from vinegar or brine. | Sour with complex, rich flavors from fermentation. |
| Storage | Usually requires refrigeration after opening. | Typically refrigerated to maintain live cultures. |
Understanding Traditional Pickling Methods
Traditional pickling methods involve immersing vegetables in a brine solution of salt, water, and sometimes vinegar, relying on natural fermentation processes to preserve the food. This fermentation encourages the growth of lactic acid bacteria, which can contribute to gut health by introducing beneficial microbes.
In contrast, probiotic pickling specifically aims to maximize live cultures by avoiding heat and excessive acidity that can kill beneficial bacteria. Understanding these traditional techniques highlights how natural fermentation supports a diverse and balanced gut microbiome through probiotic-rich foods.
What Is Probiotic Pickling?
| Probiotic pickling involves fermenting vegetables using natural bacteria such as Lactobacillus strains, promoting the growth of beneficial gut microbes. |
| This fermentation process increases the production of probiotics, which enhance digestive health by balancing the gut microbiome and improving nutrient absorption. |
| Unlike traditional pickling with vinegar, probiotic pickling relies on natural lactic acid fermentation, making it a powerful functional food for supporting immune function and gut integrity. |
Key Differences Between Pickling and Probiotic Pickling
Traditional pickling preserves food using vinegar or brine, which inhibits bacterial growth and results in a tangy taste but lacks live beneficial microorganisms. Probiotic pickling employs natural fermentation processes where lactic acid bacteria thrive, enhancing gut health by introducing probiotics.
Key differences include the presence of live cultures in probiotic pickling, which support digestion and immunity, whereas traditional pickling offers preservation without probiotic benefits. Probiotic pickled foods often have higher concentrations of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus, essential for maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
Fermentation vs. Vinegar: Impact on Gut Health
Fermentation-based pickling promotes the growth of beneficial probiotics that enhance gut microbiota diversity and improve digestion. In contrast, vinegar-based pickling uses acetic acid for preservation, which does not support probiotic development or gut flora balance. Consuming fermented pickles can boost immune function and reduce inflammation by supplying live microorganisms essential for gut health.
Microbial Benefits in Probiotic Pickling
Pickling preserves food through fermentation or acid, but probiotic pickling specifically promotes beneficial microbial growth. The live cultures in probiotic pickling enhance gut flora diversity and aid digestion.
Probiotic pickling involves natural fermentation where Lactobacillus bacteria proliferate, producing lactic acid that improves intestinal health. This process boosts immune function by supporting a balanced gut microbiome and increasing short-chain fatty acid production. Unlike traditional pickling, probiotic pickling provides active enzymes and vitamins that contribute to overall gut well-being.
Nutritional Changes During the Pickling Process
How do nutritional changes differ between traditional pickling and probiotic pickling for gut health? Traditional pickling often involves vinegar, which preserves food but can reduce some heat-sensitive nutrients, while probiotic pickling relies on fermentation that enhances beneficial bacteria and increases bioavailability of vitamins like B12 and K2. This fermentation process promotes gut microbiome diversity, supporting improved digestion and immune function compared to non-fermented pickled foods.
Shelf Life and Safety: Pickling vs. Probiotic Pickling
Pickling preserves vegetables through vinegar or brine, offering a long shelf life but lacking live probiotics essential for gut health. Probiotic pickling employs fermentation, producing beneficial bacteria that support digestion yet requires careful handling to ensure safety and shorter preservation periods.
- Vinegar-based Pickling Extends Shelf Life - Acidic environments inhibit microbial growth, allowing pickled foods to last months or even years when sealed properly.
- Probiotic Pickling Supports Gut Health - Fermentation generates live Lactobacillus strains that enhance the intestinal microbiome and improve digestion.
- Safety Concerns in Probiotic Pickling - Improper fermentation conditions can lead to contamination or pathogen growth, necessitating strict hygiene and monitoring.
Flavor Profiles: Fermented vs. Vinegar-Pickled Foods
Fermented pickling relies on natural lactic acid bacteria, creating complex, tangy flavors rich in umami and beneficial probiotics that support gut health. Vinegar-pickled foods feature a sharp, acidic taste derived from acetic acid, but lack live probiotics essential for digestive wellness. The distinctive sourness of fermented pickles enhances both flavor and microbiome diversity, making them superior for gut-friendly diets compared to vinegar-pickled alternatives.
DIY: How to Make Probiotic Pickles at Home
Probiotic pickling involves fermenting cucumbers in a saltwater brine that encourages beneficial bacteria growth, enhancing gut health more effectively than traditional vinegar-based pickling. Making probiotic pickles at home requires minimal ingredients and allows control over fermentation time, ensuring maximum probiotic benefits.
- Use non-iodized salt - Sea salt or kosher salt helps maintain the right environment for lactic acid bacteria without inhibiting fermentation.
- Maintain proper brine ratio - A common 2% salt-to-water concentration prevents spoilage and promotes healthy bacterial growth.
- Ferment at room temperature - Keeping pickles at 65-75degF for 1-4 weeks optimizes probiotic development and flavor complexity.
Related Important Terms
Anaerobic Lacto-Fermentation
Anaerobic lacto-fermentation in probiotic pickling enhances gut health by fostering beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus, which produce lactic acid and improve digestion. In contrast, traditional pickling often relies on vinegar or brine without promoting live probiotics, limiting its impact on the microbiome.
Synbiotic Brining
Synbiotic brining combines prebiotic fibers with probiotic bacteria during the pickling process, enhancing gut health by promoting beneficial microflora growth more effectively than traditional pickling. This method improves digestion and boosts immune function by fostering a balanced intestinal microbiome through synergistic synbiotic interactions.
Wild Ferment Probiotics
Wild Ferment Probiotics harness the natural microbial diversity found in traditional pickling processes, enhancing gut health through a rich concentration of live beneficial bacteria. Unlike standard pickling, which often involves vinegar and heat that kill probiotics, wild fermentation preserves and promotes the growth of gut-friendly lactobacilli and bifidobacteria essential for digestive balance.
Spontaneous Ferment Pickling
Spontaneous ferment pickling harnesses natural lactic acid bacteria present on vegetables and in the environment, promoting a diverse probiotic profile essential for gut health. Unlike traditional vinegar-based pickling, this method enhances microbial complexity and bioavailability of nutrients, supporting improved digestion and immune function.
Prebiotic Brining Agents
Prebiotic brining agents such as inulin, chicory root, and Jerusalem artichoke enhance traditional pickling by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, thereby improving digestive health more effectively than standard vinegar-based pickling. Unlike probiotic pickling, which introduces live microorganisms, prebiotic brining supports the microbiome by providing dietary fibers that selectively stimulate beneficial bacterial activity in the gut.
Gut Microbiome Enrichment Pickles
Pickling preserves vegetables through fermentation, enhancing gut microbiome enrichment by promoting beneficial bacteria growth in probiotic pickling processes. Probiotic pickles contain live cultures such as Lactobacillus, which improve gut health by increasing microbial diversity and supporting digestion.
Live-Culture Pickling
Live-culture pickling involves fermenting vegetables with beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus, which enhances gut health by increasing the population of probiotics that support digestion and immune function. Unlike traditional pickling that uses vinegar and offers minimal probiotic benefits, live-culture pickling promotes a rich diversity of live microbes essential for maintaining a balanced intestinal microbiome.
Starter Culture Pickling
Starter culture pickling uses specific beneficial bacteria strains to ferment vegetables, enhancing probiotic content and promoting balanced gut microbiota more effectively than traditional pickling methods. This targeted fermentation supports improved digestion and boosts immune function by increasing the bioavailability of nutrients and fostering healthy microbial diversity.
Unpasteurized Pickle Ferments
Unpasteurized pickle ferments retain live, beneficial bacteria that enhance gut microbiota diversity and support digestive health, unlike traditional pickling methods that often involve pasteurization, which kills probiotics. Consuming these naturally fermented pickles provides essential Lactobacillus strains that improve nutrient absorption and strengthen immune function.
Pickling vs Probiotic Pickling for gut health. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com