Poaching preserves moisture by gently cooking food in a simmering liquid, preventing drying out and maintaining delicate textures. En papillote, which involves steaming food wrapped in parchment, traps steam and natural juices, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes with excellent moisture retention. Both methods excel at keeping food moist, but en papillote enhances flavor infusion while poaching offers a more uniform cooking environment.
Table of Comparison
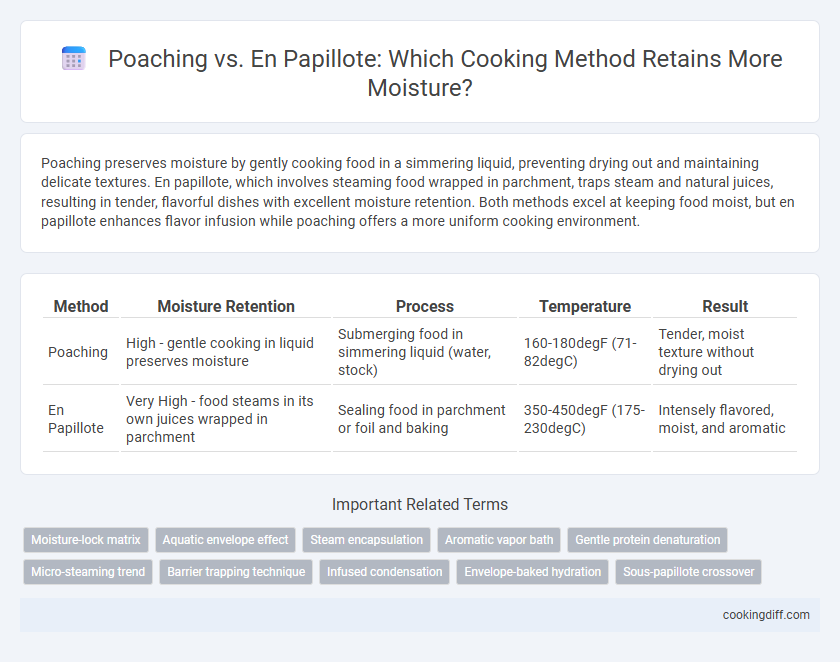
| Method | Moisture Retention | Process | Temperature | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poaching | High - gentle cooking in liquid preserves moisture | Submerging food in simmering liquid (water, stock) | 160-180degF (71-82degC) | Tender, moist texture without drying out |
| En Papillote | Very High - food steams in its own juices wrapped in parchment | Sealing food in parchment or foil and baking | 350-450degF (175-230degC) | Intensely flavored, moist, and aromatic |
Introduction to Moisture Retention in Cooking
| Poaching maintains moisture by gently cooking food in liquid at low temperatures, preventing dryness and preserving tenderness. En papillote, a method of steaming food wrapped in parchment or foil, traps steam and natural juices, enhancing moisture retention and intensifying flavors. Both techniques lock in moisture effectively but differ in heat transfer and flavor development, with poaching providing subtle infusion and en papillote creating a self-steaming environment. |
Understanding Poaching: Definition and Techniques
How does poaching compare to en papillote in retaining moisture in food? Poaching involves cooking food gently in a simmering liquid, which allows it to absorb moisture while maintaining a tender texture. En papillote traps steam within a parchment or foil packet, effectively sealing in the food's natural juices and enhancing flavor retention.
What is En Papillote? Method Explained
En papillote is a French cooking technique that involves sealing food, typically fish or vegetables, in a parchment paper pouch to steam in its own moisture and flavors. This method preserves the natural juices better than poaching, which submerges the food in liquid and can dilute taste and texture. En papillote enhances moisture retention by trapping steam, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes without added fat or water loss.
Key Differences: Poaching vs En Papillote
Poaching involves simmering food gently in water or broth, which helps retain moisture through direct liquid contact, while en papillote traps steam inside a parchment packet to preserve juices and flavors. Both methods are effective for moisture retention but differ in technique and flavor infusion.
- Moisture Retention Method - Poaching relies on liquid immersion to keep food moist, whereas en papillote uses steam trapped within the parchment to maintain moisture.
- Flavor Development - Poaching imparts subtle flavors from the cooking liquid, while en papillote enhances natural flavors by steaming food with herbs and aromatics sealed inside.
- Cooking Environment - Poaching occurs in an open pot with circulating liquid, while en papillote cooks in a closed packet, creating a mini steam oven effect.
How Poaching Retains Moisture in Foods
Poaching involves cooking food gently in simmering liquid at low temperatures, which helps to preserve its natural moisture content. Compared to en papillote, poaching prevents moisture loss by immersing the food directly in water or broth, maintaining its succulence.
During poaching, the gentle heat penetrates the food evenly, minimizing cellular breakdown and reducing the evaporation of internal juices. The surrounding liquid acts as a heat buffer, ensuring the food retains its texture and flavor while staying moist. This method is especially effective for delicate proteins like fish and eggs, where moisture retention is crucial for optimal taste and tenderness.
En Papillote: Moisture Retention Mechanisms
En Papillote cooking traps steam inside a parchment or foil packet, creating a moist, enclosed environment that enhances moisture retention in the food. This gentle method prevents water-soluble nutrients and natural juices from leaching out, preserving flavor and texture better than poaching. The sealed packet allows the food to cook in its own steam, intensifying moisture levels without direct contact with water.
Temperature Control: Poaching vs En Papillote
Poaching involves cooking food gently in simmering liquid at temperatures between 160degF and 180degF, which ensures precise temperature control for even moisture retention. En papillote, cooking food sealed in parchment, uses steam and higher oven temperatures around 350degF, creating a moist environment that traps juices but offers less direct temperature regulation.
- Poaching maintains lower temperatures - This method allows delicate proteins to cook evenly without drying out by keeping the temperature consistent and below boiling point.
- En papillote relies on steam within a sealed packet - Steam generated here retains moisture efficiently but varying oven temperatures can affect heat distribution.
- Poaching provides superior temperature control - The submersion in liquid at steady low heat reduces the risk of overcooking, optimizing moisture retention.
Flavor Infusion and Its Role in Moisture Retention
Poaching gently cooks food in liquid at low temperatures, allowing subtle flavors to infuse into the food while preserving moisture through slow heat absorption. This method enhances delicate textures and ensures the food remains tender and juicy by preventing moisture loss.
En papillote traps steam and flavors inside a parchment or foil packet, creating a self-basting environment that intensifies flavor infusion while locking in moisture. The sealed cooking environment of en papillote minimizes evaporation, resulting in a rich, aromatic, and moist dish.
Ideal Ingredients for Each Technique
Poaching is ideal for delicate ingredients like fish fillets, poultry, and eggs, where gentle, low-temperature cooking in seasoned liquid preserves moisture and texture. This method works best with flavorful broths, wine, or court bouillon to infuse subtle aromas while preventing dryness.
En papillote excels with vegetables, seafood, and thin cuts of meat, wrapping ingredients in parchment paper to trap steam and natural juices during baking. Herbs, citrus slices, and olive oil are perfect companions, enhancing aroma and moisture retention without direct heat exposure.
Related Important Terms
Moisture-lock matrix
Poaching utilizes a gentle cooking method where food is submerged in liquid at low temperatures, creating a moisture-lock matrix that preserves natural juiciness and prevents dryness. En papillote cooking traps steam inside parchment, forming a sealed environment that intensifies moisture retention by enveloping the food in its own vapor.
Aquatic envelope effect
Poaching preserves moisture in delicate proteins by cooking them in a gently heated aquatic environment, which creates an aquatic envelope effect that minimizes moisture loss. En papillote, though also steam-based, encloses food in parchment, trapping steam and flavors but typically retains slightly less moisture than direct poaching due to the contained yet variable steam distribution.
Steam encapsulation
Steam encapsulation in en papillote cooking creates a sealed environment that traps moisture and preserves the natural juices of food, resulting in enhanced tenderness and flavor retention compared to traditional poaching. Unlike poaching, which submerges food in liquid causing some nutrient leaching, en papillote's steam retention minimizes water contact, effectively locking in moisture and delicate aromatics.
Aromatic vapor bath
Poaching uses a gentle aromatic vapor bath to envelop food, preserving moisture and infusing delicate flavors more effectively than en papillote, which relies on steam trapped in parchment. The aromatic vapor bath in poaching maintains a consistent low temperature, ensuring even cooking and superior moisture retention without drying out the ingredients.
Gentle protein denaturation
Poaching preserves moisture through gentle protein denaturation by cooking proteins at low temperatures, preventing toughening and excessive moisture loss. En papillote also retains moisture by sealing steam and flavors within parchment, but poaching's precise temperature control ensures more consistent tenderization and juiciness.
Micro-steaming trend
Poaching preserves moisture by gently cooking food in liquid at low temperatures, but En Papillote enhances moisture retention through micro-steaming, where steam trapped inside parchment paper intensifies hydration and flavor concentration. This emerging micro-steaming trend leverages natural condensation, creating a sealed cooking environment that outperforms traditional poaching in maintaining juiciness and nutrient absorption.
Barrier trapping technique
Poaching uses a gentle simmering technique that surrounds food with liquid to retain moisture, while en papillote traps steam within a parchment or foil barrier, creating a self-basting environment that enhances moisture retention and flavor concentration. The en papillote method's sealed barrier effectively traps natural juices and aromatic steam, offering superior moisture preservation compared to traditional poaching.
Infused condensation
Poaching preserves moisture by gently cooking food in a flavorful liquid, allowing infused condensation to continuously baste the ingredients and retain juiciness. En papillote traps steam and aromatic elements within parchment, creating a self-basting environment that seals in natural moisture and intensifies infused flavors.
Envelope-baked hydration
Envelope-baked hydration in en papillote cooking seals steam and natural juices, preserving moisture more effectively than traditional poaching, which can dilute flavors due to water immersion. This method enhances texture and retains essential nutrients by creating a self-contained steam environment around the food.
Poaching vs En Papillote for moisture retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com