Low-temp poaching preserves meat tenderness and juiciness by cooking at a gentle, consistent temperature, reducing nutrient loss and maintaining flavor integrity compared to traditional poaching methods. Poaching at lower temperatures minimizes protein denaturation and moisture escape, resulting in a more succulent texture and enhanced mouthfeel. This method is especially beneficial for delicate meats, offering a healthier cooking alternative with superior taste and texture retention.
Table of Comparison
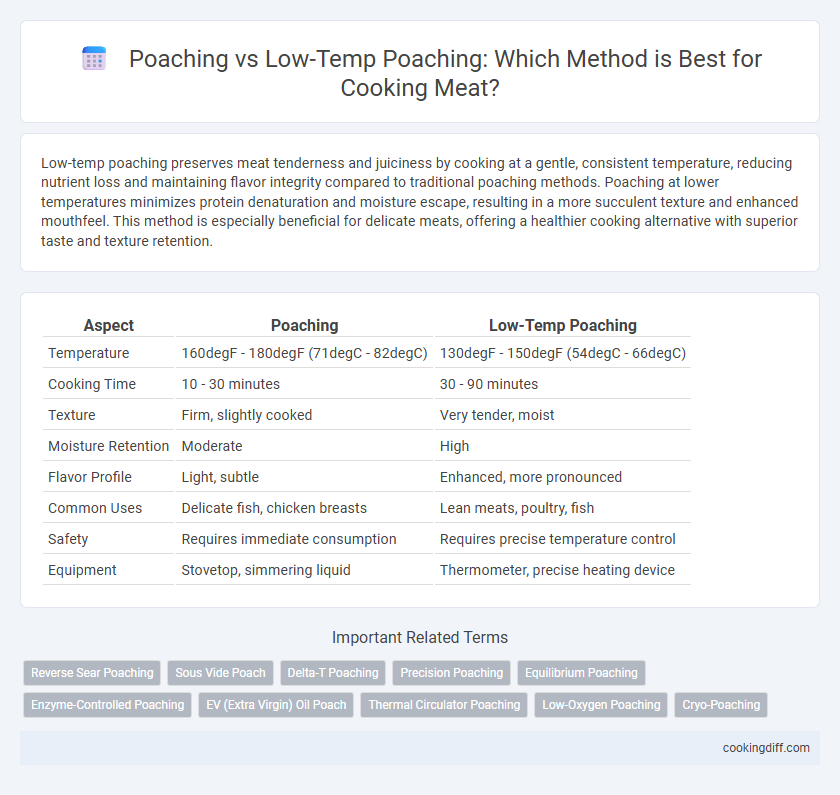
| Aspect | Poaching | Low-Temp Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 160degF - 180degF (71degC - 82degC) | 130degF - 150degF (54degC - 66degC) |
| Cooking Time | 10 - 30 minutes | 30 - 90 minutes |
| Texture | Firm, slightly cooked | Very tender, moist |
| Moisture Retention | Moderate | High |
| Flavor Profile | Light, subtle | Enhanced, more pronounced |
| Common Uses | Delicate fish, chicken breasts | Lean meats, poultry, fish |
| Safety | Requires immediate consumption | Requires precise temperature control |
| Equipment | Stovetop, simmering liquid | Thermometer, precise heating device |
Understanding Traditional Poaching Techniques
Traditional poaching involves cooking meat in water or broth at temperatures just below boiling, typically between 160degF and 180degF, resulting in tender and flavorful dishes. Low-temp poaching, however, uses precise temperature control often below 160degF to maintain moisture and delicate texture without overcooking.
- Temperature Control - Traditional poaching uses higher temperatures compared to low-temp methods, affecting meat juiciness and texture.
- Cooking Duration - Low-temp poaching generally requires longer cooking times for even heat distribution and optimal tenderness.
- Flavor Extraction - Traditional poaching enhances flavor infusion in broths while low-temp poaching focuses on preserving the meat's natural taste.
What is Low-Temperature Poaching?
Low-temperature poaching involves cooking meats in a water bath maintained between 140degF and 160degF, allowing gentle heat penetration that preserves moisture and tenderness. This method contrasts with traditional poaching, which uses higher temperatures and shorter cooking times, often leading to firmer textures.
Maintaining a precise low temperature minimizes protein coagulation and nutrient loss, resulting in juicier, more evenly cooked meats. Low-temp poaching is preferred for delicate cuts, enhancing flavor retention and reducing the risk of overcooking compared to conventional poaching techniques.
Key Differences Between Standard and Low-Temp Poaching
Standard poaching typically involves cooking meats at temperatures between 160degF and 180degF, resulting in a faster cooking process. Low-temp poaching uses temperatures around 140degF to 160degF, preserving moisture and tenderness more effectively.
- Temperature Range - Standard poaching utilizes higher temperatures that cook meat quickly while low-temp poaching relies on gentler heat for gradual cooking.
- Texture and Moisture - Low-temp poaching better maintains meat's juiciness and tender texture compared to the firmer results of standard poaching.
- Cooking Time - Standard poaching requires less time but may risk overcooking, whereas low-temp poaching takes longer yet enhances flavor infusion and tenderness.
Choosing between these methods depends on desired texture and cooking time preferences for optimal meat quality.
Temperature Control: The Secret to Juicy Meats
Poaching meat at higher temperatures can cause proteins to contract rapidly, leading to tougher, less juicy results. Low-temperature poaching maintains a steady heat around 140-160degF (60-71degC), allowing gradual protein coagulation that preserves moisture and tenderness. Precise temperature control is essential to achieving succulent meats with enhanced flavor and texture.
Flavor and Texture: How Poaching Methods Affect Taste
Traditional poaching immerses meat in simmering liquid at temperatures between 160degF and 180degF, preserving moisture and yielding tender textures while allowing subtle infusion of flavors from herbs and spices. Low-temperature poaching, often conducted sous vide around 130degF to 150degF, results in more evenly cooked meat with enhanced juiciness and intensified natural taste due to minimal protein denaturation. Flavor profiles can vary significantly; traditional poaching offers a delicate, gently infused taste, whereas low-temp poaching emphasizes pure meat flavor with superior tenderness and mouthfeel.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Poaching
What are the advantages and disadvantages of traditional poaching for meats? Traditional poaching offers precise temperature control that preserves moisture and tenderness, enhancing the meat's natural flavors. However, it can sometimes result in less flavorful meat compared to low-temp poaching and requires constant attention to avoid overcooking or undercooking.
Advantages of Low-Temperature Poaching for Meats
Low-temperature poaching preserves meat tenderness by cooking at precise, controlled temperatures, preventing overcooking and moisture loss. This method enhances flavor retention and results in uniformly cooked meat with a better texture.
- Enhanced Moisture Retention - Cooking meat at lower temperatures reduces evaporation, keeping it juicier and more succulent.
- Improved Tenderness - Gentle heat breaks down connective tissues slowly, making the meat easier to chew without becoming tough.
- Consistent Cooking - Low-temp poaching ensures even heat distribution, avoiding dry edges and undercooked centers.
Meat Types Best Suited for Each Poaching Method
Traditional poaching is ideal for delicate meats like chicken breasts and fish fillets, where gentle, low-temperature cooking preserves moisture and texture. Low-temp poaching excels with tougher cuts such as pork shoulder and brisket, breaking down connective tissues over extended periods for tender results.
Chicken breasts and fish fillets benefit from traditional poaching's quick, controlled heat that prevents overcooking and maintains a tender bite. Pork shoulder and brisket require low-temp poaching to slowly render fat and collagen, enhancing juiciness and flavor depth. Both methods suit different textures and cooking times, optimizing taste and tenderness for various meat types.
Step-by-Step Guide: Poaching vs Low-Temp Poaching
| Step | Poaching | Low-Temp Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heat liquid to 160-180degF (71-82degC) for gentle cooking. | Set water bath to 140-160degF (60-71degC) for precise temperature control. |
| 2 | Submerge meat entirely in simmering liquid to cook quickly. | Place vacuum-sealed meat in water bath for extended cooking time. |
| 3 | Cook meat for 10-20 minutes depending on thickness. | Cook meat for 1-3 hours to enhance tenderness and flavor infusion. |
| 4 | Remove meat and rest briefly before serving. | Remove meat from bag, pat dry, and optionally sear for texture. |
Related Important Terms
Reverse Sear Poaching
Reverse sear poaching combines low-temperature poaching with a final high-heat sear, preserving meat's moisture and tenderness while creating a flavorful crust. This method optimizes heat control, resulting in evenly cooked meat with enhanced juiciness compared to traditional poaching methods.
Sous Vide Poach
Sous vide poaching maintains precise low temperatures, preserving meat's tenderness and moisture far better than traditional poaching methods that often risk overcooking. This controlled environment enhances flavor infusion by allowing proteins to cook evenly in a sealed bag, minimizing nutrient loss and yielding superior texture and juiciness.
Delta-T Poaching
Delta-T poaching offers precise temperature control by maintaining a minimal temperature gradient between the cooking liquid and the meat, resulting in improved moisture retention and enhanced tenderness compared to traditional poaching methods. Low-temp poaching, characterized by cooking meats at temperatures typically between 60degC and 80degC, reduces overcooking risks but lacks the nuanced thermal regulation provided by Delta-T techniques, which optimize heat transfer for superior texture and flavor preservation.
Precision Poaching
Precision poaching utilizes controlled low-temperature water baths to evenly cook meats while preserving texture and moisture, contrasting traditional poaching methods that often result in uneven heat distribution and potential overcooking. This technique enhances flavor retention and tenderness by maintaining precise temperature ranges typically between 130degF and 160degF, optimizing protein denaturation without compromising juiciness.
Equilibrium Poaching
Equilibrium poaching maintains a precise water temperature typically between 140degF to 160degF, allowing meat to cook evenly while preserving moisture and tenderness, unlike traditional low-temp poaching which may vary in temperature and risk uneven cooking. This method ensures the meat's proteins coagulate optimally, preventing overcooking and enhancing the overall texture and flavor profile.
Enzyme-Controlled Poaching
Enzyme-controlled low-temperature poaching preserves the integrity of meat proteins by using precise temperatures that activate endogenous enzymes, resulting in tender and flavorful cuts without the toughness caused by conventional poaching methods. This technique optimizes enzymatic breakdown of connective tissues while minimizing nutrient loss and moisture evaporation, enhancing both texture and nutritional value.
EV (Extra Virgin) Oil Poach
Poaching meats in Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EV oil) preserves tenderness and infuses rich, fruity antioxidants, unlike traditional water poaching which can dilute flavor and nutrients. Low-temperature EV oil poaching enhances moisture retention and delivers a deeply flavored, healthful cooking method rich in monounsaturated fats and polyphenols.
Thermal Circulator Poaching
Thermal circulator poaching ensures precise temperature control, preserving meat tenderness and moisture better than traditional poaching methods that typically expose meat to fluctuating heat. This low-temperature poaching technique reduces protein denaturation and overcooking risks, resulting in juicier, more uniformly cooked meats.
Low-Oxygen Poaching
Low-oxygen poaching preserves meat tenderness and moisture by minimizing oxidation and nutrient loss during low-temperature cooking, enhancing flavor and texture compared to traditional poaching. This method reduces the risk of overcooking and maintains the structural integrity of proteins through a controlled, oxygen-limited environment.
Poaching vs Low-temp Poaching for Meats Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com