Poaching uses gently simmering liquid to cook food evenly and retain moisture, resulting in tender textures without added fat. Milk poaching enhances dishes by infusing subtle sweetness and creaminess, creating rich, flavorful profiles especially suited for delicate proteins like chicken or fish. Choosing milk over water or broth can intensify taste and produce uniquely soft, succulent results.
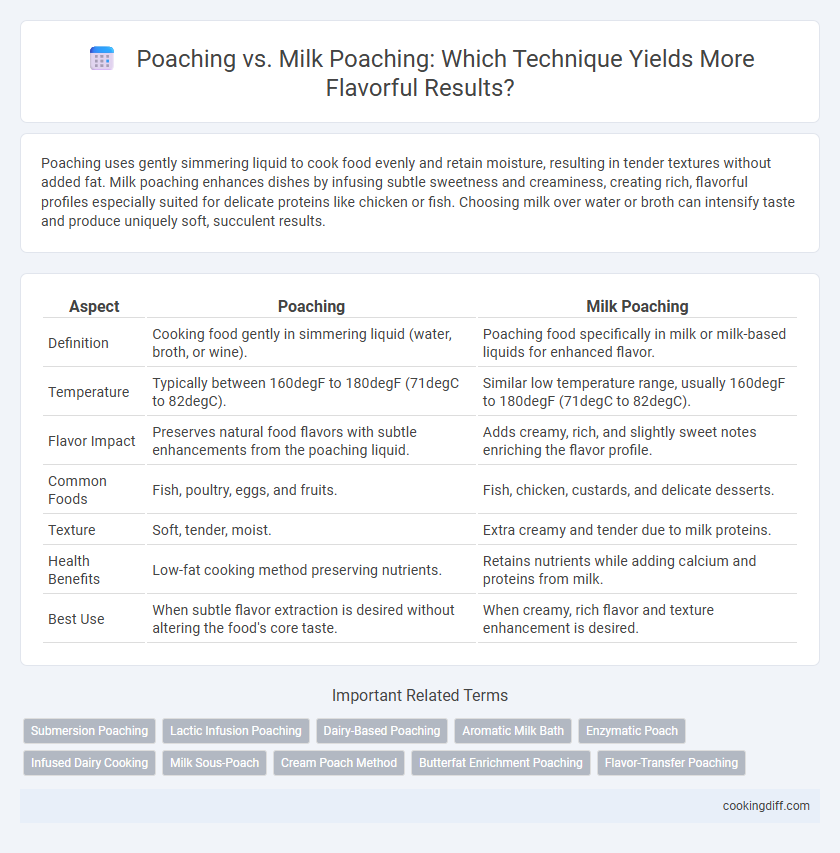
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Poaching | Milk Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food gently in simmering liquid (water, broth, or wine). | Poaching food specifically in milk or milk-based liquids for enhanced flavor. |
| Temperature | Typically between 160degF to 180degF (71degC to 82degC). | Similar low temperature range, usually 160degF to 180degF (71degC to 82degC). |
| Flavor Impact | Preserves natural food flavors with subtle enhancements from the poaching liquid. | Adds creamy, rich, and slightly sweet notes enriching the flavor profile. |
| Common Foods | Fish, poultry, eggs, and fruits. | Fish, chicken, custards, and delicate desserts. |
| Texture | Soft, tender, moist. | Extra creamy and tender due to milk proteins. |
| Health Benefits | Low-fat cooking method preserving nutrients. | Retains nutrients while adding calcium and proteins from milk. |
| Best Use | When subtle flavor extraction is desired without altering the food's core taste. | When creamy, rich flavor and texture enhancement is desired. |
Introduction to Poaching: Classic vs. Milk Techniques
| Poaching | Classic poaching uses water or broth at low temperatures (160-180degF) to gently cook foods, preserving delicate textures and enhancing natural flavors without added fats. |
| Milk Poaching | Milk poaching incorporates dairy's mild sweetness and creaminess, enriching dishes like fish or fruit with subtle caramelization and a tender mouthfeel, ideal for nuanced flavor profiles. |
| Technique Comparison | Classic poaching emphasizes purity and simplicity, while milk poaching introduces complexity and a soft, velvety texture, offering diverse culinary outcomes depending on ingredient type and desired taste. |
Understanding Traditional Poaching
Traditional poaching involves cooking food gently in water or broth at low temperatures to preserve natural flavors and moisture. Milk poaching infuses a creamy, subtle sweetness that complements delicate ingredients without overpowering them.
- Temperature Control - Traditional poaching requires maintaining water just below boiling, between 160degF and 180degF, to achieve tender textures.
- Flavor Infusion - Milk poaching allows dairy proteins and fats to subtly enhance the dish's richness, creating a unique flavor profile.
- Culinary Applications - Both methods are ideal for poultry, fish, and eggs, but milk poaching is often preferred for recipes desiring a silky, creamy finish.
What Is Milk Poaching?
What is milk poaching and how does it differ from traditional poaching methods? Milk poaching involves gently cooking food in milk instead of water or broth, which adds a creamy texture and subtle sweetness to the dish. This technique enhances flavor without overpowering the natural taste of ingredients like fish or eggs, making it ideal for delicate recipes.
Flavor Infusion: Water vs. Milk
Poaching in water allows for a clean, subtle flavor that highlights the natural taste of the ingredient without overpowering it. Using milk for poaching introduces a creamy richness that enhances flavor infusion, particularly in delicate proteins like fish or poultry. The fat content in milk helps to tenderize and add a smooth texture, resulting in a more flavorful and moist outcome compared to water poaching.
Texture Differences: Moisture and Tenderness
Poaching preserves moisture and tenderness by gently cooking food in water, resulting in a delicate texture. Milk poaching infuses richness and creaminess, enhancing flavor while maintaining a soft, tender bite.
- Moisture retention - Poaching in water keeps food moist without adding fat, ideal for lean proteins.
- Enhanced tenderness - Milk poaching breaks down proteins softly, creating a creamy, tender texture.
- Flavor infusion - Milk imparts subtle sweetness and depth, differentiating it from plain water poaching.
The choice between water and milk poaching depends on the desired flavor profile and texture outcome.
Best Foods for Classic Poaching
Classic poaching excels with delicate foods like fish, eggs, and poultry, ensuring gentle cooking that preserves texture and moisture. Milk poaching enhances flavors in dishes such as custards and certain white fish, infusing a subtle creaminess that water alone cannot provide. For optimal results, use low simmering temperatures and mild seasonings to complement the natural taste of these foods during poaching.
Foods That Shine with Milk Poaching
Poaching is a gentle cooking technique that uses water or broth to preserve the natural texture and flavor of foods, ideal for delicate items like eggs and fish. Milk poaching introduces a creamy richness, enhancing the flavor profile of foods such as chicken breasts and fruits like pears.
Foods that shine with milk poaching absorb the subtle sweetness and velvety texture, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes. This method is especially effective for recipes requiring a mild, comforting taste, making dishes more complex without overwhelming their natural essence.
Nutritional Impact: Comparing the Methods
Poaching in water preserves more natural nutrients in foods like fish and chicken due to the gentle cooking process that minimizes nutrient loss. Milk poaching, however, infuses dishes with additional proteins, calcium, and fat from the milk, enhancing both flavor and nutritional content.
While water poaching retains a lighter nutritional profile, milk poaching adds beneficial vitamins such as vitamin D and riboflavin. The choice between the two methods impacts both the nutritional density and flavor complexity of the final dish.
Step-by-Step Guide: Poaching Techniques Explained
Poaching involves gently cooking food in simmering liquid, preserving delicate textures and enhancing natural flavors. Milk poaching uses milk as the cooking medium, imparting a creamy richness ideal for dishes like fish or poultry.
- Temperature Control - Maintain liquid temperature between 160degF and 180degF to avoid boiling and ensure even cooking.
- Choice of Liquid - Use water, broth, or milk depending on the desired flavor profile and moisture retention.
- Cooking Duration - Adjust poaching time based on the ingredient thickness, typically ranging from 10 to 20 minutes for optimal tenderness.
Related Important Terms
Submersion Poaching
Submersion poaching immerses food completely in a flavorful liquid at a controlled, low temperature, preserving moisture and infusing taste evenly compared to traditional milk poaching which relies on dairy's fat content to enhance creaminess. This method reduces the risk of curdling while maximizing the extraction of aromatic herbs and spices, delivering consistently tender and richly flavored dishes.
Lactic Infusion Poaching
Lactic infusion poaching enhances flavor by gently cooking ingredients in a milk-based liquid, allowing lactic acids to tenderize proteins and impart a subtle tang. This method contrasts with traditional poaching, which typically uses water or broth, offering a richer, creamier taste profile ideal for delicate dishes.
Dairy-Based Poaching
Dairy-based poaching enhances flavor by gently simmering ingredients in milk or cream, infusing dishes with rich, creamy textures and subtle sweetness that water or broth cannot achieve. This method preserves moisture while imparting delicate dairy notes, making it ideal for seafood, poultry, and delicate vegetables seeking enhanced taste profiles.
Aromatic Milk Bath
Poaching emphasizes gently cooking ingredients in flavorful liquids to enhance taste, while milk poaching specifically uses an aromatic milk bath infused with spices or herbs to create a subtle, creamy flavor profile. The milk's fat content and fragrant additives elevate dishes by tenderizing proteins and adding nuanced sweetness, making milk poaching ideal for delicate foods like fish or poultry.
Enzymatic Poach
Enzymatic poaching leverages natural enzymes to tenderize and enhance flavor in proteins, creating a more complex taste profile compared to traditional milk poaching which primarily imparts creaminess and subtle sweetness. This method preserves the protein's texture while intensifying umami notes, making enzymatic poach a preferred technique for chefs seeking depth and robustness in culinary dishes.
Infused Dairy Cooking
Poaching uses gentle heat to cook ingredients in water or broth, preserving natural flavors, while milk poaching infuses dairy's creamy richness directly into foods like chicken or fish for enhanced taste and texture. Infused dairy cooking through milk poaching creates tender, flavor-packed dishes by combining moisture retention with subtle creaminess, ideal for delicate proteins and smooth sauces.
Milk Sous-Poach
Milk sous-poach involves gently cooking proteins in warm milk at controlled temperatures, enhancing flavor and tenderness without the harshness of traditional poaching methods. This technique leverages milk's natural fats and sugars to infuse subtle creamy notes, yielding more flavorful and moist results compared to water or broth poaching.
Cream Poach Method
The Cream Poach Method enhances flavor by gently cooking ingredients in a rich, creamy liquid that infuses subtle dairy notes and maintains moisture, unlike traditional water poaching which can dilute taste. This technique is especially effective for delicate proteins and fruits, producing tender textures and a harmonious blend of flavors ideal for gourmet dishes.
Butterfat Enrichment Poaching
Butterfat enrichment poaching enhances flavor by submerging ingredients in melted butter, allowing rich, creamy notes to infuse the food, unlike traditional water-based poaching which can dilute taste. This method preserves moisture while intensifying buttery richness, making it ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables seeking a flavorful, silky texture.
Poaching vs Milk Poaching for Flavorful Results Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com