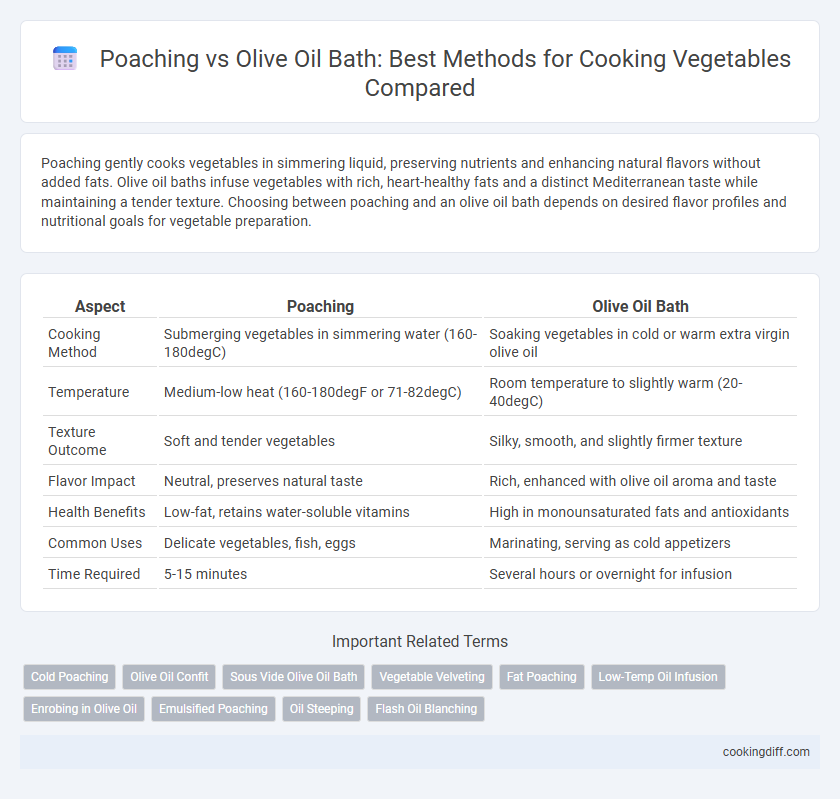
Poaching gently cooks vegetables in simmering liquid, preserving nutrients and enhancing natural flavors without added fats. Olive oil baths infuse vegetables with rich, heart-healthy fats and a distinct Mediterranean taste while maintaining a tender texture. Choosing between poaching and an olive oil bath depends on desired flavor profiles and nutritional goals for vegetable preparation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Poaching | Olive Oil Bath |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Submerging vegetables in simmering water (160-180degC) | Soaking vegetables in cold or warm extra virgin olive oil |
| Temperature | Medium-low heat (160-180degF or 71-82degC) | Room temperature to slightly warm (20-40degC) |
| Texture Outcome | Soft and tender vegetables | Silky, smooth, and slightly firmer texture |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, preserves natural taste | Rich, enhanced with olive oil aroma and taste |
| Health Benefits | Low-fat, retains water-soluble vitamins | High in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants |
| Common Uses | Delicate vegetables, fish, eggs | Marinating, serving as cold appetizers |
| Time Required | 5-15 minutes | Several hours or overnight for infusion |
Understanding Poaching: A Gentle Cooking Technique
Poaching is a gentle cooking technique where vegetables are submerged in a simmering liquid at a low temperature, typically between 160degF and 180degF, preserving their texture and nutrients. This method contrasts with the olive oil bath, which involves cooking vegetables in hot oil, resulting in a richer flavor but higher fat content.
Understanding poaching helps maintain the delicate structure and vibrant color of vegetables, making it ideal for health-conscious recipes. It also prevents overcooking and nutrient loss, which can occur with the higher temperatures used in olive oil baths.
What Is an Olive Oil Bath for Vegetables?
| Olive Oil Bath for Vegetables | An olive oil bath involves gently coating vegetables in olive oil to enhance flavor and texture during cooking, creating a silky surface and preserving nutrients. |
| Poaching vs Olive Oil Bath | Unlike poaching, which cooks vegetables in water or broth at low temperatures, an olive oil bath uses fat as the cooking medium, providing a rich taste and preventing nutrient loss through water leaching. |
| Benefits | Olive oil baths increase absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, while poaching is better suited for delicate vegetables requiring moist heat without added fats. |
Flavor Impact: Poaching vs Olive Oil Bath
Poaching vegetables preserves their natural, delicate flavors by cooking them gently in water or broth, preventing overpowering tastes. Olive oil baths infuse vegetables with richness and a fruity, aromatic depth that enhances their overall flavor profile.
- Poaching retains subtlety - It allows the original vegetable flavors to remain light and fresh without added fats.
- Olive oil bath adds richness - The oil imparts a smooth, slightly peppery taste that complements roasted or sauteed vegetables.
- Technique influences texture - Poached vegetables tend to be tender and moist, while those in olive oil baths are silkier and more flavorful due to oil absorption.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Wins?
Poaching vegetables preserves a higher level of water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex compared to an olive oil bath, which can cause nutrient leaching due to prolonged heat exposure. Olive oil baths enhance fat-soluble vitamin absorption but may reduce overall nutrient density if vegetables are cooked at high temperatures for extended periods. Therefore, poaching generally wins in nutrient retention, especially for delicate, vitamin-rich vegetables.
Texture and Color: Comparing Results
Poaching vegetables preserves a tender texture while maintaining vibrant color due to the gentle cooking temperature. Olive oil bath enhances color saturation and adds a glossy finish but may slightly soften the vegetable's firmness.
Poaching uses simmering water to cook vegetables evenly without breaking down pigments, ensuring bright and natural hues. In contrast, an olive oil bath coats vegetables, intensifying color appearance through light reflection but can lead to a softer mouthfeel. Both methods retain nutrients well but differ notably in texture and visual impact.
Cooking Temperatures and Times
Poaching vegetables involves cooking them gently in simmering liquid at temperatures between 160degF and 180degF (71degC to 82degC) for a short time, usually 5 to 10 minutes, preserving their texture and nutrients. In contrast, the olive oil bath method cooks vegetables at higher temperatures, around 250degF to 300degF (121degC to 149degC), often for 10 to 20 minutes, infusing rich flavors while softening the vegetables. The precise temperature control in poaching minimizes nutrient loss, whereas the olive oil bath enhances taste but may lead to slight nutrient degradation due to prolonged heat exposure.
Ideal Vegetables for Poaching
Poaching is a gentle cooking technique ideal for tender vegetables that require careful heat control to maintain texture and flavor. Vegetables with high water content and delicate structures, such as asparagus, zucchini, and green beans, are best suited for poaching compared to an olive oil bath.
- Asparagus - Poaching preserves its crisp-tender texture without overpowering its natural flavor.
- Zucchini - Maintains moisture and subtle taste through gentle simmering in water or broth.
- Green Beans - Retains vibrant color and firmness that can diminish in an olive oil bath.
Best Vegetables for Olive Oil Baths
Vegetables such as asparagus, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts benefit the most from an olive oil bath due to their firm textures that absorb the oil's nutrients while retaining crispness. Unlike poaching, which relies on water or broth at low heat, an olive oil bath gently infuses these vegetables with healthy fats and enhances flavor profiles.
Poaching is ideal for tender vegetables like zucchini or tomatoes that require delicate cooking without added fats. In contrast, the olive oil bath method enriches nutrient-dense, sturdy vegetables with monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, making it the preferred technique for maximizing health benefits and taste in robust vegetables.
Health Considerations: Fat vs Water-Based Cooking
Is cooking vegetables through poaching or an olive oil bath healthier? Poaching uses water as the cooking medium, which significantly reduces fat intake and preserves nutrients like vitamin C and folate. An olive oil bath introduces healthy monounsaturated fats and antioxidants but increases calorie content, making the choice dependent on dietary fat needs and health goals.
Related Important Terms
Cold Poaching
Cold poaching preserves the nutritional value and texture of vegetables more effectively than an olive oil bath, as it involves gently cooking in water below boiling point without harsh heat or added fats. Unlike olive oil baths that may add calories and alter flavor profiles, cold poaching maintains the vegetables' natural taste and enhances their antioxidant retention.
Olive Oil Confit
Olive oil confit preserves vegetables by slowly cooking them in rich olive oil, enhancing their flavor and texture while locking in nutrients, unlike poaching which uses water-based heat that can dilute taste and nutrient content. This method offers a luxurious alternative to poaching, especially for root vegetables and garlic, resulting in a tender, aromatic dish rich in healthy fats and antioxidants inherent in extra virgin olive oil.
Sous Vide Olive Oil Bath
Sous vide olive oil bath provides precise temperature control that preserves vegetable texture and nutrients better than traditional poaching, which often leads to nutrient loss in water. The oil bath's gentle cooking environment enhances flavor infusion and maintains vibrant color, making it a superior method for vegetable preparation in culinary applications.
Vegetable Velveting
Poaching preserves the vegetable's natural texture and flavor by gently cooking in lightly simmering water, while an olive oil bath during vegetable velveting coats the vegetables, creating a silky, tender texture that enhances stir-fry dishes. Vegetable velveting with olive oil helps retain moisture and prevents overcooking, making it ideal for crisp, vibrant vegetables in Asian cuisine.
Fat Poaching
Fat poaching vegetables in olive oil retains essential nutrients and enhances flavor through gentle heat transfer, compared to water-based poaching which can leach vitamins into the cooking liquid. This technique creates a tender, silky texture while infusing the produce with healthy monounsaturated fats, making it a superior method for preserving both nutrient content and taste.
Low-Temp Oil Infusion
Poaching vegetables preserves delicate flavors and textures by cooking them gently in a flavorful liquid at low temperatures, preventing nutrient loss and maintaining moisture. Low-temp olive oil bath, an infusion method, enhances nutrient absorption and imparts rich antioxidants from extra virgin olive oil, creating a gourmet taste profile while avoiding oxidation.
Enrobing in Olive Oil
Poaching vegetables in water preserves texture and nutrients but lacks the rich flavor infusion achieved by enrobing them in olive oil, which forms a protective coating during cooking and enhances mouthfeel. Olive oil bath not only infuses antioxidants like polyphenols but also facilitates even heat distribution, resulting in a more flavorful, tender vegetable with improved nutrient absorption.
Emulsified Poaching
Emulsified poaching offers a gentle cooking method that preserves the delicate texture and nutrients of vegetables by using a combination of fat and liquid, unlike traditional poaching which relies solely on water or broth. This technique enhances flavor absorption and prevents nutrient loss better than the olive oil bath method, which can sometimes result in uneven cooking due to oil's higher heat retention.
Oil Steeping
Poaching vegetables involves cooking them gently in simmering water or broth, preserving texture and nutrients, whereas an olive oil bath, or oil steeping, infuses flavors deeply by cooking vegetables slowly in warm oil, enhancing richness and aroma. Olive oil steeping allows better absorption of antioxidants and healthy fats, making it a flavorful and nutritious alternative to traditional poaching methods.
Poaching vs Olive Oil Bath for Vegetables Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com