Poaching is a gentle cooking method that uses simmering liquid to evenly cook food without drying it out, commonly applied to proteins and delicate ingredients. Olive oil poaching, on the other hand, involves cooking vegetables slowly in warm olive oil, which enhances flavor and preserves nutrients while imparting a rich, smooth texture. This technique also maintains the vibrant color and crispness of vegetables, making it a healthier and more flavorful alternative to traditional water-based poaching.
Table of Comparison
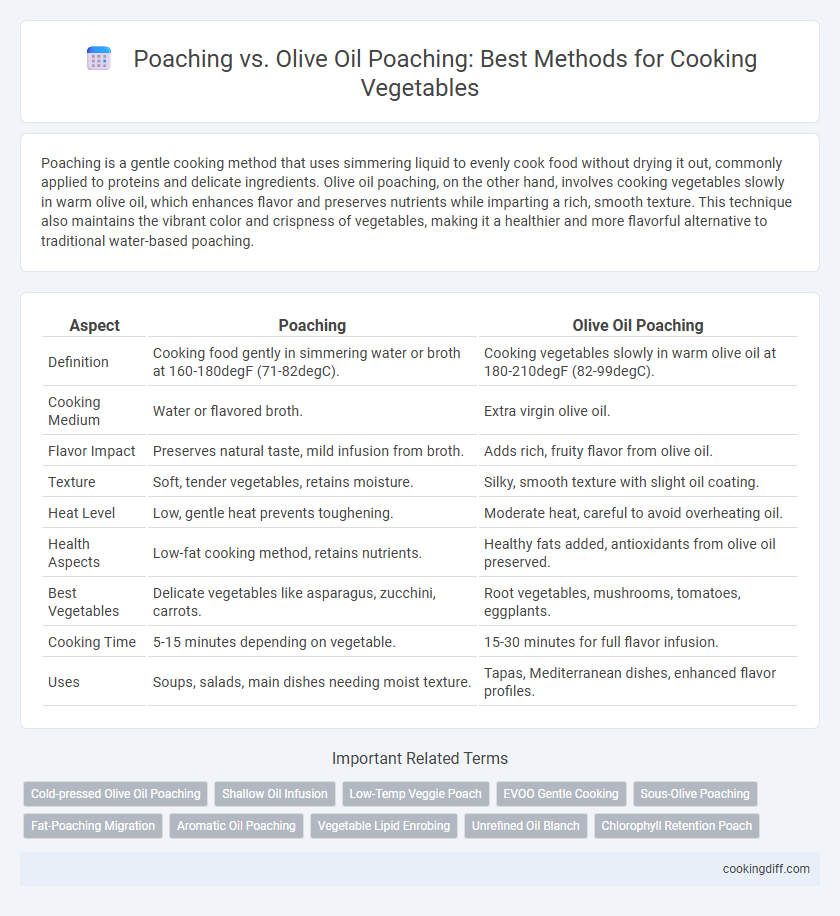
| Aspect | Poaching | Olive Oil Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food gently in simmering water or broth at 160-180degF (71-82degC). | Cooking vegetables slowly in warm olive oil at 180-210degF (82-99degC). |
| Cooking Medium | Water or flavored broth. | Extra virgin olive oil. |
| Flavor Impact | Preserves natural taste, mild infusion from broth. | Adds rich, fruity flavor from olive oil. |
| Texture | Soft, tender vegetables, retains moisture. | Silky, smooth texture with slight oil coating. |
| Heat Level | Low, gentle heat prevents toughening. | Moderate heat, careful to avoid overheating oil. |
| Health Aspects | Low-fat cooking method, retains nutrients. | Healthy fats added, antioxidants from olive oil preserved. |
| Best Vegetables | Delicate vegetables like asparagus, zucchini, carrots. | Root vegetables, mushrooms, tomatoes, eggplants. |
| Cooking Time | 5-15 minutes depending on vegetable. | 15-30 minutes for full flavor infusion. |
| Uses | Soups, salads, main dishes needing moist texture. | Tapas, Mediterranean dishes, enhanced flavor profiles. |
Understanding Traditional Poaching for Vegetables
| Method | Description | Temperature | Medium | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Poaching | Cooking vegetables gently in simmering water or broth at low temperatures to preserve texture and nutrients. | 160-180degF (71-82degC) | Water or broth | Ideal for delicate vegetables like asparagus, carrots, and green beans. |
| Olive Oil Poaching | Submerging vegetables in warm olive oil at low temperatures to infuse flavor and retain moisture while cooking evenly. | 180-210degF (82-99degC) | Extra virgin olive oil | Used for robust vegetables such as artichokes, tomatoes, and eggplants. |
| Key Differences | Traditional poaching uses water or broth providing a lighter taste, while olive oil poaching enriches flavor and texture via fat infusion. | N/A | N/A | Choice depends on desired flavor profile and vegetable type. |
What Is Olive Oil Poaching?
What is olive oil poaching and how does it differ from traditional poaching? Olive oil poaching involves gently cooking vegetables in warm olive oil at low temperatures, preserving their texture and enhancing flavor. Unlike traditional poaching in water or broth, this method infuses vegetables with healthy fats while maintaining nutrients and providing a rich, silky finish.
Key Differences Between Water and Olive Oil Poaching
Poaching vegetables in water preserves their natural flavor and texture through gentle cooking at low temperatures. Olive oil poaching, by contrast, infuses vegetables with rich flavors and enhances their nutrient absorption due to healthy fats.
- Heat Medium - Water poaching uses boiling or simmering water, while olive oil poaching employs heated oil at lower temperatures.
- Flavor Impact - Water poaching maintains a neutral taste, whereas olive oil poaching adds a distinct richness and aroma.
- Nutrient Retention - Olive oil poaching helps retain fat-soluble vitamins in vegetables better than water poaching.
Flavor Impact: Water vs. Olive Oil
Poaching vegetables in water preserves their natural flavor but can result in a milder taste due to the absence of fat-soluble flavor compounds. This method is ideal for delicate vegetables where subtlety is desired.
Olive oil poaching infuses vegetables with rich, fruity notes from the oil, enhancing their flavor and adding a smooth mouthfeel. The fat in olive oil helps retain and amplify aromatic compounds, making the vegetables more flavorful and aromatic.
Texture and Mouthfeel of Poached Vegetables
Traditional water poaching of vegetables results in a softer texture with a more diluted mouthfeel due to water's higher heat conductivity and moisture absorption. Olive oil poaching enhances the vegetables' natural flavors, providing a silkier, richer mouthfeel and retaining a firmer texture because of the oil's lower heat transfer rate. The choice between water and olive oil poaching significantly impacts the sensory experience, balancing tenderness versus flavor intensity and mouthfeel richness.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Wins?
Water poaching preserves water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex more effectively due to the low cooking temperature and absence of fat. Olive oil poaching enhances the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K while providing beneficial monounsaturated fats.
- Water Poaching Nutrient Retention - Retains higher levels of hydrophilic vitamins by minimizing nutrient leaching in water.
- Olive Oil Poaching Benefits - Increases bioavailability of fat-soluble vitamins through oil-based heat transfer.
- Overall Nutrient Balance - Combining both methods can optimize the retention of diverse nutrients in vegetables.
Best Vegetables for Traditional Poaching
Traditional poaching is a gentle cooking method ideal for delicate vegetables like asparagus, zucchini, and carrots, preserving their texture and flavor. In contrast, olive oil poaching imparts a rich, fruity taste while cooking at slightly higher temperatures, making it suitable for sturdier vegetables like bell peppers and eggplant.
When choosing the best vegetables for traditional poaching, focus on those with thin skins and tender flesh, such as green beans and peas, which absorb subtle flavors without becoming mushy. Olive oil poaching enhances the depth of flavor in root vegetables like potatoes and beets, offering a richer taste profile and softer consistency.
Vegetables That Shine in Olive Oil Poaching
Olive oil poaching enhances the natural flavors and textures of vegetables, creating a rich and tender result compared to traditional water poaching. Vegetables retain vibrant colors and absorb subtle fruity notes from the olive oil during the gentle cooking process.
- Carrots - Olive oil poaching softens carrots while preserving their sweetness and adding a silky texture.
- Asparagus - This method keeps asparagus crisp-tender and infuses them with delicate olive oil aroma.
- Artichokes - Poaching artichokes in olive oil enriches their earthy flavor and maintains a creamy consistency.
Olive oil poaching transforms simple vegetables into gourmet dishes with enhanced taste and mouthfeel.
Health Considerations: Oil vs. Water Poaching
Poaching vegetables in water preserves nutrients and reduces calorie intake, making it a heart-healthy cooking method compared to oil poaching. Olive oil poaching, while adding beneficial monounsaturated fats and antioxidants like vitamin E, increases the dish's overall fat content and calories.
Water poaching minimizes fat absorption and retains water-soluble vitamins, essential for a balanced diet. Olive oil poaching enhances flavor and delivers healthy fats that support cardiovascular health but may not be suitable for low-fat dietary needs. Choosing between the two methods depends on individual health goals and nutritional preferences.
Related Important Terms
Cold-pressed Olive Oil Poaching
Cold-pressed olive oil poaching preserves the nutritional integrity and delicate flavors of vegetables by gently cooking them at low temperatures, unlike traditional poaching which often uses water or broth that can dilute taste and nutrients. The rich antioxidants and monounsaturated fats in cold-pressed olive oil enhance both the health benefits and sensory experience of poached vegetables.
Shallow Oil Infusion
Shallow oil infusion during olive oil poaching enhances vegetable flavor by gently saturating the surface with aromatic compounds while preserving texture and nutrients. Compared to traditional poaching methods using water, olive oil poaching with shallow oil levels offers a richer taste profile and improved nutrient retention due to minimal heat-induced degradation.
Low-Temp Veggie Poach
Low-temperature vegetable poaching preserves nutrients and texture by gently cooking vegetables in water or broth below boiling point, contrasting with olive oil poaching that infuses richer flavor through slow cooking in oil at moderate heat. This method ensures vibrant color retention and delicate mouthfeel while minimizing fat absorption, making it ideal for health-conscious dishes.
EVOO Gentle Cooking
Poaching with Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) offers a gentle cooking method that preserves the nutrients and vibrant flavors of vegetables while infusing them with the rich, antioxidant properties of high-quality EVOO. Unlike traditional water poaching, EVOO gentle cooking promotes better texture retention and enhances the natural taste profiles of vegetables without the risk of nutrient loss from high temperatures or water exposure.
Sous-Olive Poaching
Sous-Olive poaching uses extra virgin olive oil at low temperatures to gently cook vegetables, preserving their nutrients and enhancing natural flavors while avoiding the harsher effects of water poaching. This method intensifies the vegetables' texture and aroma by infusing them with rich olive oil antioxidants, providing a healthier and more flavorful alternative to traditional poaching.
Fat-Poaching Migration
Poaching vegetables in olive oil, also known as fat-poaching, enhances flavor retention by allowing fat-soluble nutrients to remain within the vegetables rather than leaching out into water as seen in traditional water poaching. This method reduces nutrient migration, preserves texture, and imparts a richer taste compared to conventional poaching techniques.
Aromatic Oil Poaching
Aromatic oil poaching enhances vegetable flavors by gently infusing herbs and spices into olive oil at low temperatures, preserving nutrients and texture better than traditional water-based poaching methods. This technique leverages olive oil's rich antioxidant content to elevate taste while providing a healthier, more aromatic alternative to conventional poaching.
Vegetable Lipid Enrobing
Poaching vegetables in traditional methods typically involves water or broth, which limits the transfer of lipids to the vegetable surface, whereas olive oil poaching significantly enhances vegetable lipid enrobing by allowing fat-soluble nutrients and flavors to bind more effectively, improving texture and nutrient retention. Olive oil's monounsaturated fats create a natural lipid barrier that promotes better nutrient absorption and preserves the vegetable's integrity during cooking.
Unrefined Oil Blanch
Poaching vegetables in unrefined olive oil preserves delicate nutrients and enhances flavor profiles more effectively than traditional water poaching by preventing nutrient leaching and promoting gentle cooking. Using unrefined oil blanching maintains vegetable texture and boosts antioxidant retention through controlled heat absorption.
Poaching vs Olive oil poaching for vegetables Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com