Poaching gently cooks food in simmering liquid, preserving moisture and delicate flavors ideal for tender proteins like fish and chicken. En papillote involves steaming food inside a parchment paper pouch, which traps steam and infuses ingredients with aromatic herbs and vegetables. Both methods use moist heat to enhance juiciness, but en papillote offers added flavor complexity through aromatic steam.
Table of Comparison
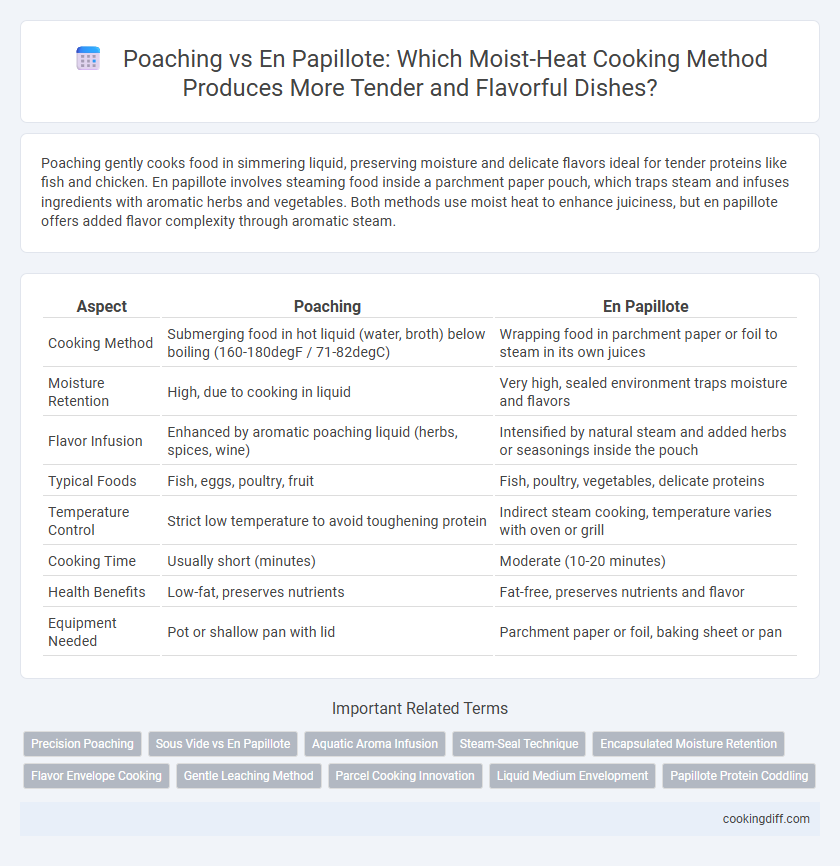
| Aspect | Poaching | En Papillote |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Submerging food in hot liquid (water, broth) below boiling (160-180degF / 71-82degC) | Wrapping food in parchment paper or foil to steam in its own juices |
| Moisture Retention | High, due to cooking in liquid | Very high, sealed environment traps moisture and flavors |
| Flavor Infusion | Enhanced by aromatic poaching liquid (herbs, spices, wine) | Intensified by natural steam and added herbs or seasonings inside the pouch |
| Typical Foods | Fish, eggs, poultry, fruit | Fish, poultry, vegetables, delicate proteins |
| Temperature Control | Strict low temperature to avoid toughening protein | Indirect steam cooking, temperature varies with oven or grill |
| Cooking Time | Usually short (minutes) | Moderate (10-20 minutes) |
| Health Benefits | Low-fat, preserves nutrients | Fat-free, preserves nutrients and flavor |
| Equipment Needed | Pot or shallow pan with lid | Parchment paper or foil, baking sheet or pan |
Understanding Moist-Heat Cooking Methods
What distinguishes poaching from en papillote in moist-heat cooking methods? Poaching involves cooking food gently in simmering liquid between 160degF and 180degF, preserving moisture and delicate textures. En papillote steams food inside a parchment or foil pouch, trapping steam and intensifying flavors while maintaining tenderness.
What Is Poaching?
Poaching is a moist-heat cooking technique that involves gently simmering food in a liquid, typically water, broth, or wine, at temperatures between 160degF and 180degF (71degC to 82degC). This method helps preserve the delicate texture and flavor of ingredients such as fish, eggs, and fruits without breaking them apart. Unlike en papillote, which uses steam trapped in parchment paper to cook, poaching relies on direct contact with hot liquid to evenly cook food while maintaining moisture.
What Does En Papillote Mean?
En papillote is a French cooking technique where food is sealed in parchment paper or foil and baked, allowing it to steam in its own juices. This method preserves moisture and infuses flavors without direct contact with water, unlike poaching.
Poaching involves gently cooking food in a simmering liquid, which can sometimes dilute flavors. En papillote offers a more concentrated flavor profile by trapping steam and aromas within the sealed packet.
Key Differences: Poaching vs En Papillote
Poaching involves gently cooking food in simmering liquid, typically water or broth, at temperatures between 160degF and 180degF, preserving moisture and delicate textures. En papillote is a moist-heat cooking method where food is sealed in parchment paper or foil and steamed in its own juices, enhancing flavor concentration and aromatic infusion.
Poaching is ideal for delicate proteins like fish and eggs, allowing even heat distribution without drying out. En papillote combines steaming and roasting, creating a self-contained environment that traps steam and flavors, which intensifies taste and keeps foods tender. Both methods emphasize gentle heat but differ in technique and flavor development, making them uniquely suited for specific culinary applications.
Types of Foods Best Suited for Poaching
| Type of Food | Why Poaching is Best |
|---|---|
| Fish and Seafood | Delicate texture preserved by gentle heat prevents toughening and maintains moisture. |
| Eggs | Slow cooking in simmering liquid results in soft, tender whites and runny yolks without added fat. |
| Chicken and Poultry | Low-temperature immersion retains juiciness and prevents drying compared to dry heat methods. |
| Fruits | Preserves shape and enhances natural flavors while softening without added fat or browning. |
Foods Ideal for En Papillote Cooking
En papillote cooking is ideal for delicate foods that benefit from gentle steaming and flavor infusion, such as fish and vegetables. Unlike poaching, which submerges food in liquid, en papillote uses tightly sealed parchment to trap moisture and aromatics.
- Fish fillets - Their tender texture cooks evenly with trapped steam, preserving moisture and subtle flavors.
- Vegetables - Thinly sliced or diced vegetables soften while retaining nutrients and vibrant colors when cooked en papillote.
- Shrimp and shellfish - These proteins cook quickly and absorb infused herbs and spices without becoming waterlogged.
Technique Comparison: Step-by-Step Guide
Poaching involves submerging food in gently simmering liquid at temperatures between 160-180degF to ensure even cooking without toughening. En papillote cooking uses parchment paper to steam food in its own juices, trapping moisture and flavor within a sealed pouch. Both techniques preserve tenderness and moisture but differ in equipment and flavor infusion methods.
Flavor Infusion: Broth vs Aromatics
Poaching uses a flavorful broth to gently infuse moisture and subtle taste into food, enhancing the natural flavors with liquid aromatics. En papillote relies on steam created by wrapping food with herbs and vegetables in parchment, concentrating flavors within the sealed environment.
- Poaching infuses flavor through broth - The food absorbs the seasoning and aroma dissolved in the poaching liquid.
- En papillote traps aromatic steam - Herbs and vegetables release intense scents and flavors during cooking inside the pouch.
- Moist heat methods enhance flavor differently - Broth imparts direct seasoning, while papillote intensifies natural essence without added liquid.
Both techniques produce tender, flavorful dishes by harnessing gentle moist-heat cooking methods.
Nutritional Considerations of Each Method
Poaching preserves water-soluble vitamins better due to lower cooking temperatures and minimal fat usage, making it a healthier choice for delicate proteins. En papillote traps steam and natural juices, enhancing flavor and nutrient retention but may result in slightly higher fat content from added oils or butter.
- Vitamin Retention - Poaching retains more B vitamins and vitamin C by avoiding high heat and direct oil contact.
- Fat Content - En papillote often involves added fats, which increases calorie content but can improve nutrient absorption.
- Mineral Preservation - Both methods conserve minerals effectively, though poaching leaches fewer minerals into cooking liquid when consumed.
Related Important Terms
Precision Poaching
Precision poaching offers exact temperature control, ensuring delicate proteins cook evenly without overcooking, unlike en papillote where heat distribution can be less consistent due to the steam and sealed environment. This method optimizes moisture retention and texture by maintaining water temperature precisely between 140degF and 180degF, minimizing the risk of dryness often associated with other moist-heat cooking techniques.
Sous Vide vs En Papillote
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control that preserves moisture and enhances the natural texture of food more consistently than en papillote, which relies on steam trapped in parchment or foil. While en papillote infuses delicate flavors and retains juices, sous vide provides uniform doneness and superior moisture retention through vacuum-sealed cooking in a water bath.
Aquatic Aroma Infusion
Poaching involves gently simmering food in liquid, allowing the aquatic aroma to infuse deeply into the protein for enhanced flavor during moist-heat cooking. En papillote, by wrapping food in parchment, traps steam and concentrates the natural juices, providing a subtler aquatic aroma infusion compared to poaching's direct liquid immersion.
Steam-Seal Technique
Poaching and en papillote are moist-heat cooking methods that preserve natural flavors and moisture, with en papillote utilizing a steam-seal technique by cooking food enclosed in parchment paper or foil, trapping steam and intensifying flavors. This steam-seal approach enhances moisture retention more effectively than poaching, which involves submerging food in gently simmering liquid.
Encapsulated Moisture Retention
Poaching and en papillote both utilize encapsulated moisture retention to cook food gently and preserve tenderness, with poaching submerging ingredients in a flavorful liquid while en papillote traps steam within parchment or foil packets. This sealed environment in en papillote enhances the concentration of natural juices and aromas, resulting in intensified flavor without dilution, contrasting the more fluid medium of poaching.
Flavor Envelope Cooking
Poaching uses gentle, submersion cooking in simmering liquid to preserve delicate flavors and moisture, while en papillote involves sealing food in parchment to steam within its own juices, enhancing natural aromas and preventing flavor loss. En papillote's flavor envelope technique intensifies taste profiles by trapping herbs, spices, and liquids, creating a concentrated, aromatic cooking environment distinct from the more uniform poaching method.
Gentle Leaching Method
Poaching offers a gentle leaching method that preserves delicate flavors and nutrients by cooking food at low temperatures in a subtle liquid environment, unlike en papillote which steams food sealed in parchment, concentrating moisture and aroma but fostering a slightly different texture. This controlled, moist-heat cooking technique minimizes nutrient loss and prevents toughening of proteins, making poaching ideal for delicate ingredients such as fish, eggs, or fruits.
Parcel Cooking Innovation
Poaching and en papillote both utilize moist-heat techniques but en papillote innovates by enclosing food in parchment paper parcels, trapping steam and enhancing flavor infusion with minimal nutrient loss. This parcel cooking method ensures even heat distribution and moisture retention, resulting in tender, aromatic dishes while maintaining the health benefits of the ingredients.
Liquid Medium Envelopment
Poaching utilizes a water or flavorful broth as a liquid medium to envelop food, ensuring gentle heat penetration and moisture retention throughout cooking. En papillote creates a sealed environment using parchment paper, trapping steam and natural juices to tenderize ingredients while preserving moisture without direct liquid immersion.
Poaching vs En Papillote for moist-heat cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com