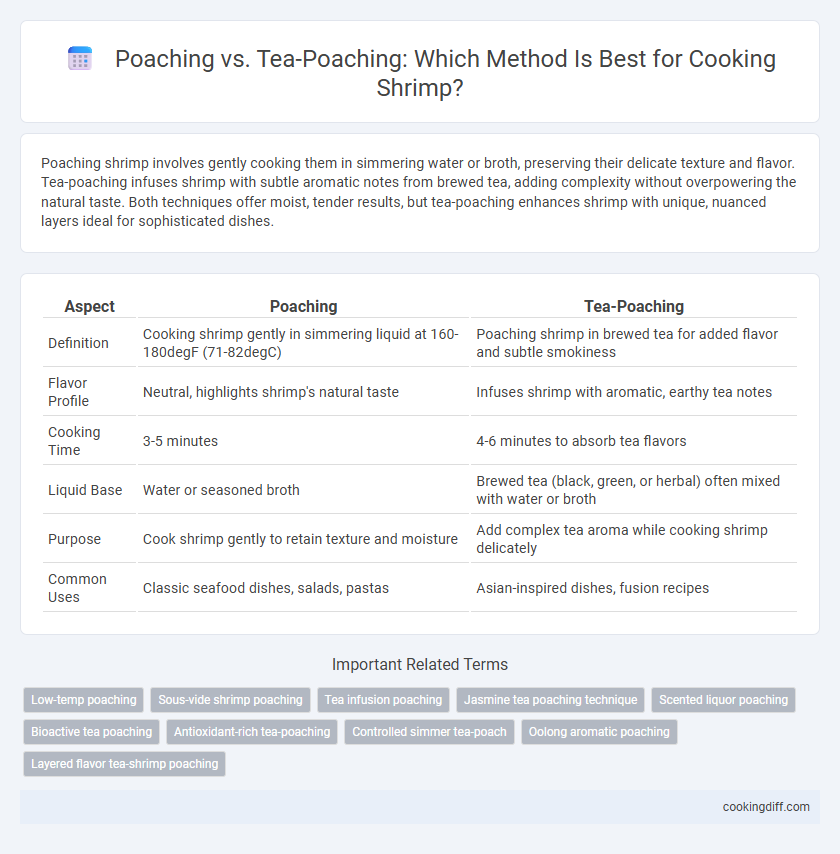
Poaching shrimp involves gently cooking them in simmering water or broth, preserving their delicate texture and flavor. Tea-poaching infuses shrimp with subtle aromatic notes from brewed tea, adding complexity without overpowering the natural taste. Both techniques offer moist, tender results, but tea-poaching enhances shrimp with unique, nuanced layers ideal for sophisticated dishes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Poaching | Tea-Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking shrimp gently in simmering liquid at 160-180degF (71-82degC) | Poaching shrimp in brewed tea for added flavor and subtle smokiness |
| Flavor Profile | Neutral, highlights shrimp's natural taste | Infuses shrimp with aromatic, earthy tea notes |
| Cooking Time | 3-5 minutes | 4-6 minutes to absorb tea flavors |
| Liquid Base | Water or seasoned broth | Brewed tea (black, green, or herbal) often mixed with water or broth |
| Purpose | Cook shrimp gently to retain texture and moisture | Add complex tea aroma while cooking shrimp delicately |
| Common Uses | Classic seafood dishes, salads, pastas | Asian-inspired dishes, fusion recipes |
Introduction to Poaching Techniques for Shrimp
Poaching shrimp involves gently cooking them in liquid at low temperatures to maintain their delicate texture and flavor. Tea-poaching incorporates aromatic tea into the poaching liquid, infusing the shrimp with subtle, fragrant notes.
- Traditional Poaching - Utilizes water or broth heated between 160-180degF to gently cook shrimp without drying them out.
- Tea-Poaching - Adds tea leaves or brewed tea to the poaching liquid, imparting unique flavors and antioxidants to the shrimp.
- Texture and Flavor - Both methods preserve shrimp's tenderness, while tea-poaching offers a nuanced taste profile ideal for gourmet dishes.
What is Traditional Poaching?
Traditional poaching is a gentle cooking technique where food, such as shrimp, is submerged in a flavorful liquid heated to a low temperature, typically between 160degF and 180degF. This method preserves the delicate texture and natural flavors of shrimp without toughening the protein.
Tea-poaching involves simmering shrimp in brewed tea, infusing the seafood with unique aromatic notes and subtle tannins. Unlike traditional poaching, tea-poaching imparts additional flavor complexity while still maintaining a tender texture. Both methods rely on controlled low heat to cook shrimp evenly and gently, minimizing moisture loss.
The Process of Tea-Poaching Shrimp
Tea-poaching shrimp involves simmering the shrimp gently in a fragrant tea infusion, which imparts subtle flavors and keeps the texture tender. Unlike traditional poaching in plain water, the tea's antioxidants and aromatic compounds enhance the shrimp's natural sweetness without overwhelming it. This method requires careful temperature control, typically around 160-180degF, to ensure even cooking and maximum flavor absorption.
Key Differences Between Poaching and Tea-Poaching
Poaching involves gently cooking shrimp in simmering water or broth, maintaining delicate textures and natural flavors. Tea-poaching infuses shrimp with subtle aromas by cooking them in brewed tea instead of plain liquid, enhancing complexity.
- Cooking Liquid - Poaching uses water or stock, while tea-poaching employs brewed tea varieties like green or black tea.
- Flavor Profile - Poaching preserves shrimp's original taste; tea-poaching imparts nuanced tea flavors and slight bitterness.
- Temperature Control - Both methods require low heat, but tea-poaching demands careful temperature to avoid tea bitterness.
Tea-poaching offers a sophisticated alternative to classic poaching, enriching shrimp with delicate aromatic notes.
Flavor Profiles: Classic Poaching vs Tea-Poaching
Classic poaching uses a gentle simmer in a flavored broth to preserve the shrimp's natural sweetness and tenderness. Tea-poaching introduces subtle earthy and smoky notes, enhancing complexity while maintaining delicate texture.
- Classic poaching - Infuses shrimp with mild aromatics like herbs and citrus without overpowering flavor.
- Tea-poaching - Imparts a nuanced depth from the tannins and smokiness of brewed tea leaves.
- Flavor complexity - Tea-poaching offers a layered taste experience compared to the straightforward freshness of classic poaching.
Temperature and Timing: Achieving Perfectly Cooked Shrimp
How does temperature influence the choice between poaching and tea-poaching for cooking shrimp? Poaching shrimp at a steady 160-180degF ensures gentle cooking that preserves texture and moisture, preventing rubberiness. Tea-poaching introduces aromatic flavors at similar temperatures but requires precise timing of 2-3 minutes to avoid overcooking and maintain shrimp's delicate bite.
Health Benefits: Nutritional Impact of Each Method
Poaching shrimp in water or broth preserves more omega-3 fatty acids and essential minerals compared to tea-poaching, which can introduce tannins and caffeine, potentially affecting nutrient absorption. Tea-poaching imparts unique antioxidants from tea leaves but may reduce vitamin B content due to the tea's acidity. Choosing plain poaching enhances the shrimp's natural nutritional profile, supporting heart health and providing lean protein without added compounds.
Presentation and Visual Appeal
Poaching shrimp preserves a natural, translucent appearance that highlights the delicate texture, resulting in a clean and elegant presentation ideal for fine dining. The shrimp maintain a firm, plump shape without added color, emphasizing freshness and subtlety on the plate.
Tea-poaching imparts a warm, amber hue and subtle aromatic flavors, enhancing visual appeal with a rustic, inviting look that complements casual or fusion cuisine. The infusion of tea leaves can create a gentle glaze on the shrimp, adding depth and an artisanal touch to the presentation.
When to Use Each Method: Culinary Applications
| Poaching | Ideal for gently cooking shrimp to maintain a delicate texture and subtle flavor, often used in salads, cold dishes, or recipes requiring tender, evenly cooked seafood. |
| Tea-poaching | Enhances shrimp with a unique, aromatic infusion by simmering in brewed tea, suitable for dishes demanding subtle herbal or smoky notes, such as Asian-inspired cuisine or elegant appetizers. |
| When to Use Each | Poaching is preferred for straightforward, mild shrimp dishes focusing on texture, while tea-poaching is chosen to introduce complex flavor layers without overpowering the shrimp's natural taste. |
Related Important Terms
Low-temp poaching
Low-temperature poaching offers gentle heat that preserves shrimp's delicate texture and prevents overcooking, unlike traditional poaching methods which often rely on higher temperatures. Tea-poaching infuses subtle flavors through antioxidants and tannins while maintaining the precise low temperature essential for tender, juicy shrimp.
Sous-vide shrimp poaching
Poaching shrimp using sous-vide ensures precise temperature control, resulting in perfectly tender and evenly cooked shrimp without the risk of overcooking common in traditional poaching methods. Unlike tea-poaching, which imparts aromatic flavors through brewed leaves, sous-vide shrimp poaching prioritizes texture and moisture retention by cooking vacuum-sealed shrimp at consistent low temperatures, enhancing their natural sweetness.
Tea infusion poaching
Tea infusion poaching enhances shrimp by gently infusing delicate flavors and antioxidants from green or black tea leaves, resulting in a subtly aromatic and tender texture that traditional poaching methods often lack. Unlike plain water poaching, tea-poaching introduces nuanced taste profiles and boosts the nutritional benefits, making it a sophisticated culinary technique for preparing succulent shrimp.
Jasmine tea poaching technique
Jasmine tea poaching infuses shrimp with delicate floral and aromatic notes while maintaining a tender, moist texture, distinguishing it from traditional poaching methods that rely solely on simmering in water or broth. This technique leverages the natural antioxidants and subtle sweetness of jasmine tea to enhance flavor complexity and create a refined seafood dish.
Scented liquor poaching
Poaching shrimp in scented liquor, a refined variation of traditional tea-poaching, infuses the seafood with aromatic flavors from ingredients like star anise, cinnamon, and Shaoxing wine, enhancing its natural sweetness and tender texture. This method contrasts with tea-poaching by leveraging the complex profiles of spiced liquors to create a more robust and fragrant dish.
Bioactive tea poaching
Bioactive tea poaching enhances shrimp flavor by infusing antioxidants and polyphenols, which not only elevate taste but also improve nutritional value compared to traditional poaching. This method preserves shrimp's texture while imparting health-benefiting compounds, making it a superior culinary technique for both flavor and wellness.
Antioxidant-rich tea-poaching
Tea-poaching shrimp enhances their flavor while infusing antioxidants from green or black tea, which helps reduce oxidative damage during cooking. Unlike traditional poaching with water, tea-poaching preserves nutrients and offers health benefits by delivering polyphenols that support cellular protection.
Controlled simmer tea-poach
Controlled simmer tea-poaching gently infuses shrimp with delicate flavors while maintaining a tender, juicy texture through precise temperature management just below boiling point. Unlike traditional poaching, this method utilizes aromatic teas that enhance the seafood's natural sweetness without overwhelming its profile, resulting in a subtly infused, perfectly cooked shrimp.
Oolong aromatic poaching
Poaching shrimp in Oolong tea infuses the seafood with a delicate, floral aroma and subtle earthy notes that traditional water-based poaching lacks, enhancing the overall flavor profile. The antioxidants and tannins in Oolong tea gently tenderize the shrimp while imparting complex, aromatic layers that elevate the dish's culinary sophistication.
Poaching vs Tea-poaching for cooking shrimp. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com