Aluminum pressure cookers heat up quickly and provide excellent heat conductivity, making them efficient for pressure-cooking. Ceramic pressure cookers, on the other hand, offer a non-reactive cooking surface that preserves the natural flavor of food and is easier to clean. Choosing between aluminum and ceramic pressure cookers depends on the importance of rapid heating versus chemical neutrality and ease of maintenance in your cooking routine.
Table of Comparison
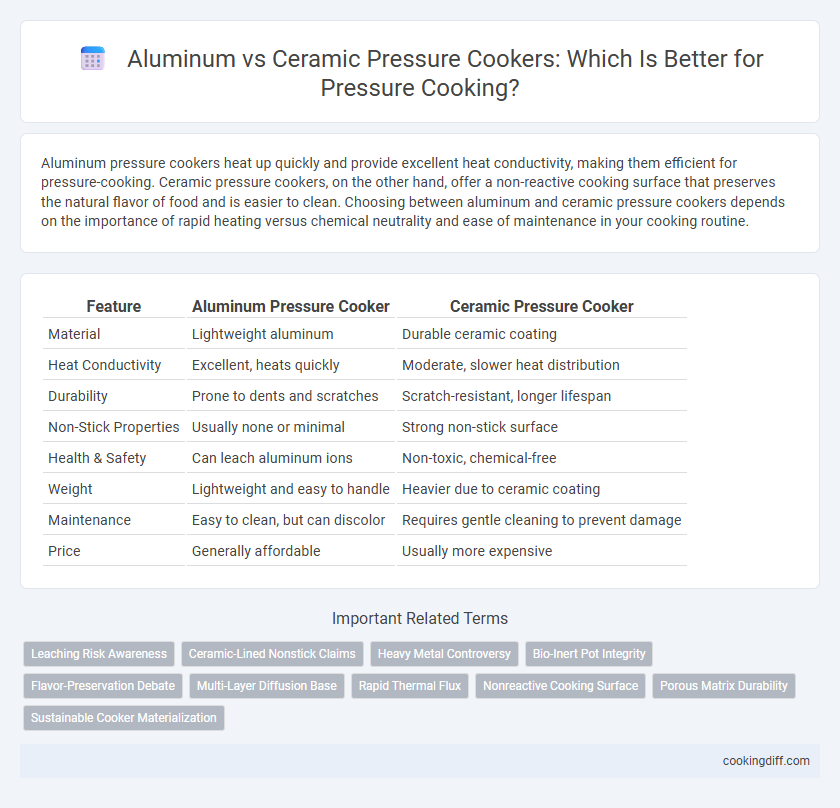
| Feature | Aluminum Pressure Cooker | Ceramic Pressure Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Lightweight aluminum | Durable ceramic coating |
| Heat Conductivity | Excellent, heats quickly | Moderate, slower heat distribution |
| Durability | Prone to dents and scratches | Scratch-resistant, longer lifespan |
| Non-Stick Properties | Usually none or minimal | Strong non-stick surface |
| Health & Safety | Can leach aluminum ions | Non-toxic, chemical-free |
| Weight | Lightweight and easy to handle | Heavier due to ceramic coating |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, but can discolor | Requires gentle cleaning to prevent damage |
| Price | Generally affordable | Usually more expensive |
Introduction to Pressure Cookers: Aluminum vs Ceramic
Aluminum and ceramic pressure cookers offer distinct benefits for efficient and safe cooking. Understanding their material properties and cooking performance helps in selecting the right pressure cooker for various culinary needs.
- Aluminum Pressure Cookers - Lightweight and excellent heat conductivity make aluminum pressure cookers ideal for fast cooking and energy efficiency.
- Ceramic Pressure Cookers - Non-reactive and durable, ceramic pressure cookers provide even heat distribution and are preferred for healthier cooking without metal leaching.
- Material Durability and Maintenance - Aluminum requires cautious cleaning to avoid corrosion, whereas ceramic offers easy maintenance and resistance to scratches and stains.
Material Composition: Aluminum vs Ceramic
Aluminum pressure cookers offer excellent heat conductivity and lightweight durability, making them efficient for fast cooking. Ceramic pressure cookers provide non-reactive surfaces and enhanced heat retention, promoting even cooking without metallic taste transfer.
- Aluminum Material - Lightweight metal with high thermal conductivity, enabling rapid heat distribution.
- Ceramic Composition - Made from clay-based materials providing a non-reactive and non-toxic cooking surface.
- Heat Retention - Ceramics retain heat longer, while aluminum heats up and cools down quickly.
Choosing between aluminum and ceramic depends on preferences for cooking speed, heat retention, and chemical reactivity during pressure-cooking.
Heat Conductivity and Cooking Efficiency
| Material | Heat Conductivity | Cooking Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Pressure Cooker | High thermal conductivity allows rapid and even heat distribution, reducing cooking time significantly. | Efficient heat transfer results in lower energy consumption and faster pressure buildup, optimizing cooking speed. |
| Ceramic Pressure Cooker | Lower heat conductivity compared to aluminum, causing slower and uneven heat transfer. | Longer preheating times and less efficient heat retention can extend cooking duration and increase energy use. |
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Aluminum pressure cookers offer excellent heat conductivity but tend to be less durable due to their susceptibility to dents and corrosion over time. Ceramic pressure cookers, while generally slower to heat, provide superior longevity with a scratch-resistant and non-reactive surface that withstands prolonged use. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing fast heat transfer or enhanced durability for long-term pressure cooking performance.
Safety Features and User Experience
Aluminum pressure cookers offer rapid heat conduction, enhancing cooking speed but may pose risks of warping or corrosion over time, requiring careful maintenance to ensure safety. Ceramic pressure cookers provide superior chemical resistance and non-reactive surfaces, minimizing contamination risks and offering a more user-friendly cleaning experience. Both types include safety valves and locking mechanisms, but ceramic models often have more advanced temperature controls for consistent pressure regulation and enhanced user safety.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Aluminum pressure cookers require regular seasoning to prevent discoloration and avoid corrosion, with cleaning relying on mild detergents and non-abrasive sponges. Ceramic pressure cookers offer easier maintenance due to their non-porous, scratch-resistant surfaces that resist food sticking and stains, allowing for simple cleaning with warm soapy water.
Aluminum models may develop black spots if not properly maintained, necessitating thorough drying to prevent oxidation. Ceramic cookers are generally dishwasher-safe, reducing manual cleaning efforts and extending the lifespan of the non-stick coating. Proper gasket and valve cleaning in both types ensures safety and effective pressure control during cooking.
Impact on Food Flavor and Nutrition
Aluminum pressure cookers heat food quickly, which can cause slight changes in flavor due to metal interaction, but they efficiently retain most nutrients. The porous nature of aluminum might sometimes give a metallic taste to very acidic dishes, potentially impacting the overall flavor profile.
Ceramic pressure cookers preserve food flavor by providing a non-reactive surface that prevents metallic tastes and maintains natural food aromas. Their slower heat conduction can help retain delicate nutrients that might degrade in rapid high heat, promoting better nutritional value.
Cost Comparison: Aluminum vs Ceramic Pressure Cookers
Which is more cost-effective for pressure-cooking: aluminum or ceramic pressure cookers? Aluminum pressure cookers typically cost less due to the lower price of the material and simpler manufacturing process. Ceramic pressure cookers, while more expensive initially, offer longer durability and resistance to corrosion, potentially reducing replacement costs over time.
Suitability for Different Cooking Styles
Aluminum pressure cookers heat up quickly and distribute heat evenly, making them well-suited for fast-cooking dishes like stews and soups. Ceramic pressure cookers offer gentle, consistent heat, ideal for slow-cooked recipes and delicate foods that require careful temperature control.
- Aluminum Cookers - Best for high-heat, rapid cooking styles requiring efficient heat conduction.
- Ceramic Cookers - Preferred for simmering and recipes needing gradual heat distribution.
- Cooking Versatility - Aluminum excels in durability and quick cooking; ceramic supports healthier cooking with less risk of food sticking.
Related Important Terms
Leaching Risk Awareness
Aluminum pressure cookers pose a higher risk of aluminum leaching into food, especially when cooking acidic or salty dishes, potentially affecting health over prolonged use. Ceramic pressure cookers offer a safer alternative with minimal leaching, maintaining food purity and reducing the risk of metal contamination during pressure-cooking.
Ceramic-Lined Nonstick Claims
Ceramic-lined nonstick pressure cookers offer superior chemical-free cooking surfaces compared to traditional aluminum pressure cookers, providing enhanced durability and resistance to scratches. These ceramic coatings ensure even heat distribution while preventing food from sticking, making them a safer and more efficient option for pressure-cooking.
Heavy Metal Controversy
Aluminum pressure cookers are lightweight and conduct heat efficiently but have raised concerns due to potential aluminum leaching, which may pose health risks from heavy metal exposure. Ceramic pressure cookers, made from non-reactive materials, offer a safer alternative by minimizing heavy metal contamination, making them preferable for health-conscious pressure cooking.
Bio-Inert Pot Integrity
Aluminum pressure cookers offer excellent thermal conductivity but may react with acidic foods, potentially compromising bio-inert pot integrity over time. Ceramic pressure cookers provide a non-reactive, bio-inert surface that preserves food purity and maintains pot durability without leaching metals during pressure-cooking.
Flavor-Preservation Debate
Aluminum pressure cookers heat food quickly but may interact with acidic ingredients, potentially altering flavor, whereas ceramic pressure cookers provide inert cooking surfaces that better preserve natural taste and nutrients. Ceramic models often excel in maintaining vibrant flavors and avoiding metallic aftertastes, making them preferred for delicate recipes demanding precise flavor preservation.
Multi-Layer Diffusion Base
A multi-layer diffusion base in aluminum pressure cookers enhances heat distribution by combining aluminum's excellent thermal conductivity with a stainless steel layer for durability, preventing hotspots and ensuring even cooking. Ceramic pressure cookers typically lack this multi-layer base, which can lead to less efficient heat transfer and uneven pressure build-up during cooking.
Rapid Thermal Flux
Aluminum pressure cookers offer superior rapid thermal flux due to their excellent thermal conductivity of approximately 235 W/m*K, enabling faster heat transfer and reduced cooking times. Ceramic pressure cookers, with significantly lower thermal conductivity around 1.5 W/m*K, provide slower heat distribution but ensure even cooking without hotspots, ideal for delicate pressure-cooking tasks.
Nonreactive Cooking Surface
Aluminum pressure cookers have a reactive surface that can interact with acidic foods, potentially altering flavor and causing discoloration, whereas ceramic pressure cookers offer a nonreactive cooking surface that preserves the natural taste and color of ingredients. The nonporous nature of ceramic coatings also prevents food from sticking and reduces the risk of metal leaching, making it a healthier option for pressure-cooking.
Porous Matrix Durability
Aluminum pressure cookers offer excellent heat conductivity but tend to have lower porous matrix durability, leading to potential corrosion and degradation over time. Ceramic pressure cookers feature a robust porous matrix that resists wear and chemical reactions, enhancing longevity and maintaining structural integrity during prolonged pressure-cooking.
Aluminum pressure cooker vs ceramic pressure cooker for pressure-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com