Roasting lamb develops rich, caramelized flavors through direct dry heat, producing a tender, succulent texture with a crispy exterior. Cold smoke roasting infuses a subtle smoky aroma without cooking the meat, requiring subsequent heat to bring lamb to a safe temperature. Choosing roasting over cold smoke roasting ensures a fully cooked, flavorful meal in one process, ideal for preserving lamb's natural juiciness and enhancing its savory taste.
Table of Comparison
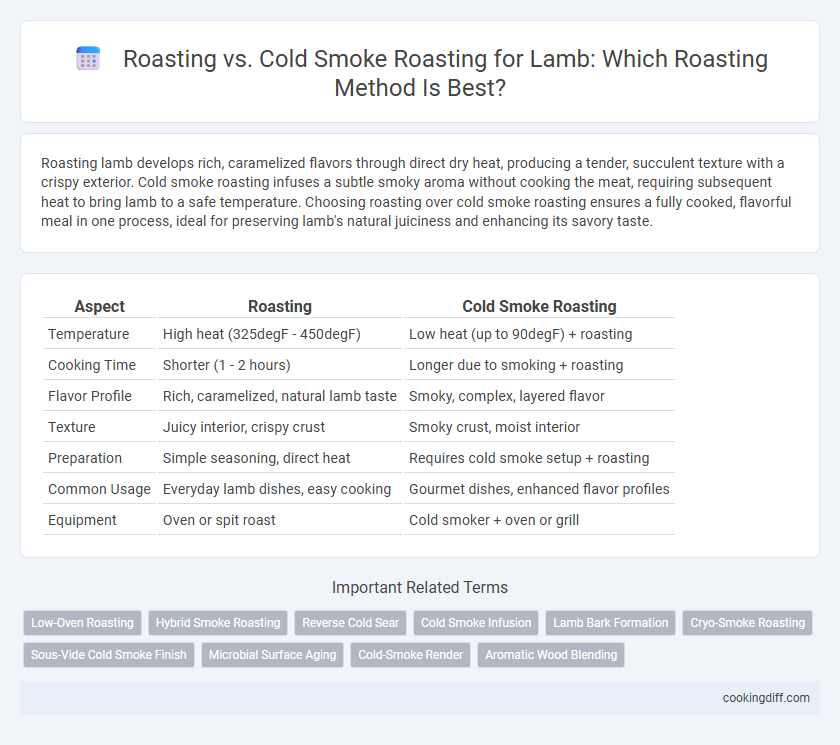
| Aspect | Roasting | Cold Smoke Roasting |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | High heat (325degF - 450degF) | Low heat (up to 90degF) + roasting |
| Cooking Time | Shorter (1 - 2 hours) | Longer due to smoking + roasting |
| Flavor Profile | Rich, caramelized, natural lamb taste | Smoky, complex, layered flavor |
| Texture | Juicy interior, crispy crust | Smoky crust, moist interior |
| Preparation | Simple seasoning, direct heat | Requires cold smoke setup + roasting |
| Common Usage | Everyday lamb dishes, easy cooking | Gourmet dishes, enhanced flavor profiles |
| Equipment | Oven or spit roast | Cold smoker + oven or grill |
Introduction to Roasting vs Cold Smoke Roasting for Lamb
Roasting lamb involves cooking it at high temperatures, typically between 325degF and 450degF, to develop a rich, caramelized crust while preserving juicy, tender meat inside. Cold smoke roasting combines low-temperature roasting with cold smoking, infusing the lamb with smoky flavors without fully cooking it during the smoking phase. This technique allows for a unique balance of savory, smoky taste and tender texture, ideal for gourmet lamb dishes.
Understanding Traditional Roasting Techniques
Roasting lamb involves cooking the meat at high, consistent temperatures to achieve a tender, juicy interior with a caramelized exterior, preserving the natural flavors. Cold smoke roasting, on the other hand, infuses smoky aromas by slowly exposing the lamb to smoke at lower temperatures without cooking it through.
- Roasting ensures thorough cooking - Heat penetrates evenly, resulting in safe, fully cooked lamb with a rich crust.
- Cold smoke roasting imparts flavor - Smoke imparts a distinctive taste while maintaining the raw texture, typically followed by further cooking.
- Traditional roasting techniques maximize tenderness - Controlled heat and resting periods allow connective tissues to break down for optimal texture.
Understanding these methods enhances the ability to choose the right technique for desired flavor and texture in lamb dishes.
What Is Cold Smoke Roasting?
Cold smoke roasting is a technique that infuses lamb with smoky flavors at lower temperatures, typically between 68degF to 86degF (20degC to 30degC), without cooking the meat. This method preserves the tenderness of the lamb while adding a distinct aroma.
Unlike traditional roasting, which uses high heat to cook the lamb thoroughly, cold smoke roasting imparts flavor over an extended period without raising the internal temperature significantly. This process requires precise temperature control to prevent bacterial growth and maintain food safety. Cold smoke roasting enhances the lamb's taste profile by combining subtle smokiness with its natural juiciness, making it a preferred method for gourmet preparations.
Key Differences Between Roasting and Cold Smoke Roasting
Roasting lamb involves cooking at high temperatures, typically between 325degF and 450degF, to achieve a tender and well-browned exterior. This method uses dry heat that penetrates the meat quickly, enhancing flavor through Maillard reactions and caramelization.
Cold smoke roasting, on the other hand, cooks lamb at much lower temperatures, usually below 90degF, allowing the smoke to infuse subtle smoky flavors without fully cooking the meat. This technique preserves moisture and imparts delicate aromas, making it ideal for slow flavor development rather than immediate doneness.
Flavor Profiles: Roasted Lamb vs Cold Smoke Roasted Lamb
Lamb roasted using high heat develops a rich, caramelized crust with intense, savory flavors that enhance its natural umami. Cold smoke roasting imparts a delicate smoky aroma and subtle woodsy notes without cooking the meat, preserving its tender texture and nuanced taste.
- Roasted Lamb - High-temperature roasting creates a Maillard reaction that intensifies meat flavor and forms a flavorful crust.
- Cold Smoke Roasted Lamb - Cold smoking introduces a light smoke flavor while maintaining the lamb's moist and tender interior.
- Flavor Complexity - Roasting produces robust, concentrated meatiness whereas cold smoke roasting offers a milder, aromatic profile with nuanced smoky undertones.
Texture Comparison: Juiciness and Tenderness
| Roasting | Cold Smoke Roasting |
|---|---|
| Roasting lamb at high temperatures seals in natural juices, resulting in a tender interior with a slightly crispy exterior texture. The Maillard reaction enhances flavor while maintaining moisture, creating a juicy and succulent bite. | Cold smoke roasting imparts a smoky flavor without cooking the meat rapidly, preserving a firmer texture with less moisture loss. This method produces a unique chewiness and a drier surface, emphasizing smoky aroma over juiciness. |
Health and Safety Considerations
Roasting lamb at high temperatures ensures the destruction of harmful bacteria such as Salmonella and E. coli, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses. Cold smoke roasting involves lower temperatures that may not eliminate all pathogens, necessitating careful monitoring of smoking times and meat quality. Proper handling and cooking methods are essential for maintaining food safety and preventing contamination during both roasting processes.
Equipment and Preparation Tips
Roasting lamb requires an oven or rotisserie equipped with reliable temperature control to achieve even cooking and a crispy exterior. Essential preparation includes seasoning the meat and allowing it to come to room temperature before roasting to ensure uniform heat distribution.
Cold smoke roasting combines a smoker with a cold smoke generator to infuse lamb with smoky flavors without overcooking. Preparation involves curing or brining the lamb beforehand to enhance moisture retention and ensure safe cold smoking temperatures below 90degF.
Best Cuts of Lamb for Each Method
Roasting lamb enhances tenderness and flavor, best suited for tender cuts like the rack or leg. Cold smoke roasting imparts a smoky aroma without cooking, ideal for firmer cuts such as shoulder or shank.
- Rack of Lamb for Roasting - This tender cut cooks evenly and develops a rich crust when roasted at high temperatures.
- Leg of Lamb for Roasting - Offers a balance of fat and muscle that retains moisture and flavor during roasting.
- Shoulder or Shank for Cold Smoke Roasting - These tougher cuts absorb smoky flavor well during low-temperature cold smoking, enhancing complexity without overcooking.
Related Important Terms
Low-Oven Roasting
Low-oven roasting lamb enhances tenderness and flavor by slowly cooking at temperatures around 250degF to 275degF, allowing collagen breakdown and even heat distribution. In contrast to cold smoke roasting, which imparts smoky aromas without substantial cooking, low-oven roasting fully cooks the meat, creating a succulent, tender texture ideal for rich lamb cuts.
Hybrid Smoke Roasting
Hybrid smoke roasting combines the intense heat of traditional roasting with the subtle infusion of cold smoke, enhancing lamb's flavor complexity and tenderness. This method optimizes Maillard reaction while preserving the aromatic compounds from cold smoke, resulting in a uniquely rich and juicy lamb experience.
Reverse Cold Sear
Reverse cold sear combines the advantages of roasting and cold smoke roasting by slowly cooking the lamb at low temperatures before finishing with a high-heat sear, enhancing tenderness and flavor retention. This technique preserves the lamb's natural juices while infusing a subtle smoky aroma, resulting in a perfectly cooked, juicy, and flavorful cut.
Cold Smoke Infusion
Cold smoke infusion imparts a subtle, aromatic flavor to lamb without cooking the meat, preserving its tender texture and moistness. Unlike traditional roasting, which uses high heat to cook, cold smoking combines low temperatures with smoky phenols to enhance the lamb's complexity and depth of taste.
Lamb Bark Formation
Roasting lamb develops a rich bark formation through Maillard reactions and caramelization at high temperatures, enhancing flavor and texture with a crispy exterior. Cold smoke roasting limits bark development because lower temperatures prevent the breakdown of proteins and sugars essential for creating the characteristic crust on lamb.
Cryo-Smoke Roasting
Cryo-Smoke Roasting enhances lamb by combining controlled low-temperature smoking with precise roasting, preserving moisture and infusing deep smoky flavors without overshadowing natural taste. This method outperforms traditional roasting and cold smoke roasting by achieving optimal tenderness and a balanced smoky aroma through advanced cryogenic smoke infusion technology.
Sous-Vide Cold Smoke Finish
Sous-vide cold smoke finish combines precise temperature control of sous-vide cooking with the distinctive flavor infusion from cold smoking, preserving lamb's tenderness and moisture while developing complex smoky aromas. This method contrasts with traditional roasting by minimizing direct heat exposure, ensuring even cooking and enhanced juiciness without overcooking the lamb.
Microbial Surface Aging
Roasting lamb involves high heat that effectively reduces microbial surface aging by killing bacteria and halting enzymatic activity, ensuring safety and a distinct cooked flavor. Cold smoke roasting, however, uses low heat and smoke to enhance flavor while allowing controlled microbial surface aging, which can tenderize the meat and develop complex aromas but requires careful monitoring to prevent spoilage.
Cold-Smoke Render
Cold-smoke rendering in lamb roasting infuses deep smoky flavors while preserving the meat's juiciness and tenderness, unlike traditional roasting which relies on high heat to cook and develop crust. This technique combines low-temperature exposure with smoke to enhance aroma and texture, creating a distinctive gourmet profile prized in culinary applications.
Roasting vs Cold Smoke Roasting for lamb. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com