Cast iron skillets offer excellent heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for roasting meats to achieve a perfect sear and tender interior. Carbon steel skillets heat up faster and are lighter, providing more responsive temperature control and easier handling during roasting. Both materials develop a natural non-stick surface over time, enhancing flavor and ensuring evenly roasted results.
Table of Comparison
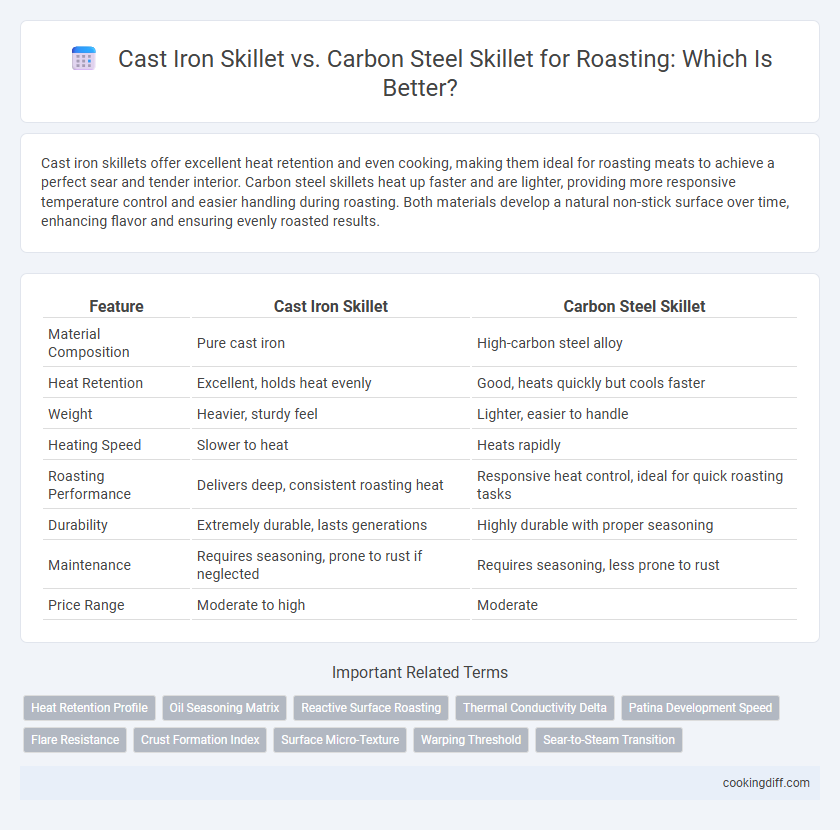
| Feature | Cast Iron Skillet | Carbon Steel Skillet |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure cast iron | High-carbon steel alloy |
| Heat Retention | Excellent, holds heat evenly | Good, heats quickly but cools faster |
| Weight | Heavier, sturdy feel | Lighter, easier to handle |
| Heating Speed | Slower to heat | Heats rapidly |
| Roasting Performance | Delivers deep, consistent roasting heat | Responsive heat control, ideal for quick roasting tasks |
| Durability | Extremely durable, lasts generations | Highly durable with proper seasoning |
| Maintenance | Requires seasoning, prone to rust if neglected | Requires seasoning, less prone to rust |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Roasting: Cast Iron vs Carbon Steel Skillets
Which skillet, cast iron or carbon steel, offers better performance for roasting? Cast iron skillets provide excellent heat retention, creating an even roasting surface that enhances flavor development. Carbon steel pans heat up more quickly and are lighter, making them versatile tools for achieving a perfect roast with superior temperature control.
Material Composition: What Sets Cast Iron and Carbon Steel Apart
Cast iron skillets are made from molten iron mixed with small amounts of carbon, which creates a dense and heavy material known for excellent heat retention and even cooking. Carbon steel skillets consist primarily of iron alloyed with a higher percentage of carbon, making them lighter and more responsive to temperature changes during roasting.
The porous surface of cast iron allows it to develop a natural non-stick layer over time, enhancing flavor through seasoning. Carbon steel's smoother surface heats evenly but requires more frequent seasoning to maintain its rust-resistant coating and optimal roasting performance.
Heat Retention and Distribution in Roasting
Cast iron skillets excel in heat retention, maintaining a consistent temperature ideal for even roasting. Carbon steel skillets heat up faster and distribute heat more evenly, reducing hot spots during roasting. Both materials enhance roasting quality, but cast iron's superior heat retention is preferred for slow, steady cooking.
Preheating Time and Temperature Response
Carbon steel skillets heat up faster than cast iron due to their thinner construction, making them ideal for quick roasting. Cast iron retains heat longer, providing a more consistent temperature but requires more time to preheat.
- Preheating Time - Carbon steel typically preheats in about 5 minutes, while cast iron may take 10-15 minutes.
- Temperature Response - Carbon steel responds quickly to temperature changes, allowing better control during roasting.
- Heat Retention - Cast iron holds heat evenly, ensuring steady cooking temperatures throughout roasting.
The choice between cast iron and carbon steel depends on whether fast preheating or consistent heat retention is prioritized for roasting.
Weight and Handling During Roasting
Carbon steel skillets are significantly lighter than cast iron, making them easier to handle during roasting. The lighter weight of carbon steel allows for quicker adjustment and less strain when moving the skillet in and out of the oven.
- Weight Difference - Cast iron typically weighs about twice as much as carbon steel skillets of the same size.
- Ease of Handling - Carbon steel's lighter weight reduces the risk of spills or drops while roasting heavy meats or vegetables.
- Heat Management - The lighter carbon steel skillet heats up faster but may require more attention to prevent overheating during roasting.
Roasting Performance: Browning, Crisping, and Flavor
Cast iron skillets provide superior heat retention, ensuring even browning and excellent crisping for roasting meats and vegetables. Their heavy mass creates a stable cooking environment, which enhances Maillard reactions and deepens flavor complexity.
Carbon steel skillets heat up faster and respond quickly to temperature changes, offering more precise control during roasting. They develop a naturally non-stick surface that promotes crisp texture while maintaining a lighter weight for easy handling.
Versatility: Oven-to-Table Use for Roasted Dishes
Cast iron skillets excel in retaining and evenly distributing heat, making them ideal for roasting a variety of dishes from meats to vegetables. Their ability to withstand high oven temperatures enhances versatility for oven-to-table roasting without warping or damage.
Carbon steel skillets also offer excellent heat conduction and responsiveness, making quick temperature adjustments easy during roasting. They are lighter than cast iron, allowing for easier handling when transferring from oven to table. Both skillets develop natural non-stick properties with seasoning, improving their performance for repeated roasting use.
Maintenance and Cleaning for Roasting Pans
Cast iron skillets require thorough seasoning and careful drying after roasting to prevent rust and maintain a non-stick surface. Carbon steel skillets also need regular seasoning but clean more easily with just hot water and a soft brush, avoiding harsh detergents. Both materials benefit from immediate drying and applying a thin layer of oil to preserve their roasting performance and longevity.
Lifespan and Durability for Regular Roasting
Cast iron skillets offer exceptional durability and can last for decades with proper care, making them ideal for regular roasting. Carbon steel skillets are also durable but may require more frequent seasoning to maintain their lifespan during consistent roasting use.
- Cast Iron Durability - Extremely resistant to wear and able to handle high heat without warping, enhancing longevity in roasting.
- Carbon Steel Maintenance - More prone to rust if not properly seasoned, requiring regular upkeep to preserve its roasting performance.
- Lifespan Comparison - Cast iron generally outlasts carbon steel skillets under continuous roasting conditions due to its robust material composition.
Related Important Terms
Heat Retention Profile
Cast iron skillets boast superior heat retention due to their dense, thick composition, maintaining high temperatures consistently perfect for even roasting. Carbon steel skillets heat up faster but lose heat more quickly, requiring more frequent temperature adjustments during roasting to achieve optimal results.
Oil Seasoning Matrix
Cast iron skillets develop a robust oil seasoning matrix through multiple layers of polymerized oil, creating a non-stick surface ideal for high-heat roasting and even heat retention. Carbon steel skillets season more quickly with thinner, smoother oil layers that offer excellent heat responsiveness but require more frequent maintenance to sustain their protective seasoning.
Reactive Surface Roasting
Cast iron skillets offer a naturally seasoned, non-reactive surface ideal for even heat distribution during roasting, preventing food from sticking and enhancing flavor development. Carbon steel skillets, while lighter and quicker to heat, feature a more reactive surface that can influence the taste and color of acidic or highly seasoned foods during roasting.
Thermal Conductivity Delta
Carbon steel skillets offer higher thermal conductivity than cast iron, enabling faster and more even heat distribution during roasting. This thermal conductivity delta allows carbon steel to respond more quickly to temperature changes, providing better control over roasting results compared to the slower, heat-retentive cast iron.
Patina Development Speed
Carbon steel skillets develop a seasoning patina faster than cast iron due to their thinner profile and higher responsiveness to heat, allowing for quicker absorption and polymerization of oils. The faster patina formation enhances non-stick properties and improves roasting performance over time with consistent use.
Flare Resistance
Cast iron skillets exhibit superior flare resistance due to their thicker material and higher heat capacity, which allows them to withstand sudden temperature changes without warping or accidentally igniting flare-ups. Carbon steel skillets, while responsive and lightweight, are more prone to flare-induced damage because of their thinner construction and faster heat conduction, making cast iron the preferred choice for consistent and safe roasting over open flames.
Crust Formation Index
Carbon steel skillets excel in crust formation during roasting due to their rapid heat conductivity and ability to maintain high temperatures, resulting in a superior Maillard reaction. Cast iron skillets offer excellent heat retention but heat up slower, which can produce a less pronounced crust compared to carbon steel.
Surface Micro-Texture
Cast iron skillets feature a naturally porous surface micro-texture that enhances seasoning retention and creates a robust non-stick layer over time, ideal for consistent heat distribution during roasting. Carbon steel skillets possess a smoother micro-texture, allowing for quicker seasoning buildup and faster heat responsiveness, making them excellent for achieving a seared crust in roasting applications.
Warping Threshold
Cast iron skillets exhibit a high warping threshold due to their dense composition and thickness, making them ideal for consistent roasting at elevated temperatures. Carbon steel skillets, while lighter and quicker to heat, have a lower warping threshold and may warp if subjected to rapid temperature changes during roasting.
Cast Iron Skillet vs Carbon Steel Skillet for roasting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com