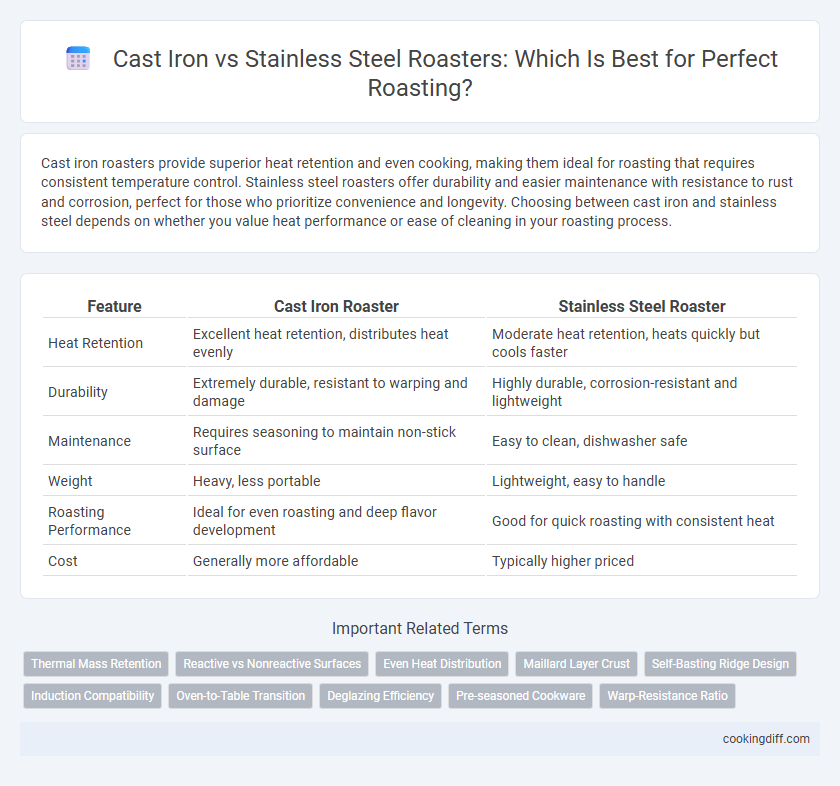
Cast iron roasters provide superior heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for roasting that requires consistent temperature control. Stainless steel roasters offer durability and easier maintenance with resistance to rust and corrosion, perfect for those who prioritize convenience and longevity. Choosing between cast iron and stainless steel depends on whether you value heat performance or ease of cleaning in your roasting process.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cast Iron Roaster | Stainless Steel Roaster |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention, distributes heat evenly | Moderate heat retention, heats quickly but cools faster |
| Durability | Extremely durable, resistant to warping and damage | Highly durable, corrosion-resistant and lightweight |
| Maintenance | Requires seasoning to maintain non-stick surface | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe |
| Weight | Heavy, less portable | Lightweight, easy to handle |
| Roasting Performance | Ideal for even roasting and deep flavor development | Good for quick roasting with consistent heat |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically higher priced |
Heat Retention: Cast Iron vs Stainless Steel
Cast iron roasters excel in heat retention, maintaining consistent temperatures ideal for even roasting. Stainless steel roasters heat up quickly but lose heat faster, requiring more frequent temperature adjustments during cooking.
- Cast Iron Heat Retention - Cast iron retains heat exceptionally well, providing steady, uniform cooking temperatures.
- Stainless Steel Heat Response - Stainless steel heats rapidly but dissipates heat quickly, leading to potential temperature fluctuations.
- Roasting Efficiency - Cast iron's superior heat retention enhances roasting quality by preventing temperature drops when food is added.
Even Cooking Performance Compared
Cast iron roasters provide superior heat retention and even heat distribution, resulting in consistent roasting performance and reduced hotspots. Stainless steel roasters heat up quickly but may have uneven temperature distribution, potentially causing irregular cooking. For optimal even cooking, cast iron remains the preferred choice due to its ability to maintain stable and uniform heat throughout the roasting process.
Durability and Longevity
Cast iron roasters offer exceptional durability, resisting warping and maintaining heat evenly for consistent roasting results over decades. Their seasoned surface enhances flavor and withstands high temperatures without degrading.
Stainless steel roasters provide excellent corrosion resistance and are less prone to rust, making them ideal for long-term use with minimal maintenance. However, they may be more susceptible to denting and uneven heat distribution compared to cast iron.
Weight and Ease of Handling
Cast iron roasters are significantly heavier than stainless steel roasters, which can make handling and maneuvering challenging during roasting. The dense material retains heat well but demands more strength and care to move safely.
Stainless steel roasters offer lightweight durability that enhances ease of handling, making them ideal for users prioritizing convenience and portability. Their corrosion resistance ensures long-lasting performance with less maintenance effort. Weighing considerably less than cast iron, stainless steel roasters reduce fatigue during frequent use and make transferring roasted foods simpler.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
| Cast Iron Roaster | Requires seasoning to maintain non-stick properties and prevent rust, demanding regular oil application after each use. Cleaning involves avoiding soap and abrasive scrubbers to preserve the seasoning layer. Proper drying and storage are crucial to prevent corrosion. |
| Stainless Steel Roaster | Offers easy maintenance with resistance to rust and corrosion, allowing cleaning with soap and water or dishwasher use. No seasoning needed, making it more convenient for frequent use. May require scrubbing to remove burnt-on food residue but generally more forgiving in cleaning methods. |
Versatility in the Kitchen
A cast iron roaster offers exceptional heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for slow roasting and braising, while its ability to go from stovetop to oven adds significant versatility. Stainless steel roasters excel in quick heating and cooling, making them perfect for roasting vegetables and meats where precise temperature control is essential.
Cast iron's durability and natural non-stick surface improve with seasoning, enhancing its usability for a variety of recipes over time. Stainless steel roasters often feature lightweight construction and compatibility with induction cooktops, increasing their convenience and multifunctionality in modern kitchens.
Nonstick Properties: Pros and Cons
Cast iron roasters develop a natural nonstick patina over time that improves with seasoning, making them ideal for roasting sticky or delicate foods. Stainless steel roasters lack this seasoning benefit but are easier to clean and resist rust without special maintenance.
- Cast iron nonstick advantage - Properly seasoned cast iron creates a durable, naturally nonstick surface perfect for roasting.
- Stainless steel ease of cleaning - Stainless steel roasters are dishwasher safe and do not require seasoning to prevent sticking.
- Maintenance trade-off - Cast iron needs regular seasoning and careful drying, while stainless steel is low-maintenance but less naturally nonstick.
Affordability and Value for Money
Which roaster offers better affordability and value for money between cast iron and stainless steel? Cast iron roasters typically provide superior heat retention and durability at a lower price point, making them a cost-effective choice for consistent roasting. Stainless steel roasters, while often more expensive, offer excellent corrosion resistance and easier maintenance, delivering long-term value for those prioritizing convenience and longevity.
Oven and Stovetop Compatibility
Cast iron roasters excel in retaining heat and are highly compatible with both ovens and stovetops, providing even roasting results. Stainless steel roasters offer quicker heating and are versatile on various heat sources but may not retain heat as long.
- Heat Retention - Cast iron's dense material ensures consistent temperature during roasting on stovetops and in ovens.
- Heating Speed - Stainless steel heats up faster, which is advantageous for quick stovetop roasting tasks.
- Oven Compatibility - Both materials are oven-safe, but cast iron's heat retention improves overall roasting quality.
Choosing between cast iron and stainless steel roasters depends on preferred heat retention and cooking speed needs.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Mass Retention
Cast iron roasters excel in thermal mass retention, providing steady and even heat distribution that ensures consistent roasting results. Stainless steel roasters heat up quickly but lose heat faster, making them less effective at maintaining constant roasting temperatures.
Reactive vs Nonreactive Surfaces
Cast iron roasters offer a reactive surface that enhances browning and flavor development through even heat retention, while stainless steel roasters provide a nonreactive surface that resists corrosion and does not alter food taste. The choice between reactive and nonreactive materials affects both the chemical interaction with food and the durability of the roasting equipment.
Even Heat Distribution
Cast iron roasters excel in even heat distribution due to their high thermal mass, ensuring consistent roasting temperatures and minimizing hotspots. Stainless steel roasters, while more responsive to temperature changes, often have less uniform heat distribution, which can lead to uneven roasting results.
Maillard Layer Crust
Cast iron roasters excel at developing a deep Maillard layer crust due to their superior heat retention and even heat distribution, which promotes consistent browning and caramelization. Stainless steel roasters heat up faster but often struggle to maintain the steady temperatures required for an optimal Maillard reaction, resulting in less pronounced crust formation.
Self-Basting Ridge Design
The self-basting ridge design in cast iron roasters promotes even heat distribution and continuous moisture retention by allowing drippings to circulate, enhancing flavor and tenderness. Stainless steel roasters with self-basting ridges offer durability and easier cleaning but typically lack the same heat retention properties for optimal self-basting performance.
Induction Compatibility
Cast iron roasters offer excellent heat retention but often require an induction-compatible base coating to work efficiently on induction cooktops, while stainless steel roasters typically feature built-in magnetic layers that ensure immediate compatibility with induction heating. Choosing stainless steel ensures faster magnetic response and uniform heat distribution on induction surfaces, enhancing control and roasting precision.
Oven-to-Table Transition
Cast iron roasters excel in retaining heat for a consistent oven-to-table transition, ensuring food stays warm longer while adding rustic charm to presentation; stainless steel roasters offer lightweight durability and easier handling but may cool faster once out of the oven, affecting the serving temperature. Choosing cast iron enhances heat retention and aesthetic appeal, whereas stainless steel provides practicality with quick cooling and simpler maintenance.
Deglazing Efficiency
Cast iron roasters excel in deglazing efficiency due to their superior heat retention and even surface, which helps dissolve caramelized food residues quickly, enhancing flavor development. Stainless steel roasters heat up rapidly and offer non-reactive surfaces but often retain less heat, making deglazing slightly less effective compared to cast iron.
Pre-seasoned Cookware
Cast iron roasters come pre-seasoned, providing a naturally non-stick surface that enhances flavor development and ensures even heat retention for superior roasting results. Stainless steel roasters, while durable and resistant to rust, lack pre-seasoning, requiring additional preparation to prevent sticking and achieve optimal browning during roasting.
Cast Iron Roaster vs Stainless Steel Roaster for Roasting Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com