Roasting potatoes delivers a crispy exterior and tender interior by cooking them evenly in high, dry heat, which enhances their natural flavors and caramelization. Convection air frying uses rapid air circulation to achieve similar crispiness but often results in a lighter texture with less oil absorption and faster cooking times. Both methods offer health-conscious alternatives to traditional frying, with roasting providing deeper flavors and air frying prioritizing speed and reduced fat content.
Table of Comparison
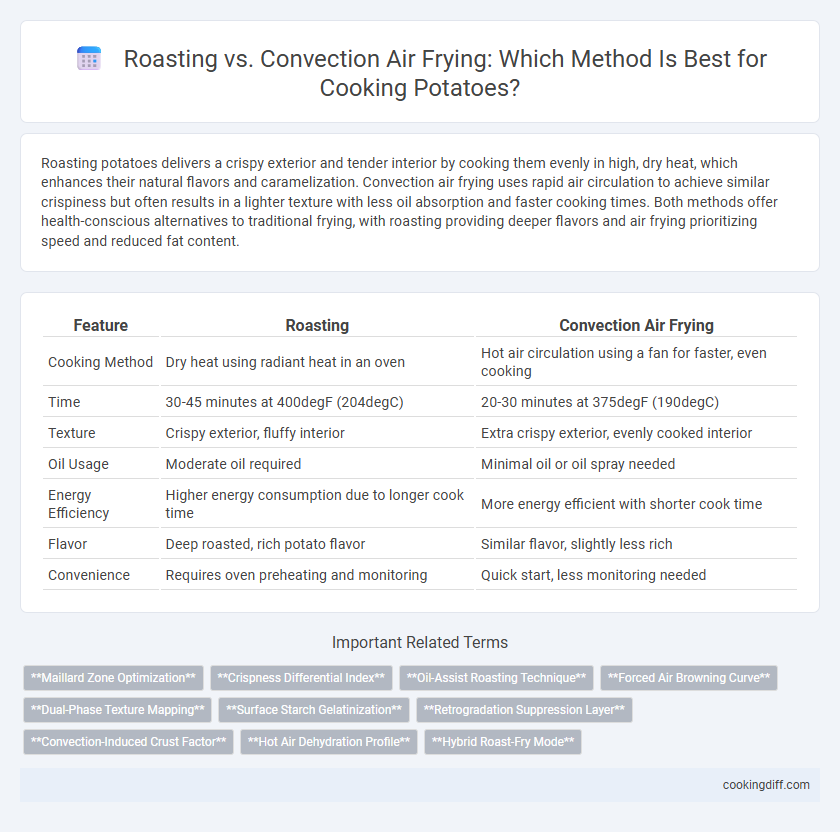
| Feature | Roasting | Convection Air Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Dry heat using radiant heat in an oven | Hot air circulation using a fan for faster, even cooking |
| Time | 30-45 minutes at 400degF (204degC) | 20-30 minutes at 375degF (190degC) |
| Texture | Crispy exterior, fluffy interior | Extra crispy exterior, evenly cooked interior |
| Oil Usage | Moderate oil required | Minimal oil or oil spray needed |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy consumption due to longer cook time | More energy efficient with shorter cook time |
| Flavor | Deep roasted, rich potato flavor | Similar flavor, slightly less rich |
| Convenience | Requires oven preheating and monitoring | Quick start, less monitoring needed |
Introduction: Roasting vs Convection Air Frying Potatoes
| Method | Cooking Process | Texture | Time | Health Aspect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roasting | Uses dry, high heat in an oven, surrounding potatoes with hot air to cook evenly. | Produces crispy edges with a soft, fluffy interior. | Typically takes 30-45 minutes at 400degF (204degC). | Requires oil, which can increase calorie content. |
| Convection Air Frying | Circulates hot air rapidly around potatoes using a fan-driven mechanism. | Achieves a uniformly crisp and golden exterior with a tender inside. | Reduces cooking time to 15-25 minutes at around 375degF (190degC). | Uses less oil, promoting a lower-fat cooking option. |
Understanding Roasting: Traditional Oven Techniques
Roasting potatoes in a traditional oven uses dry heat evenly circulated around the food, enhancing caramelization and depth of flavor. This method allows for precise temperature control, resulting in crispy exteriors and fluffy interiors.
- Even Heat Distribution - Conventional ovens provide consistent radiant heat that surrounds potatoes for uniform cooking.
- Maillard Reaction - High-temperature roasting induces the Maillard reaction, creating golden-brown, flavorful crusts on potato surfaces.
- Moisture Retention - Slow roasting preserves internal moisture, yielding tender and creamy potato textures after baking.
What Is Convection Air Frying?
Convection air frying is a cooking method that circulates hot air rapidly around the food to create a crispy exterior similar to frying but with significantly less oil. Unlike traditional roasting, which relies on radiant heat from an oven, convection air fryers use a built-in fan to enhance heat distribution and reduce cooking time. This technique is especially effective for potatoes, producing a crunchy texture and evenly cooked interior without the excess grease of deep frying.
Cooking Time Comparison: Roasting vs Air Frying
Roasting potatoes typically takes 30 to 45 minutes at 400degF, allowing for even caramelization and crispy edges. Convection air frying reduces cooking time significantly, often requiring only 15 to 20 minutes due to rapid air circulation and higher heat concentration. Choosing air frying over roasting can save up to 50% of cooking time while still achieving a golden, crispy texture.
Texture and Crispiness: Which Method Wins?
Roasting potatoes in an oven typically produces a golden, crispy exterior with a fluffy interior due to the dry heat that evenly caramelizes the potato's surface. The high temperature and radiant heat cause Maillard reactions, enhancing texture and deepening flavor complexity.
Convection air frying circulates hot air rapidly around the potatoes, resulting in a quicker cooking time and a consistently crispy crust with less oil compared to traditional roasting. This method excels at delivering a crunchy texture while maintaining a tender inside, making it an efficient alternative for crispy potatoes.
Flavor Differences in Roasted and Air-Fried Potatoes
Roasting potatoes develops a deep, caramelized flavor due to the Maillard reaction that occurs at high oven temperatures. Convection air frying produces a lighter, crisp texture with a slightly less intense roasted taste because of the rapid hot air circulation.
- Roasted potatoes have a richer, more complex flavor - This results from prolonged exposure to dry heat which enhances sweetness and umami.
- Air-fried potatoes are crispier on the outside - Hot air circulation reduces moisture quickly, creating a crunchy exterior.
- Flavor intensity is more pronounced in roasting - Roasting allows natural sugars to brown unevenly, intensifying overall taste.
The choice between roasting and air frying depends on the desired balance between flavor depth and texture crispness.
Health Considerations: Oil Usage and Nutrition
Roasting potatoes typically requires more oil than convection air frying, which can increase calorie and fat intake, impacting heart health and weight management. Convection air frying uses hot air circulation to cook potatoes with minimal oil, preserving their nutritional value while reducing unhealthy fat consumption.
Convection air frying maintains more nutrients such as vitamin C and potassium by shortening cooking times and using less oil compared to traditional roasting. This method also produces fewer harmful compounds like acrylamide, which forms at high temperatures in oil-rich roasting environments. Therefore, convection air frying offers a healthier alternative to roasting by balancing taste, texture, and nutritional benefits.
Energy Efficiency and Convenience
Which method is more energy efficient and convenient for cooking potatoes, roasting or convection air frying? Convection air frying uses rapid hot air circulation, reducing cooking time and energy consumption compared to traditional roasting. Its compact size and easy cleanup offer greater convenience for quick potato preparation.
Best Potatoes to Use for Each Method
Russet potatoes are ideal for roasting due to their high starch content, which results in a fluffy interior and crispy exterior. Waxy potatoes like red or Yukon Gold perform best in convection air frying, as they hold their shape and develop a tender texture with a golden crust.
- Russet Potatoes for Roasting - Their starchiness creates perfect crispiness and a soft inside when roasted at high temperatures.
- Red Potatoes for Air Frying - Their waxy texture retains firmness and moisture, ensuring even cooking without becoming mushy.
- Yukon Gold for Versatility - Balanced starch and moisture content make them suitable for both roasting and convection air frying methods.
Related Important Terms
Maillard Zone Optimization
Roasting potatoes in a traditional oven enables precise Maillard zone optimization by maintaining consistent high heat that promotes even browning and caramelization, enhancing flavor and texture. Convection air frying circulates hot air rapidly, which accelerates the Maillard reaction on the surface but may produce uneven browning due to faster moisture evaporation from thinner potato layers.
Crispness Differential Index
The Crispness Differential Index reveals that roasting potatoes achieves a higher external crunch and a creamier interior compared to convection air frying, which tends to produce a more uniform but less intense crispness. Roasting's direct dry heat promotes greater Maillard reaction, enhancing texture contrast and maximizing the crispness differential.
Oil-Assist Roasting Technique
The oil-assist roasting technique enhances potato texture by using a small amount of oil to promote even caramelization and crispiness, which convection air frying mimics but often lacks the depth of flavor from direct contact with the hot pan. This method optimizes Maillard reactions and moisture evaporation, resulting in golden, crispy exteriors and fluffy interiors that surpass the typically lighter, less intensely browned finish of air-fried potatoes.
Forced Air Browning Curve
Roasting achieves a consistent forced air browning curve by circulating dry hot air at high temperatures, promoting Maillard reactions and caramelization on potato surfaces. Convection air frying intensifies this effect with rapid air circulation and elevated heat, producing a crisper exterior through enhanced moisture evaporation and more uniform browning patterns.
Dual-Phase Texture Mapping
Dual-Phase Texture Mapping in roasting achieves a perfect balance between a crispy exterior and fluffy interior by slowly caramelizing the potato surface while evenly cooking the inside. Convection air frying, while faster, often results in a less distinct texture contrast due to rapid air circulation that uniformly dries the potato.
Surface Starch Gelatinization
Roasting potatoes promotes surface starch gelatinization through direct radiant heat, creating a crisp, caramelized crust that enhances texture and flavor. Convection air frying uses rapid hot air circulation to achieve similar gelatinization with less oil, producing a crispy exterior but often with a lighter crust compared to traditional roasting.
Retrogradation Suppression Layer
Roasting potatoes creates a crispy texture while promoting the formation of a retrogradation suppression layer, which helps maintain starch softness and extends freshness. Convection air frying also forms this layer but often results in a drier interior due to more intense airflow, affecting moisture retention and starch retrogradation differently.
Convection-Induced Crust Factor
Roasting potatoes creates a deeper Maillard reaction due to direct heat, resulting in a thicker, caramelized crust, while convection air frying relies on rapid air circulation to form a lighter, crispier surface. The convection-induced crust factor enhances texture by promoting even browning and moisture evaporation, but roasting typically achieves a more robust, flaky crust ideal for savory dishes.
Hot Air Dehydration Profile
Roasting and convection air frying both utilize hot air dehydration but differ in airflow and temperature control, with roasting typically employing slower, less intense heat leading to gradual moisture evaporation and a crisp exterior, while convection air frying uses rapid, high-velocity hot air circulation to accelerate dehydration, resulting in a faster cooking time and a uniformly crispy texture. The enhanced hot air dehydration profile in convection air frying reduces oil absorption in potatoes compared to roasting, producing a healthier, crunchier finish.
Roasting vs Convection Air Frying for potatoes. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com