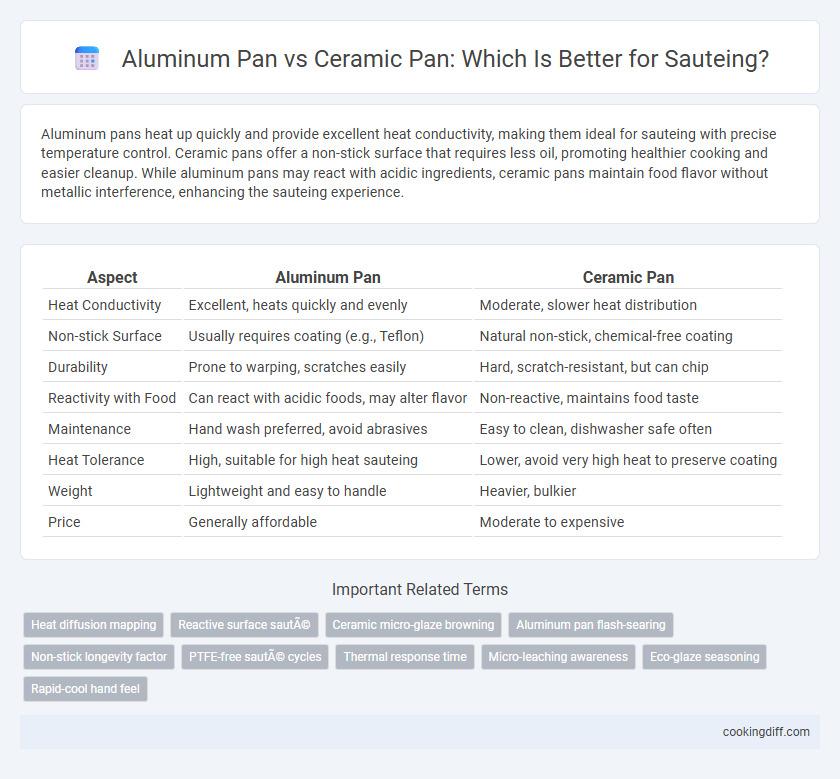
Aluminum pans heat up quickly and provide excellent heat conductivity, making them ideal for sauteing with precise temperature control. Ceramic pans offer a non-stick surface that requires less oil, promoting healthier cooking and easier cleanup. While aluminum pans may react with acidic ingredients, ceramic pans maintain food flavor without metallic interference, enhancing the sauteing experience.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Aluminum Pan | Ceramic Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | Excellent, heats quickly and evenly | Moderate, slower heat distribution |
| Non-stick Surface | Usually requires coating (e.g., Teflon) | Natural non-stick, chemical-free coating |
| Durability | Prone to warping, scratches easily | Hard, scratch-resistant, but can chip |
| Reactivity with Food | Can react with acidic foods, may alter flavor | Non-reactive, maintains food taste |
| Maintenance | Hand wash preferred, avoid abrasives | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe often |
| Heat Tolerance | High, suitable for high heat sauteing | Lower, avoid very high heat to preserve coating |
| Weight | Lightweight and easy to handle | Heavier, bulkier |
| Price | Generally affordable | Moderate to expensive |
Introduction: Aluminum vs Ceramic Pans for Sautéing
Aluminum and ceramic pans offer distinct advantages and challenges when used for sauteing. Understanding their thermal properties and cooking performance is essential for selecting the best option.
- Aluminum pans heat quickly - This metal conducts heat efficiently, allowing for rapid temperature changes ideal for sauteing.
- Ceramic pans provide even heat distribution - Their coating maintains consistent temperatures, reducing the risk of hot spots and burning.
- Durability and maintenance differ - Aluminum pans are prone to scratching and warping, while ceramic surfaces are more fragile but easier to clean.
Heat Conductivity: Aluminum vs Ceramic
Aluminum pans offer superior heat conductivity, allowing for rapid and even heat distribution ideal for precise sauteing. This efficient thermal transfer prevents hot spots and ensures food cooks uniformly, enhancing texture and flavor.
Ceramic pans have lower heat conductivity compared to aluminum, resulting in slower and less even heating. While ceramic retains heat well, it may cause inconsistent sauteing performance, requiring careful temperature control.
Weight and Handling in Sautéing
| Aluminum Pan | Lightweight design enables quick maneuvering and effortless tossing during sauteing, improving cooking control and speed. |
| Ceramic Pan | Heavier construction provides stability but may cause wrist fatigue during extended sauteing, affecting precise handling and quick movements. |
Nonstick Performance: Which Pan Excels?
Aluminum pans offer excellent heat conductivity, ensuring even cooking and reliable nonstick performance when properly anodized or coated. Ceramic pans provide a chemical-free nonstick surface that excels at resisting high temperatures but may lose effectiveness faster over time. For consistent nonstick performance during sauteing, anodized aluminum pans often outperform ceramic counterparts due to superior durability and heat distribution.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Which type of pan offers better durability and lifespan for sauteing, aluminum or ceramic? Aluminum pans are known for their excellent heat conduction and resistance to warping, providing long-lasting performance when properly maintained. Ceramic pans, while offering a non-stick surface and aesthetic appeal, tend to be more prone to chipping and surface wear, potentially reducing their overall lifespan in high-heat cooking tasks like sauteing.
Reactivity with Ingredients
Aluminum pans react with acidic ingredients, potentially altering the flavor and discoloring both the pan and food. Ceramic pans provide a non-reactive surface, preserving the natural taste and appearance of sauteed dishes.
When sauteing tomatoes or citrus-based sauces, aluminum pans may impart a metallic taste due to their high reactivity. In contrast, ceramic pans resist this chemical interaction, ensuring flavors remain pure and vibrant. Choosing ceramic pans reduces the risk of unwanted flavor contamination during cooking.
Ease of Cleaning After Sautéing
Aluminum pans often develop food residue that can stick during sauteing, requiring thorough scrubbing to clean effectively. Their surface may discolor over time, making stain removal more challenging after cooking.
Ceramic pans feature a non-stick surface that significantly reduces food adhesion, simplifying cleaning after sauteing. The smooth ceramic coating resists staining and typically wipes clean with minimal effort.
Health and Safety Considerations
Aluminum pans, while excellent for heat conduction, may leach small amounts of metal into food when cooking acidic ingredients, raising potential health concerns. Ceramic pans are non-reactive and free from toxic chemicals, making them safer for sauteing, particularly at high temperatures. Choosing ceramic cookware reduces exposure to aluminum and eliminates risks associated with synthetic coatings, promoting safer cooking practices.
Price and Value for Home Cooks
Aluminum pans are generally more affordable and heat up quickly, making them a budget-friendly choice for home cooks focused on value. Ceramic pans, while pricier, offer non-stick benefits and better durability, which can justify the investment for long-term use.
- Cost Efficiency - Aluminum pans typically cost 30-50% less than ceramic alternatives, appealing to budget-conscious buyers.
- Heat Conductivity - Aluminum's superior heat conduction allows for faster cooking and energy savings.
- Durability and Maintenance - Ceramic pans resist scratches and require less oil, enhancing cooking quality despite higher upfront costs.
Related Important Terms
Heat diffusion mapping
Aluminum pans offer superior heat diffusion for sauteing with rapid, even heat distribution that minimizes hot spots and ensures consistent cooking. Ceramic pans provide moderate heat diffusion but retain heat longer, which may cause uneven cooking during quick sauteing tasks.
Reactive surface sauté
Aluminum pans offer excellent heat conductivity but are reactive with acidic ingredients, potentially altering flavor during sauteing, while ceramic pans provide a non-reactive surface that preserves taste and prevents chemical interactions. For sauteing acidic foods, ceramic pans maintain food integrity, whereas aluminum requires anodized or coated variants to avoid reactivity.
Ceramic micro-glaze browning
Ceramic pans with micro-glaze surfaces offer superior browning during sauteing by promoting even heat distribution and minimizing food sticking, which enhances caramelization and flavor development. In contrast, aluminum pans heat quickly but may cause uneven browning and increased food adhesion without proper seasoning or coatings.
Aluminum pan flash-searing
Aluminum pans offer superior heat conductivity essential for flash-searing, allowing rapid temperature spikes that create a perfect crust on sauteed foods. Ceramic pans retain heat evenly but lack the quick responsiveness of aluminum, making them less ideal for high-heat techniques like flash-searing.
Non-stick longevity factor
Aluminum pans typically offer faster heat conduction but can lose non-stick properties more quickly when used for sauteing at high temperatures. Ceramic pans provide longer-lasting non-stick surfaces due to their advanced coating technology, maintaining efficient sauteing performance over extended use.
PTFE-free sauté cycles
Aluminum pans offer rapid heat conductivity and even distribution, ideal for PTFE-free saute cycles where precise temperature control prevents food from sticking without synthetic coatings. Ceramic pans provide a natural non-stick surface free from PTFE, maintaining durability and heat retention while ensuring safe, chemical-free sauteing.
Thermal response time
Aluminum pans offer rapid thermal response time due to their excellent heat conductivity, allowing quick temperature adjustments essential for precise sauteing. Ceramic pans heat more slowly and retain heat longer, which can result in less control during fast cooking but provides even heat distribution for consistent browning.
Micro-leaching awareness
Aluminum pans offer excellent heat conduction for sauteing but carry a risk of micro-leaching aluminum ions into food, particularly with acidic ingredients, which raises health concerns. Ceramic pans provide a non-reactive surface that minimizes micro-leaching, making them a safer option for sauteing sensitive foods while maintaining even heat distribution.
Eco-glaze seasoning
Aluminum pans heat quickly and provide excellent heat conductivity for precise sauteing, while ceramic pans with Eco-glaze seasoning offer a non-toxic, eco-friendly surface that enhances food release and durability. The Eco-glaze seasoning on ceramic pans reduces the need for excess oil, promoting healthier cooking and easier cleanup compared to untreated aluminum surfaces.
Aluminum pan vs ceramic pan for sautéing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com