Sauteing involves cooking food quickly in a small amount of oil or fat, enhancing flavor and creating a crispy texture. Steam sauteing, on the other hand, uses steam to cook food without oil, preserving moisture and nutrients while reducing fat intake. This oil-free method is ideal for those seeking a healthier alternative without sacrificing tenderness and natural flavors.
Table of Comparison
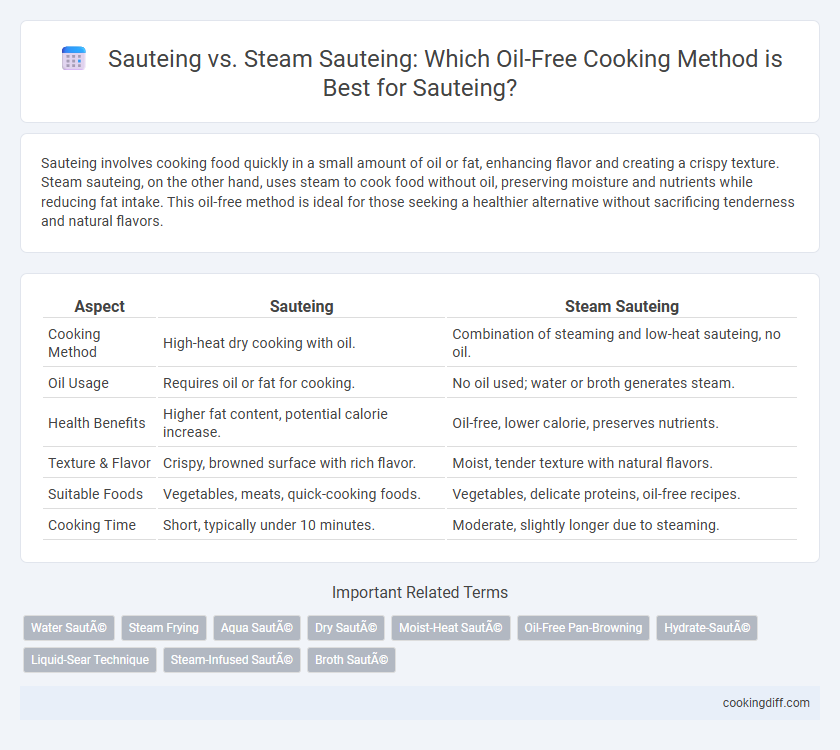
| Aspect | Sauteing | Steam Sauteing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High-heat dry cooking with oil. | Combination of steaming and low-heat sauteing, no oil. |
| Oil Usage | Requires oil or fat for cooking. | No oil used; water or broth generates steam. |
| Health Benefits | Higher fat content, potential calorie increase. | Oil-free, lower calorie, preserves nutrients. |
| Texture & Flavor | Crispy, browned surface with rich flavor. | Moist, tender texture with natural flavors. |
| Suitable Foods | Vegetables, meats, quick-cooking foods. | Vegetables, delicate proteins, oil-free recipes. |
| Cooking Time | Short, typically under 10 minutes. | Moderate, slightly longer due to steaming. |
Understanding Sautéing and Steam Sautéing Techniques
Sauteing involves cooking food quickly in a small amount of oil over high heat to achieve a browned, flavorful exterior. Steam sauteing combines minimal oil with steaming techniques, using water or broth to gently cook food while retaining moisture and nutrients, ideal for oil-free or low-fat cooking. Understanding these methods enhances culinary flexibility, offering options for both rich flavors and healthier, oil-free dishes.
Key Differences Between Sautéing and Steam Sautéing
Sauteing involves cooking food quickly in a small amount of oil over high heat, enhancing flavor through browning. Steam sauteing uses minimal or no oil, combining steam and sauteing techniques to cook food gently while preserving nutrients and moisture.
- Heat Source and Method - Sauteing uses direct high heat and oil, while steam sauteing relies on steam with low or no oil for cooking.
- Health Considerations - Steam sauteing is oil-free or uses significantly less oil, making it a healthier alternative to traditional sauteing.
- Flavor and Texture Outcome - Sauteing produces a crisp, brown exterior, whereas steam sauteing retains more natural moisture and a tender texture.
Benefits of Oil-Free Cooking Methods
Sauteing without oil or using steam sauteing techniques reduces calorie intake and preserves natural food flavors, promoting a healthier diet. These oil-free methods also minimize the risk of harmful compounds formed during high-heat cooking with oil.
- Lower calorie content - Oil-free sauteing decreases fat consumption, aiding in weight management and cardiovascular health.
- Preservation of nutrients - Steam sauteing retains water-soluble vitamins and antioxidants better than traditional oil sauteing.
- Reduced harmful compounds - Avoiding oil at high heat minimizes formation of acrylamide and trans fats, supporting long-term wellness.
How Traditional Sautéing Works Without Oil
Traditional sauteing typically uses oil to conduct heat and prevent food from sticking to the pan, creating a crispy texture and enhanced flavor through the Maillard reaction. Without oil, food may adhere to the surface, making it challenging to achieve the same browning and texture.
Steam sauteing cooks food by trapping moisture and heat, allowing oil-free cooking through steam rather than direct contact with hot fat. This method preserves nutrients and reduces fat content while maintaining tenderness, but it lacks the caramelization and crispiness of oil-based sauteing. Using non-stick pans and high heat can help replicate some effects of traditional sauteing without oil.
The Science Behind Steam Sautéing
Steam sauteing uses water or broth instead of oil to cook food quickly at high heat, leveraging steam to retain moisture and enhance tenderness. This method minimizes fat content while preserving nutrients that often degrade under traditional sauteing's higher temperatures and oil exposure. The science behind steam sauteing lies in steam's ability to create a moist cooking environment, reducing oxidation and Maillard reactions compared to oil-based sauteing.
Flavor and Texture: Sautéing vs. Steam Sautéing
| Technique | Flavor | Texture |
|---|---|---|
| Sauteing | Enhances natural flavors through caramelization and Maillard reactions, creating rich, deep taste profiles without masking original ingredients. | Produces a crisp, golden-brown exterior while maintaining tender interiors, offering a satisfying contrast in texture. |
| Steam Sauteing | Preserves the fresh, delicate flavors of vegetables by limiting direct contact with high heat and minimizing browning. | Results in a softer, more uniformly cooked texture with less crust or crispness compared to traditional sauteing. |
Nutritional Impact of Oil-Free Cooking
How does sauteing compare to steam sauteing in preserving nutrients during oil-free cooking? Steam sauteing retains more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, as it uses steam heat, minimizing nutrient loss. Standard sauteing without oil may cause slight nutrient degradation due to direct heat, but both methods support healthier cooking by avoiding added fats.
Choosing the Right Cookware for Oil-Free Sautéing
Choosing the right cookware is essential for effective oil-free sauteing, as it directly impacts heat distribution and food release. Non-stick pans and ceramic-coated skillets are ideal for preventing sticking without oil, while stainless steel pans can work well with proper preheating techniques.
- Non-stick pans - Provide a smooth surface that minimizes food sticking, enabling oil-free cooking.
- Ceramic-coated skillets - Offer a durable, chemical-free non-stick surface suitable for sauteing without oil.
- Stainless steel pans - Require careful heat management to prevent sticking but are highly durable and versatile for oil-free methods.
Selecting cookware with superior heat conduction ensures even cooking and enhances the sauteing process without added fats.
Tips for Best Results: Steam Sautéing vs. Dry Sautéing
Steam sauteing uses steam to cook vegetables quickly with minimal oil, preserving nutrients and vibrant colors while avoiding the need for added fats. Dry sauteing, on the other hand, relies on high heat and the natural moisture of ingredients, making it ideal for achieving a caramelized texture without oil.
For best results in steam sauteing, maintain a moderate temperature and add small amounts of water or broth to generate steam, preventing sticking and overcooking. In dry sauteing, ensure the pan is preheated thoroughly and ingredients are evenly spread to promote even browning and enhance flavor without oil.
Related Important Terms
Water Sauté
Water sauteing uses water or broth instead of oil to cook vegetables quickly over high heat, preserving nutrients and reducing fat content. This oil-free technique prevents sticking and browns food gently while maintaining vibrant flavors and textures, making it ideal for health-conscious cooking.
Steam Frying
Steam sauteing, also known as steam frying, uses minimal oil by combining high heat with steam to cook food quickly while preserving nutrients and moisture. This method contrasts with traditional sauteing that relies on oil for heat transfer, making steam sauteing a healthier option for oil-free cooking without sacrificing flavor or texture.
Aqua Sauté
Aqua Saute uses water or vegetable broth instead of oil, making it ideal for oil-free cooking while preserving the texture and flavor of vegetables through gentle steaming and sauteing. This method reduces calorie intake and enhances nutrient retention compared to traditional sauteing, which relies heavily on oil for cooking.
Dry Sauté
Dry sauteing uses a hot pan without oil to cook vegetables quickly, preserving nutrients and enhancing natural flavors through caramelization. Steam sauteing combines a small amount of water or broth with heat, allowing food to cook softly while minimizing fat, but dry sauteing offers a richer texture and more intense taste without added liquids.
Moist-Heat Sauté
Moist-heat sauteing uses steam generated from added liquids or vegetables to cook food gently without oil, preserving nutrients and reducing fat content. Steam sauteing maintains food texture and flavor by combining high heat with moisture, making it an ideal oil-free cooking method compared to traditional dry sauteing.
Oil-Free Pan-Browning
Oil-free pan-browning in sauteing utilizes high heat and natural moisture to develop a rich, caramelized crust without added fats, preserving flavor and texture in vegetables and proteins. Steam sauteing combines minimal water with controlled heat to soften ingredients while maintaining vibrant color and nutrients, offering a healthy alternative that reduces oil use without sacrificing taste.
Hydrate-Sauté
Hydrate-saute leverages steam to tenderize vegetables without oil, preserving nutrients and maintaining vibrant color and texture. This method combines the quick, high-heat cooking benefits of traditional sauteing with steam's moisture, resulting in healthier, oil-free dishes ideal for low-fat diets.
Liquid-Sear Technique
The Liquid-Sear Technique in steam sauteing uses water or broth instead of oil to quickly cook and caramelize foods, making it ideal for oil-free cooking while retaining flavor and texture. This method allows for a crispy exterior similar to traditional sauteing but with lower fat content and enhanced moisture retention.
Steam-Infused Sauté
Steam-infused sauteing combines high-heat cooking with a controlled steam release, preserving nutrients and natural moisture without added oil, making it an ideal technique for oil-free meals. This method enhances flavor retention and texture by gently infusing vegetables or proteins with steam while maintaining the quick, browning benefits of traditional sauteing.
Sautéing vs Steam Sautéing for oil-free cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com