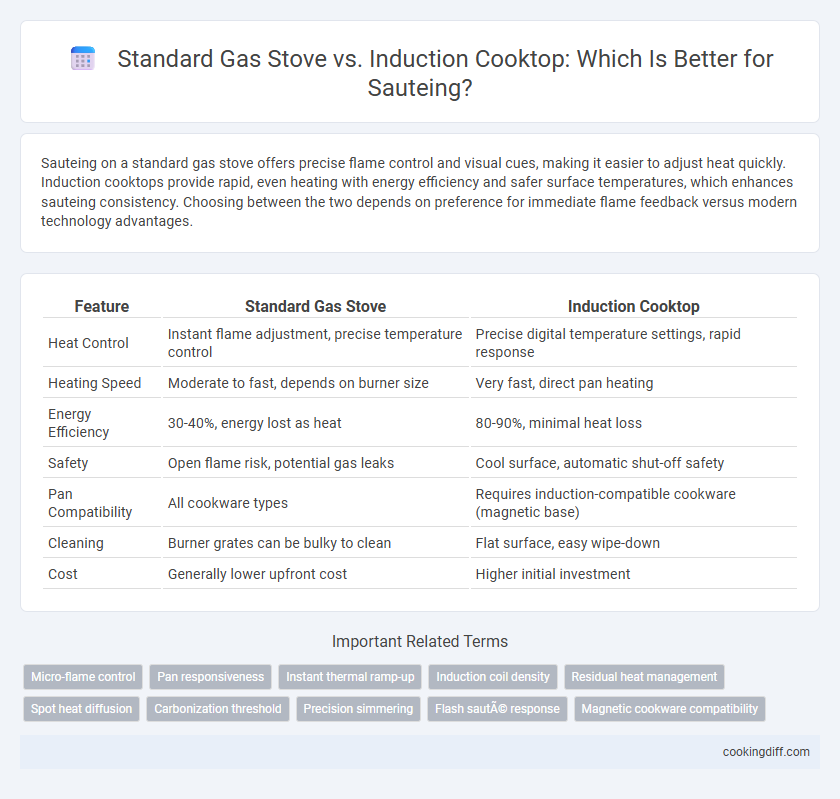
Sauteing on a standard gas stove offers precise flame control and visual cues, making it easier to adjust heat quickly. Induction cooktops provide rapid, even heating with energy efficiency and safer surface temperatures, which enhances sauteing consistency. Choosing between the two depends on preference for immediate flame feedback versus modern technology advantages.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Standard Gas Stove | Induction Cooktop |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Control | Instant flame adjustment, precise temperature control | Precise digital temperature settings, rapid response |
| Heating Speed | Moderate to fast, depends on burner size | Very fast, direct pan heating |
| Energy Efficiency | 30-40%, energy lost as heat | 80-90%, minimal heat loss |
| Safety | Open flame risk, potential gas leaks | Cool surface, automatic shut-off safety |
| Pan Compatibility | All cookware types | Requires induction-compatible cookware (magnetic base) |
| Cleaning | Burner grates can be bulky to clean | Flat surface, easy wipe-down |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Sautéing: Gas Stove vs Induction Cooktop
Which cooking method delivers better control and efficiency for sauteing, a standard gas stove or an induction cooktop? Standard gas stoves provide precise flame adjustments and immediate heat changes essential for sauteing, while induction cooktops offer rapid, consistent heating with superior energy efficiency. The choice depends on whether flame control or speed and temperature consistency are prioritized in the sauteing process.
Heat Control and Responsiveness
Induction cooktops offer rapid heat adjustments and precise temperature control, making them ideal for sauteing delicate ingredients. Standard gas stoves provide visible flame control but respond slower to temperature changes, requiring more attention to maintain consistent heat.
- Heat Control - Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields for instant heat modulation, ensuring exact cooking temperatures during sauteing.
- Responsiveness - Gas stoves have slower heat changes due to the physical flame but allow visual adjustments by flame size.
- Efficiency - Induction delivers heat directly to the pan, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency during sauteing.
For professional-level sauteing, induction cooktops provide superior responsiveness and heat control compared to standard gas stoves.
Temperature Precision in Sautéing
Induction cooktops offer superior temperature precision for sauteing, allowing cooks to maintain consistent heat levels between 100degF and 500degF with minimal fluctuation. Standard gas stoves provide less exact control, often resulting in temperature spikes that can cause uneven cooking or burning. Precise temperature regulation on induction surfaces enhances the caramelization process and preserves the texture of sauteed ingredients.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Sauteing on an induction cooktop uses electromagnetic energy to heat the pan directly, resulting in higher energy efficiency and faster cooking times compared to a standard gas stove that loses heat through open flames. Induction cooktops convert about 85-90% of energy into heat, whereas gas stoves operate at approximately 40-55% efficiency, impacting overall energy consumption during sauteing.
- Induction Efficiency - Direct heating minimizes energy loss by transferring up to 90% of energy to the pan during sauteing.
- Gas Stove Efficiency - Open flame causes heat loss, with only about 40-55% of the gas energy effectively utilized when sauteing.
- Energy Cost Impact - Higher efficiency of induction cooktops reduces cooking time and gas or electricity costs, yielding long-term savings.
Pan Compatibility and Material Considerations
Standard gas stoves offer broad pan compatibility, accommodating materials like stainless steel, cast iron, and aluminum without issue. Their open flame effectively handles various pan thicknesses, making them versatile for sauteing.
Induction cooktops require ferromagnetic cookware, such as cast iron or stainless steel with magnetic properties, limiting compatible pan choices. Cookware material directly impacts heat efficiency on induction surfaces, making material consideration crucial for optimal saute results.
Speed of Heating and Cooling
Induction cooktops offer rapid heating and precise temperature control for sauteing, outperforming standard gas stoves in speed and efficiency. Gas stoves provide immediate visual flame adjustment but cool down more slowly, impacting cooking responsiveness.
- Induction cooktop heats faster - Magnetic induction directly heats the pan, enabling quicker temperature increases for sauteing.
- Gas stove heat dissipates slower - Flame heats the pan and surroundings, causing slower cooling after adjusting the heat.
- Induction offers better temperature control - Instant on-and-off heating allows precise saute timing and prevents overheating.
Safety Features for Sautéing
Standard gas stoves present open flames which increase the risk of burns and accidental fires during sauteing, requiring constant vigilance for safety. Induction cooktops offer enhanced safety with no open flame and automatic shut-off features that minimize burn hazards.
Induction cooktops heat cookware directly through electromagnetic energy, reducing the chance of accidental fires and lowering surface temperatures, which prevents burns. Gas stoves have visible flames that can easily ignite nearby flammable materials, making them less safe in cluttered kitchens. Sauteing on induction cooktops promotes a safer cooking environment by swiftly stopping heat when pots are removed.
Flavor and Texture Outcomes
Standard gas stoves provide direct flame heat that allows precise control, which can enhance the Maillard reaction for rich, caramelized flavors and crisp textures in sauteed foods. The open flame creates slight variations in heat distribution, often contributing to more complex browning and texture development.
Induction cooktops offer rapid and consistent heating through electromagnetic energy, resulting in even cooking that preserves the natural moisture and tenderness of sauteed ingredients. This precise temperature control minimizes the risk of burning, ensuring more uniform texture and subtle flavor retention.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Sauteing on an induction cooktop offers significantly easier cleaning due to its smooth, flat glass surface that resists food buildup and spills, unlike the grates and burners of a standard gas stove. Gas stoves require frequent removal and scrubbing of burner components to maintain hygiene, increasing maintenance time and effort. Induction cooktops also avoid residue burns common on gas burners, ensuring a cleaner cooking environment with minimal upkeep.
Related Important Terms
Micro-flame control
Induction cooktops offer precise micro-flame control through instant heat adjustments, enabling chefs to maintain consistent temperatures essential for perfect sauteing. Standard gas stoves provide visible flames but lack the immediate responsiveness of induction, making fine-tuning heat levels less accurate during delicate sauteing tasks.
Pan responsiveness
Induction cooktops provide superior pan responsiveness for sauteing, offering instant and precise temperature adjustments that prevent food from burning or sticking. Standard gas stoves deliver less precise heat control, resulting in slower response times and potentially uneven cooking during sauteing.
Instant thermal ramp-up
Induction cooktops provide instant thermal ramp-up due to electromagnetic heating, allowing precise temperature control crucial for sauteing delicate ingredients. Standard gas stoves rely on flame heat, which heats cookware less efficiently and causes slower temperature adjustments during cooking.
Induction coil density
Induction cooktops feature a high coil density that provides rapid and precise heat control, ensuring even sauteing without hotspots common in standard gas stoves. This dense induction coil design enhances energy efficiency by directly heating the cookware, resulting in faster cooking times and consistent temperature maintenance.
Residual heat management
Induction cooktops provide precise residual heat management by rapidly cooling down after use, preventing overcooking or burning during sauteing. Standard gas stoves retain residual heat longer, which can lead to uneven cooking and require careful temperature adjustments to maintain optimal sauteing conditions.
Spot heat diffusion
Standard gas stoves provide uneven spot heat diffusion with visible flames that concentrate heat directly on the pan's bottom, causing hot spots ideal for quick searing but requiring constant adjustment. Induction cooktops offer superior, uniform spot heat diffusion through electromagnetic fields that evenly distribute heat across the pan, enhancing precise temperature control for consistent sauteing results.
Carbonization threshold
Induction cooktops offer precise temperature control that helps maintain the sauteing temperature below the carbonization threshold, reducing the risk of burnt or carbonized food. Standard gas stoves have less accurate heat regulation, often causing uneven heating and increasing the likelihood of surpassing the carbonization point during sauteing.
Precision simmering
Induction cooktops offer superior precision simmering for sauteing due to their rapid heat adjustments and consistent temperature control, preventing food from burning or sticking. Standard gas stoves provide visible flame control but often lack the exact temperature regulation needed for delicate simmering, making induction a preferred choice for precision cooking.
Flash sauté response
Induction cooktops provide superior flash saute response due to rapid and precise heat adjustments enabled by electromagnetic heating, ensuring immediate temperature control and consistent cooking results. Standard gas stoves offer visible flame control but often lag in quick temperature changes, leading to less precise heat management during flash sauteing.
Standard gas stove vs Induction cooktop for sautéing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com