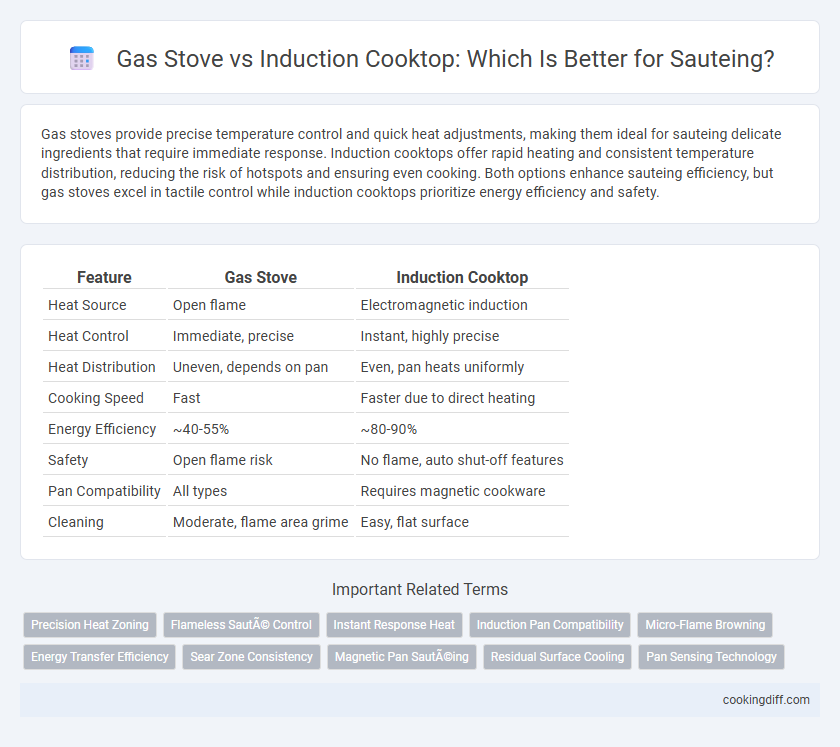
Gas stoves provide precise temperature control and quick heat adjustments, making them ideal for sauteing delicate ingredients that require immediate response. Induction cooktops offer rapid heating and consistent temperature distribution, reducing the risk of hotspots and ensuring even cooking. Both options enhance sauteing efficiency, but gas stoves excel in tactile control while induction cooktops prioritize energy efficiency and safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gas Stove | Induction Cooktop |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Open flame | Electromagnetic induction |
| Heat Control | Immediate, precise | Instant, highly precise |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven, depends on pan | Even, pan heats uniformly |
| Cooking Speed | Fast | Faster due to direct heating |
| Energy Efficiency | ~40-55% | ~80-90% |
| Safety | Open flame risk | No flame, auto shut-off features |
| Pan Compatibility | All types | Requires magnetic cookware |
| Cleaning | Moderate, flame area grime | Easy, flat surface |
Introduction: Sautéing Techniques and Heat Sources
Sauteing requires precise temperature control to achieve the perfect sear and texture on ingredients. Gas stoves provide instant flame adjustments, allowing chefs to modify heat quickly during cooking.
Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, offering even heat distribution and efficient energy use. This technology maintains consistent temperatures, ideal for delicate sauteing tasks.
Gas Stove vs Induction Cooktop: How They Work
Gas stoves generate an open flame that directly heats the cookware, providing instant temperature control ideal for sauteing. Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to heat the pan itself, resulting in rapid and even heat distribution.
Gas stoves offer visual and tactile feedback for precise flame adjustment, which many chefs prefer for sauteing delicate ingredients. Induction cooktops heat faster and maintain consistent temperatures without the heat loss typical of gas flames. Both methods have unique benefits, but induction is often praised for energy efficiency and safety in sauteing.
Heat Control and Responsiveness for Sautéing
Gas stoves offer immediate heat adjustments ideal for precise sauteing, while induction cooktops provide rapid heat changes with even temperature distribution. Both appliances enhance responsiveness, but induction ensures consistent surface heat, reducing the risk of burning.
- Gas Stove Heat Control - Allows chefs to instantly modify flame intensity for dynamic sauteing techniques.
- Induction Cooktop Responsiveness - Delivers quick temperature adjustments through electromagnetic heating for uniform cooking.
- Temperature Consistency - Induction cooktops maintain steady heat levels, preventing hotspots common in gas stoves during sauteing.
Temperature Consistency and Hotspots
| Gas Stove | Gas stoves provide immediate heat control but tend to create hotspots, leading to uneven sauteing and inconsistent temperature distribution across the pan. |
| Induction Cooktop | Induction cooktops offer precise temperature consistency by directly heating the pan's surface evenly, minimizing hotspots and ensuring uniform sauteing results. |
Speed and Efficiency in Preheating
Induction cooktops offer faster and more efficient preheating compared to gas stoves, delivering precise temperature control for sauteing. Gas stoves provide immediate heat but often lose energy through open flames, making them less efficient in preheating.
- Rapid Heat Transfer - Induction technology directly heats the cookware, reducing preheat time significantly.
- Energy Efficiency - Induction cooktops convert up to 90% of energy into heat, minimizing energy loss during preheating.
- Consistent Temperature - Gas stoves may have uneven heat distribution, impacting saute quality and speed.
Choosing induction for sauteing ensures faster meal preparation with lower energy consumption.
Cookware Compatibility: What Works Best for Each
Gas stoves offer universal compatibility with all types of cookware, making them ideal for sauteing with various pans and skillets. Induction cooktops require magnetic-based cookware for efficient heating, which can limit options but ensures rapid and even temperature control.
- Gas stove compatibility - Works effectively with stainless steel, cast iron, aluminum, copper, and non-magnetic cookware.
- Induction cooktop requirement - Needs ferromagnetic cookware such as cast iron or stainless steel with a magnetic base.
- Cookware performance - Induction heats cookware quickly and evenly, enhancing sauteing precision compared to fluctuating heat on gas stoves.
Safety Considerations for Sautéing
Gas stoves provide immediate flame control, which can reduce the risk of overheating oil during sauteing, though open flames pose a burn hazard. Proper ventilation is necessary to prevent the buildup of combustible gases and ensure kitchen safety.
Induction cooktops offer precise temperature regulation and automatically shut off when cookware is removed, significantly lowering the risk of accidental burns or fires. Their surface remains cool to the touch, enhancing safety during rapid sauteing tasks.
Flavor Development: Searing and Browning Differences
Gas stoves provide instant, high heat that enhances searing and browning, essential for developing rich flavors in sauteed dishes. Induction cooktops offer precise temperature control, ensuring consistent heat that prevents burning while promoting even Maillard reaction for optimal flavor development. The direct flame of gas can create subtle smoky notes, whereas induction's smooth surface maintains clean, controlled cooking conditions crucial for delicate sauteing.
Cleaning and Maintenance After Sautéing
Which is easier to clean and maintain after sauteing, a gas stove or an induction cooktop? Induction cooktops have a smooth, flat surface that resists stains and can be quickly wiped down, preventing buildup from oils and food particles. Gas stoves require careful cleaning of grates and burners to remove grease and avoid blockages, making maintenance more time-consuming after cooking.
Related Important Terms
Precision Heat Zoning
Gas stoves provide immediate flame control with adjustable heat levels, allowing chefs to intuitively manage precise heat zoning essential for perfect sauteing. Induction cooktops use electromagnetic fields to deliver consistent and precise heat directly to the cookware, offering superior temperature accuracy and faster response times ideal for delicate saute techniques.
Flameless Sauté Control
Induction cooktops provide precise flameless saute control by rapidly adjusting heat through electromagnetic energy, offering consistent temperature management ideal for delicate sauteing techniques. Gas stoves, while offering visual flame cues and wider heat variability, lack the instant temperature response and safety benefits of induction's flame-free operation.
Instant Response Heat
Gas stoves provide instant response heat, allowing precise temperature control essential for sauteing, while induction cooktops offer faster heat-up times and consistent heat distribution, enhancing cooking efficiency. Both methods ensure quick temperature adjustments, but induction cooktops are more energy-efficient and safer due to their rapid heating technology.
Induction Pan Compatibility
Induction cooktops require cookware made of magnetic materials such as cast iron or stainless steel to ensure optimal heat transfer during sauteing, unlike gas stoves that are compatible with virtually any pan type. Proper induction pan compatibility enhances precise temperature control and even heat distribution, crucial for achieving perfect sauteing results.
Micro-Flame Browning
Gas stoves provide precise temperature control with visible micro-flame browning, allowing chefs to achieve distinct caramelization and enhanced flavor development during sauteing. Induction cooktops offer rapid heating and consistent surface temperatures but may lack the subtle micro-flame browning effect that contributes to the complex taste and texture in sauteed dishes.
Energy Transfer Efficiency
Induction cooktops offer superior energy transfer efficiency for sauteing by directly heating the cookware through electromagnetic fields, resulting in faster temperature adjustments and reduced heat loss compared to gas stoves. Gas stoves lose more heat to the surrounding air, leading to lower efficiency and less precise temperature control during sauteing.
Sear Zone Consistency
Gas stoves provide uneven sear zone consistency due to fluctuating flame patterns, which can cause hot and cool spots on the pan during sauteing. Induction cooktops offer precise and uniform heat distribution, maintaining a consistent sear zone that ensures even cooking and better caramelization of ingredients.
Magnetic Pan Sautéing
Magnetic pans on induction cooktops offer precise temperature control and rapid heat adjustments ideal for sauteing, providing consistent and even cooking results. In contrast, gas stoves heat unevenly and rely on open flames, which can cause hot spots and less efficient heat distribution during magnetic pan sauteing.
Residual Surface Cooling
Induction cooktops offer superior control over residual surface cooling, as the glass surface quickly returns to a lower temperature once the heat is turned off, reducing the risk of overcooking or burns during sauteing. In contrast, gas stoves maintain heat on the burner and surrounding surfaces longer, causing slower cooling and increasing the chance of unintended cooking or safety hazards.
Gas stove vs induction cooktop for sautéing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com