A basic soup pot offers versatility and ease of use for simmering a variety of pet foods, providing even heat distribution and durability. Japanese donabe, made from earthenware, excels in retaining heat and enhancing flavors through its porous material, which slowly releases moisture during simmering. While a soup pot is practical for everyday cooking, a donabe delivers a unique, gentle simmering experience that can improve the taste and texture of your pet's meals.
Table of Comparison
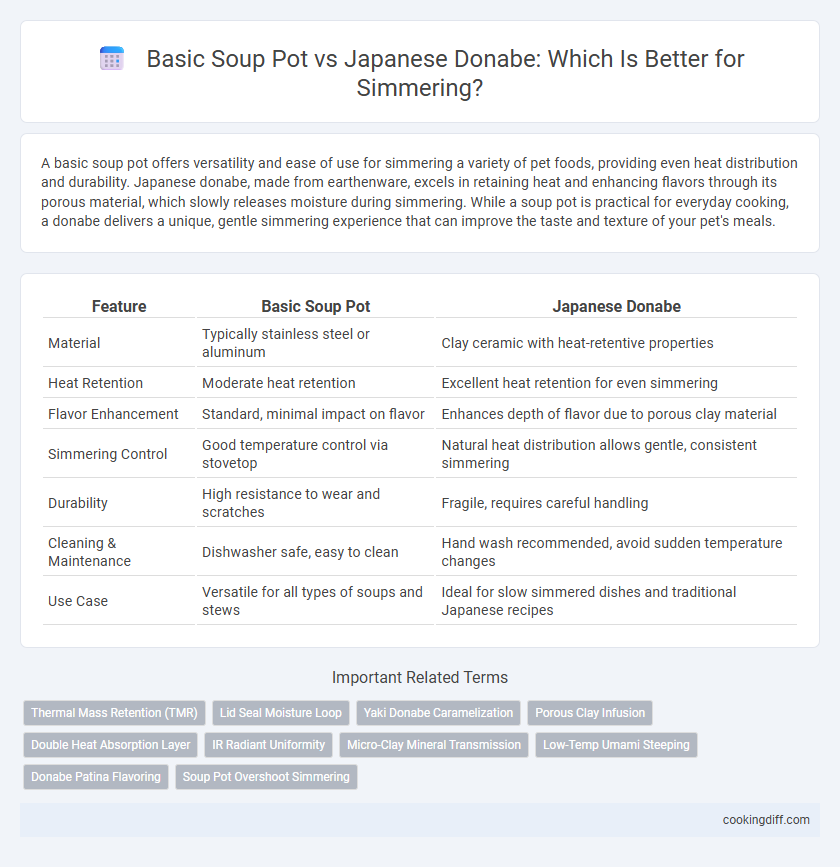
| Feature | Basic Soup Pot | Japanese Donabe |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Typically stainless steel or aluminum | Clay ceramic with heat-retentive properties |
| Heat Retention | Moderate heat retention | Excellent heat retention for even simmering |
| Flavor Enhancement | Standard, minimal impact on flavor | Enhances depth of flavor due to porous clay material |
| Simmering Control | Good temperature control via stovetop | Natural heat distribution allows gentle, consistent simmering |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and scratches | Fragile, requires careful handling |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Dishwasher safe, easy to clean | Hand wash recommended, avoid sudden temperature changes |
| Use Case | Versatile for all types of soups and stews | Ideal for slow simmered dishes and traditional Japanese recipes |
Overview: Basic Soup Pot vs Japanese Donabe
A basic soup pot, typically made from stainless steel or aluminum, offers even heat distribution and durability for everyday simmering tasks. Japanese donabe, crafted from clay, provides excellent heat retention and imparts a unique flavor due to its porous texture.
While basic soup pots are versatile and suitable for stovetop use, donabe excels in slow-cooking and simmering dishes like hot pot and stews, enhancing the umami flavors. Donabe's natural material requires careful seasoning and maintenance but delivers authentic Japanese culinary results. The choice depends on cooking style, desired flavor infusion, and heat control preferences.
Material Composition: Metal vs Clay
Basic soup pots, typically made from stainless steel or aluminum, provide quick and even heat distribution ideal for rapid simmering. Japanese donabe, crafted from porous clay, offers superior heat retention and moisture regulation, allowing slow, gentle simmering that enhances flavor depth.
- Metal Composition - Metals like stainless steel conduct heat efficiently for consistent temperature control.
- Clay Properties - Porous clay absorbs and slowly releases heat, facilitating even cooking over extended periods.
- Heat Retention - Donabe's thick walls maintain low simmer temperatures, preventing sudden temperature spikes common in metal pots.
Heat Retention and Distribution
Simmering requires consistent heat retention and even heat distribution to ensure flavors meld perfectly. Basic soup pots often lack the thermal mass of Japanese donabe, resulting in quicker temperature fluctuations.
- Heat Retention - Japanese donabe's thick earthenware walls retain heat longer, providing steady simmering without constant energy input.
- Heat Distribution - Donabe offers more uniform heat distribution, preventing hot spots that can cause uneven cooking in basic metal soup pots.
- Material Impact - Basic soup pots, typically made from thin metal, heat up fast but cool down quickly, making temperature control more challenging.
For optimal simmering, Japanese donabe enhances flavor development through superior heat performance compared to basic soup pots.
Impact on Soup Flavor Development
Basic soup pots made of stainless steel or aluminum offer quick heat conduction but often lack the ability to maintain consistent low temperatures ideal for deep simmering, resulting in less nuanced flavor development. Japanese donabe, crafted from porous clay, provides superior heat retention and distributes heat evenly, allowing slow, gentle simmering that enhances the extraction of complex flavors from ingredients. The micro-porous surface of donabe also absorbs and redistributes moisture, contributing to richer, more concentrated soup flavors compared to basic metal pots.
Simmering Techniques: Similarities and Differences
Basic soup pots, typically made from stainless steel or enamel-coated cast iron, provide even heat distribution essential for consistent simmering. Japanese donabe, crafted from earthenware, offers superior heat retention and imparts subtle earthy flavors during the simmering process.
Both vessels require low, steady heat to maintain a gentle simmer, preserving nutrients and developing complex flavors over time. However, donabe's porous material enhances moisture circulation inside the pot, while basic soup pots rely on their tight-fitting lids and metal construction for temperature control.
Traditional Uses in Global Cuisine
| Basic Soup Pot | Widely used in Western and global cuisines for simmering stocks, stews, and broths, made typically from stainless steel or aluminum, offering even heat distribution and durability. |
| Japanese Donabe | Traditional earthenware pot essential in Japanese cuisine, ideal for slow simmering dishes like nabe and oden, known for retaining heat and enhancing umami through gradual cooking. |
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Basic soup pots, typically made from stainless steel or aluminum, offer high durability and resist corrosion, making them easy to maintain for everyday use. Japanese donabe pots, crafted from clay, require careful handling to avoid cracking but develop a seasoned surface that enhances flavor over time. Regular seasoning and gentle cleaning with a soft brush are essential for donabe maintenance, whereas basic soup pots usually only need standard dishwashing.
Versatility for Simmered Dishes
The basic soup pot offers broad versatility for simmered dishes, accommodating a variety of soups, stews, and sauces with ease. Japanese donabe excels in simmering by retaining heat evenly, enhancing flavors especially in traditional recipes like nabemono and oden.
- Basic soup pot versatility - Suitable for high-volume cooking and a wide range of simmered dishes.
- Heat retention in donabe - Clay construction ensures steady, gentle simmering essential for delicate flavors.
- Traditional use of donabe - Ideal for Japanese simmered meals, promoting authentic taste and texture.
Cooking Experience: Aesthetics and Ritual
How does the cooking experience differ between a basic soup pot and a Japanese donabe for simmering? A basic soup pot offers practicality with its straightforward design and efficient heat distribution, making daily simmering simple and effective. The Japanese donabe enhances the ritual of cooking with its traditional clay material and rustic aesthetics, providing a tactile connection to the simmering process that transforms meal preparation into a mindful experience.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Mass Retention (TMR)
Japanese donabe excels in thermal mass retention (TMR) due to its thick clay walls, enabling consistent heat distribution and prolonged simmering, which enhances flavor development in soups. Basic soup pots, often made of thinner metal, lose heat more quickly, requiring higher temperature adjustments and less stable simmering conditions.
Lid Seal Moisture Loop
A Japanese donabe features a unique lid seal moisture loop that traps steam and circulates moisture evenly, enhancing flavor extraction during simmering compared to a basic soup pot. This design maintains consistent temperature and prevents evaporation, resulting in richer, more tender dishes.
Yaki Donabe Caramelization
The Basic soup pot offers even heat distribution for gentle simmering, while the Japanese Yaki Donabe excels in caramelization due to its high-heat tolerance and porous clay material, enhancing flavor depth. Yaki Donabe's ability to retain and concentrate heat creates superior browning and rich umami development during simmering compared to conventional metal pots.
Porous Clay Infusion
Japanese donabe enhances simmering by utilizing porous clay that absorbs and evenly distributes heat and moisture, infusing flavors deeply into ingredients. Basic soup pots lack this natural porous structure, often resulting in less effective heat retention and flavor infusion during slow cooking.
Double Heat Absorption Layer
A basic soup pot typically features a single-layered bottom that provides direct heat but can result in uneven simmering, whereas a Japanese donabe incorporates a double heat absorption layer made of ceramic and clay, ensuring slow, consistent warmth ideal for delicate simmering. This design retains heat efficiently, promoting uniform cooking and enhancing the flavors of simmered dishes.
IR Radiant Uniformity
Basic soup pots often rely on direct conduction heat with uneven temperature distribution, leading to inconsistent simmering results, while Japanese donabe utilizes IR radiant uniformity to evenly distribute heat, ensuring a gentle and stable simmer. The porous clay material of donabe enhances heat retention and radiation, promoting thorough cooking and improved flavor development through uniform simmering.
Micro-Clay Mineral Transmission
Japanese donabe, crafted from micro-porous clay, enables superior mineral transmission during simmering, enhancing flavor and nutrient absorption compared to basic soup pots made of metal or non-porous materials. The clay's micro-structure retains and gradually releases heat and minerals, promoting even cooking and deeper infusion of ingredients in simmered dishes.
Low-Temp Umami Steeping
A Basic soup pot provides even heat distribution suitable for general simmering, but a Japanese donabe excels in low-temp umami steeping due to its earthenware material that retains moisture and enhances flavor extraction. The porous nature of donabe allows gentle heat diffusion, preserving delicate ingredients and intensifying the umami profile over extended cooking times.
Donabe Patina Flavoring
The Japanese donabe develops a unique patina over time that enhances the depth and complexity of flavors during simmering, unlike basic soup pots that typically lack this seasoning effect. This natural seasoning process in donabe vessels improves heat retention and imparts a subtle earthiness, elevating the overall taste profile of soups and stews.
Basic soup pot vs Japanese donabe for simmering. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com