Ceramic pots provide even heat distribution and excellent heat retention, making them ideal for gentle, slow simmering of delicate dishes without scorching. Carbon steel woks heat up quickly and offer great temperature control but require constant attention to maintain a steady simmer, as their heat dissipates faster. Choosing between the two depends on the desired simmering precision and the type of cuisine being prepared.
Table of Comparison
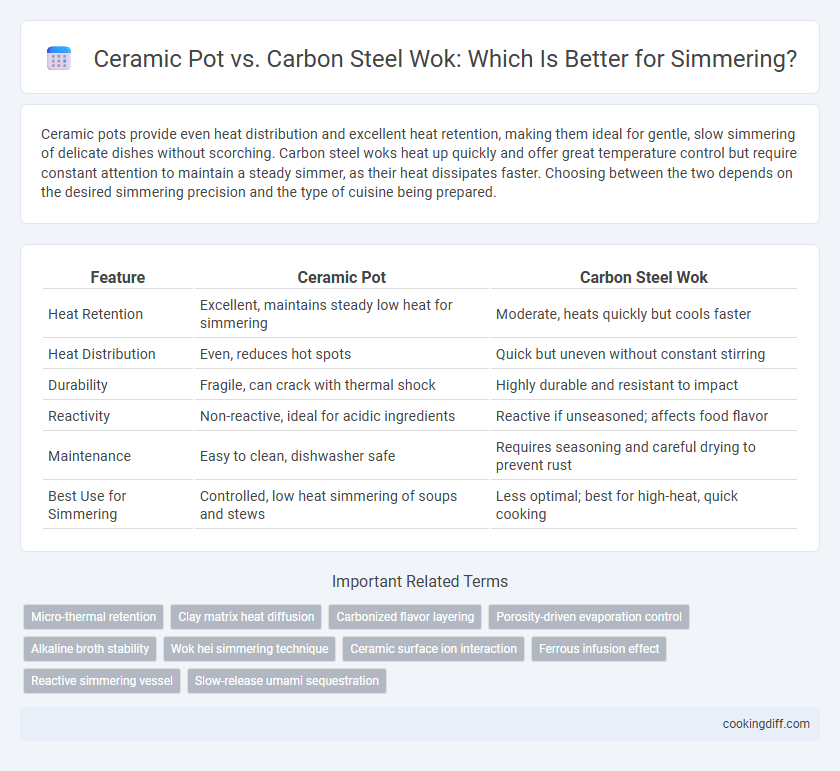
| Feature | Ceramic Pot | Carbon Steel Wok |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Excellent, maintains steady low heat for simmering | Moderate, heats quickly but cools faster |
| Heat Distribution | Even, reduces hot spots | Quick but uneven without constant stirring |
| Durability | Fragile, can crack with thermal shock | Highly durable and resistant to impact |
| Reactivity | Non-reactive, ideal for acidic ingredients | Reactive if unseasoned; affects food flavor |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires seasoning and careful drying to prevent rust |
| Best Use for Simmering | Controlled, low heat simmering of soups and stews | Less optimal; best for high-heat, quick cooking |
Introduction: Ceramic Pot vs Carbon Steel Wok for Simmering
Ceramic pots offer excellent heat retention and even distribution, making them ideal for gentle simmering of soups and stews. Carbon steel woks heat up quickly and provide precise temperature control, suitable for simmering with frequent stirring. Choosing between a ceramic pot and carbon steel wok depends on the desired cooking style and temperature consistency needed for simmering.
Material Composition and Heat Properties
Ceramic pots offer excellent heat retention and distribute heat evenly, ideal for steady simmering without hot spots. Carbon steel woks heat up quickly but require constant attention to maintain low simmer temperatures due to rapid heat conduction.
- Ceramic Pot Composition - Made from porous clay materials that absorb and radiate heat uniformly for consistent simmering.
- Carbon Steel Wok Composition - Constructed from thin, high-carbon steel that conducts heat rapidly and cools quickly when removed from heat.
- Heat Properties - Ceramic pots retain heat longer and provide gentle simmering, whereas carbon steel woks demand precise temperature control to prevent overheating during simmering.
Heat Distribution and Retention
Ceramic pots offer excellent heat retention, allowing for consistent low-temperature simmering without rapid heat loss. Their thick walls distribute heat evenly, reducing hotspots and preventing food from burning during prolonged cooking.
Carbon steel woks heat up quickly and provide responsive temperature control, but their heat retention is lower compared to ceramic pots. While carbon steel distributes heat efficiently on the cooking surface, it requires continuous adjustment to maintain steady simmering temperatures.
Reactivity and Impact on Food Flavor
How do ceramic pots and carbon steel woks differ in reactivity and impact on food flavor when simmering? Ceramic pots are non-reactive, ensuring that acidic or delicate ingredients retain their true flavor without metallic aftertaste. Carbon steel woks can react with acidic foods, potentially altering the flavor profile but also contributing to a unique, slightly seasoned taste over time.
Simmering Performance: Moisture Control
Ceramic pots excel at retaining moisture during simmering due to their non-reactive and porous surface that allows gentle steam circulation. Carbon steel woks, with their thin metal construction and open shape, tend to evaporate moisture more quickly, requiring frequent monitoring to maintain optimal liquid levels.
- Ceramic Pot Moisture Retention - The porous ceramic surface traps steam, enhancing even cooking and maintaining consistent moisture levels.
- Carbon Steel Wok Evaporation - The wok's wide, shallow design facilitates faster evaporation, which can reduce simmering liquid rapidly.
- Simmering Control - Ceramic pots require less attention to liquid levels, while carbon steel woks need careful heat and moisture monitoring to prevent drying out.
Versatility in Cooking Techniques
Ceramic pots excel in even heat distribution, making them ideal for slow simmering and maintaining consistent temperatures in soups and stews. Carbon steel woks offer superior heat responsiveness and high-temperature searing capabilities, allowing for versatile cooking techniques beyond simmering, such as stir-frying and steaming. Choosing between the two depends on whether precise low-heat cooking or quick temperature adjustments are prioritized in your kitchen.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
| Ceramic pot maintenance requires gentle cleaning with non-abrasive sponges and mild detergents to preserve its glazed surface and prevent cracking. |
| Carbon steel wok demands regular seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface and prevent rust, paired with prompt drying after washing to avoid oxidation. |
| Unlike carbon steel woks, ceramic pots do not need seasoning but are sensitive to sudden temperature changes, requiring careful cleaning to avoid thermal shock damage. |
Durability and Longevity
Ceramic pots offer excellent durability due to their non-reactive, heat-retentive properties, making them ideal for long, slow simmering without affecting the flavor of food. Their resistance to scratches and stains ensures longevity with proper care, though they can be prone to chipping if dropped.
Carbon steel woks excel in durability through their robust construction and ability to withstand high heat, developing a natural non-stick patina over time that enhances longevity. Frequent seasoning and maintenance prevent rust, allowing carbon steel woks to last for decades under regular use, making them a resilient choice for simmering.
Suitability for Various Simmered Dishes
Ceramic pots provide even heat distribution and excellent heat retention, making them ideal for slow-cooked soups, stews, and braised dishes that require gentle simmering. Carbon steel woks heat up quickly and allow for precise temperature control, suitable for Asian-style simmered recipes and quick-cooked broths.
The porous surface of ceramic pots helps retain moisture and enhances the infusion of flavors during long simmering processes. Carbon steel woks, with their high heat conductivity, enable rapid adjustments, perfect for dishes needing a quick simmer or slight boil. Both cookware types excel in simmering but cater to different culinary techniques and recipe requirements.
Related Important Terms
Micro-thermal retention
Ceramic pots excel in micro-thermal retention due to their thick walls and porous structure, ensuring even, steady heat ideal for long, slow simmering. Carbon steel woks, while quick to heat, lose micro-thermal retention rapidly, making them less suitable for maintaining consistent low temperatures during simmering.
Clay matrix heat diffusion
Ceramic pots excel in simmering due to their clay matrix's superior heat diffusion, ensuring even temperature distribution for gentle cooking. Carbon steel woks, while quick to heat, often create hot spots, making them less ideal for steady, controlled simmering.
Carbonized flavor layering
A carbon steel wok excels in simmering by fostering carbonized flavor layering due to its unique heat retention and seasoning properties that build complex tastes over time. Unlike ceramic pots, which offer even heat distribution, carbon steel enhances depth and richness in slow-cooked dishes through its ability to develop a seasoned, non-stick surface that intensifies flavor profiles.
Porosity-driven evaporation control
Ceramic pots offer low porosity, minimizing evaporation and maintaining consistent moisture levels during simmering, which is ideal for slow-cooked dishes needing gentle heat and retained liquids. Carbon steel woks exhibit higher porosity, allowing increased evaporation that enhances flavor concentration but requires more attention to liquid management during simmering.
Alkaline broth stability
Ceramic pots provide superior alkaline broth stability during simmering due to their non-reactive surface, preventing the broth's pH from altering and preserving flavor integrity. Carbon steel woks, however, can react with alkaline ingredients, potentially causing metallic tastes and affecting the broth's chemical balance.
Wok hei simmering technique
Ceramic pots excel in even heat distribution and retention, ideal for low, consistent simmering to develop deep flavors, while carbon steel woks, prized for wok hei, allow rapid temperature control and high heat that enhance smoky, aromatic notes during quick simmering techniques. The wok hei simmering technique leverages the wok's ability to maintain intense heat and quick evaporation, creating complex, layered tastes that ceramic pots cannot replicate.
Ceramic surface ion interaction
Ceramic pots excel in simmering due to their non-reactive surface, which minimizes ion exchange and preserves the food's natural flavors without imparting metallic tastes. Carbon steel woks, while excellent for high-heat cooking, may release trace metal ions during prolonged simmering, potentially affecting the dish's subtle flavor profile.
Ferrous infusion effect
Ceramic pots provide even heat distribution ideal for gentle simmering without releasing metals into food, preserving pure flavors. Carbon steel woks, due to their ferrous content, can impart trace iron into dishes during simmering, potentially enhancing nutritional value and altering taste profiles subtly.
Reactive simmering vessel
Ceramic pots provide an inert, non-reactive cooking surface ideal for simmering acidic dishes without flavor alteration, while carbon steel woks react with acidic ingredients, potentially affecting taste and requiring seasoning to maintain a non-stick, rust-resistant surface. Choosing a ceramic pot ensures consistent heat retention and gentle simmering, whereas a carbon steel wok offers rapid heat response but demands careful maintenance to avoid reactive metallic flavors during prolonged simmering.
Ceramic pot vs Carbon steel wok for simmering. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com