Simmering provides a gentle and consistent heat ideal for cooking delicate foods without breaking them apart. Delta cooking, which involves precise temperature control within a narrow range, offers more exactness but can be less forgiving for fragile ingredients. Both methods preserve texture, yet simmering allows slight movement that helps infuse flavors while maintaining the integrity of tender items.
Table of Comparison
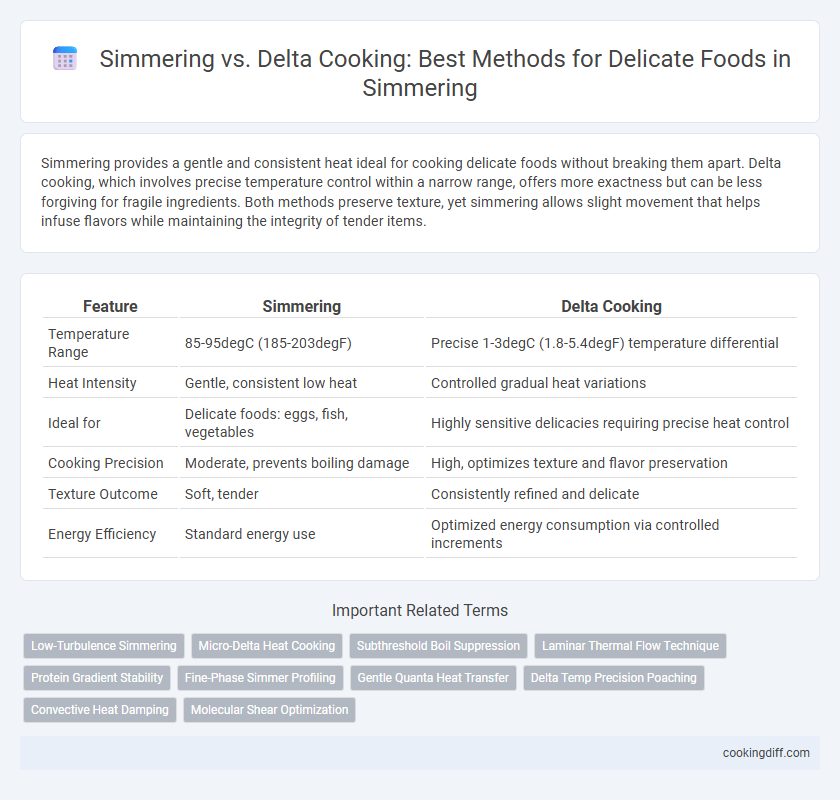
| Feature | Simmering | Delta Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 85-95degC (185-203degF) | Precise 1-3degC (1.8-5.4degF) temperature differential |
| Heat Intensity | Gentle, consistent low heat | Controlled gradual heat variations |
| Ideal for | Delicate foods: eggs, fish, vegetables | Highly sensitive delicacies requiring precise heat control |
| Cooking Precision | Moderate, prevents boiling damage | High, optimizes texture and flavor preservation |
| Texture Outcome | Soft, tender | Consistently refined and delicate |
| Energy Efficiency | Standard energy use | Optimized energy consumption via controlled increments |
Understanding Simmering: Gentle Heat Explained
What makes simmering ideal for cooking delicate foods compared to delta cooking? Simmering involves maintaining a gentle heat just below boiling, typically between 185degF and 205degF (85degC to 96degC), which prevents the food from breaking apart. This slow, consistent heat is crucial for delicate ingredients, preserving their texture and flavor better than delta cooking methods that fluctuate in temperature.
What is Delta Cooking? A Precise Approach
Delta cooking is a precise culinary technique that maintains temperature within a very narrow range, ideal for delicate foods requiring gentle heat. Unlike simmering, which allows slight temperature fluctuations near boiling, delta cooking ensures consistent heat to preserve texture and flavor.
- Precision Temperature Control - Delta cooking keeps the temperature stable within a small delta, often less than 2degC, preventing overcooking.
- Enhanced Food Texture - This method helps retain the delicate structure of ingredients like fish and eggs by avoiding harsh temperature spikes.
- Consistent Flavor Preservation - By maintaining a steady heat, delta cooking minimizes nutrient loss and preserves the natural flavors of delicate foods.
Key Differences Between Simmering and Delta Cooking
Simmering involves cooking food in liquid at temperatures just below boiling, typically between 185degF to 205degF, ensuring gentle heat for delicate ingredients like eggs and fish. Delta Cooking uses precise temperature gradients to create a controlled cooking environment that gradually increases heat, ideal for preserving texture and flavor in sensitive foods.
The key difference lies in temperature control: simmering maintains a constant heat level, while Delta Cooking emphasizes a gradual temperature change to optimize cooking results. This method minimizes overcooking and maximizes nutrient retention, making Delta Cooking especially beneficial for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Impact on Texture: Simmering vs Delta Cooking
Simmering provides a gentle heat that preserves the integrity and softness of delicate foods without causing them to break down excessively. Delta cooking uses precise temperature fluctuations, which can enhance texture by gradually firming the food while retaining moisture.
- Simmering maintains tenderness - The consistent low heat prevents delicate foods from becoming mushy, ensuring a soft yet intact texture.
- Delta cooking controls firmness - Temperature modulation in delta cooking firms delicate foods subtly, improving bite without drying them out.
- Texture impact varies by method - Simmering favors softness and moisture retention, while delta cooking balances tenderness with structural firmness for optimal texture.
Preserving Nutrients: Which Method Wins?
| Simmering gently cooks delicate foods at lower temperatures (185-205degF), preserving more vitamins and minerals compared to Delta Cooking, which uses higher heat bursts that can degrade sensitive nutrients. Studies show simmering retains up to 40% more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex in vegetables. This controlled temperature method minimizes nutrient loss, making simmering the preferred technique for maximizing nutritional value in delicate ingredients. |
Flavor Development: Subtlety in Delicate Foods
Simmering gently extracts and melds flavors in delicate foods, preserving their subtle nuances without overwhelming the palate. Delta cooking, which applies precise temperature variations, can intensify flavor contrasts but risks disrupting the delicate balance in sensitive ingredients. For recipes requiring refined taste profiles, simmering offers a softer, more harmonious flavor development essential for gourmet results.
Ideal Foods for Simmering Techniques
Simmering is ideal for delicate foods such as eggs, fish, and vegetables that require gentle, consistent heat to maintain texture and prevent overcooking. Unlike Delta Cooking, which involves precise temperature control for rapid cooking, simmering uses a lower temperature range of 185-205degF (85-96degC) to gently cook food without boiling. This technique preserves the integrity of fragile ingredients, making it perfect for slow-cooked soups, stews, and sauces.
When to Choose Delta Cooking for Fragile Ingredients
Delta cooking provides precise temperature control that is ideal for fragile ingredients such as fish, custards, and delicate vegetables, minimizing the risk of overcooking. Its gradual heat application maintains food integrity, preventing the breakdown of structure and texture often caused by simmering.
This method is particularly suitable when cooking dishes requiring uniform heat distribution and gentle handling, ensuring nutritional value and flavor retention. For delicate recipes where surface agitation could damage the product, delta cooking offers a superior alternative to simmering.
Time and Temperature Control in Delicate Cooking
Simmering offers precise temperature control ideal for delicate foods, maintaining temperatures just below boiling (85-95degC) to prevent overcooking. Delta cooking adjusts heat dynamically but may cause temperature fluctuations unsuitable for fragile ingredients.
- Simmering temperature control - Maintains a steady, gentle heat conducive to preserving texture and flavor in delicate foods.
- Delta cooking variability - Involves variable heat application which can stress sensitive food components.
- Cooking time sensitivity - Simmering allows for longer, controlled cooking times without the risk of rapid temperature spikes.
For delicate dishes, simmering ensures consistent temperature and time management, optimizing texture and taste.
Related Important Terms
Low-Turbulence Simmering
Low-turbulence simmering provides a gentler cooking environment than delta cooking, minimizing agitation and preserving the structural integrity of delicate foods such as custards and poached eggs. This method maintains consistent low heat and reduces surface disturbance, ensuring even heat distribution while preventing protein coagulation and texture breakdown.
Micro-Delta Heat Cooking
Simmering maintains a consistent temperature just below boiling, ideal for gently cooking delicate foods without breaking them apart, while Micro-Delta Heat Cooking utilizes precise temperature control with minimal fluctuations to preserve texture and flavor even more effectively. The Micro-Delta technique ensures uniform heat distribution by keeping temperature variation within fractions of a degree, outperforming traditional simmering and delta cooking methods for sensitive ingredients like fish and custards.
Subthreshold Boil Suppression
Simmering maintains a consistent temperature just below boiling point, effectively preventing the vigorous bubbles characteristic of a delta cooking or rolling boil, which can damage delicate foods. Subthreshold boil suppression in simmering ensures gentle heat transfer, preserving texture and flavor by minimizing agitation during the cooking process.
Laminar Thermal Flow Technique
Simmering utilizes a gentle, consistent heat ideal for delicate foods, while Delta Cooking employs the Laminar Thermal Flow Technique to create precise, evenly distributed heat layers that preserve texture and flavor. This technique ensures minimal agitation and uniform temperature control, enhancing the cooking quality of sensitive ingredients without overcooking or breaking down their structure.
Protein Gradient Stability
Simmering maintains a stable protein gradient by gently heating without rapid temperature fluctuations, preserving the texture and integrity of delicate foods. Delta Cooking, with its temperature oscillations, can cause uneven protein denaturation, risking toughness and loss of moisture in sensitive ingredients.
Fine-Phase Simmer Profiling
Fine-phase simmer profiling in Simmering allows precise temperature control between 85degC to 96degC, preserving the delicate texture and flavor of sensitive foods better than Delta Cooking, which relies on broader temperature variations and less nuanced heat distribution. This targeted heat modulation minimizes cellular damage and moisture loss, ensuring optimal cooking results for items such as custards, seafood, and tender vegetables.
Gentle Quanta Heat Transfer
Simmering utilizes gentle quanta heat transfer to maintain a low, consistent temperature ideal for delicate foods, preventing agitation and preserving texture. In contrast, delta cooking involves abrupt temperature changes that can damage fragile ingredients by causing uneven heat distribution and increased thermal stress.
Delta Temp Precision Poaching
Delta Cooking technology offers superior temperature control with precise temperature increments ideal for delicate foods, ensuring gentle and consistent heat transfer that prevents overcooking or toughening. Simmering, while effective for broader heat applications, lacks the fine temperature precision of Delta Temp Precision Poaching, making Delta Cooking preferable for maintaining moisture and texture in sensitive ingredients like fish and eggs.
Convective Heat Damping
Simmering provides gentle convective heat damping crucial for delicate foods, maintaining stable temperatures just below boiling to prevent breakdown. Delta Cooking, by contrast, may deliver inconsistent heat distribution, risking textural damage in sensitive ingredients due to less effective convective heat regulation.
Simmering vs Delta Cooking for delicate foods. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com