Simmering offers gentle, uniform heat that maintains delicate flavors and prevents overcooking, ideal for consistent temperature control in slow cooking. Immersion circulation enhances heat distribution through continuous liquid movement, ensuring even cooking and eliminating hot spots for precise, consistent results. Choosing between simmering and immersion circulation depends on the need for static gentle heat versus dynamic, uniform temperature control in cooking processes.
Table of Comparison
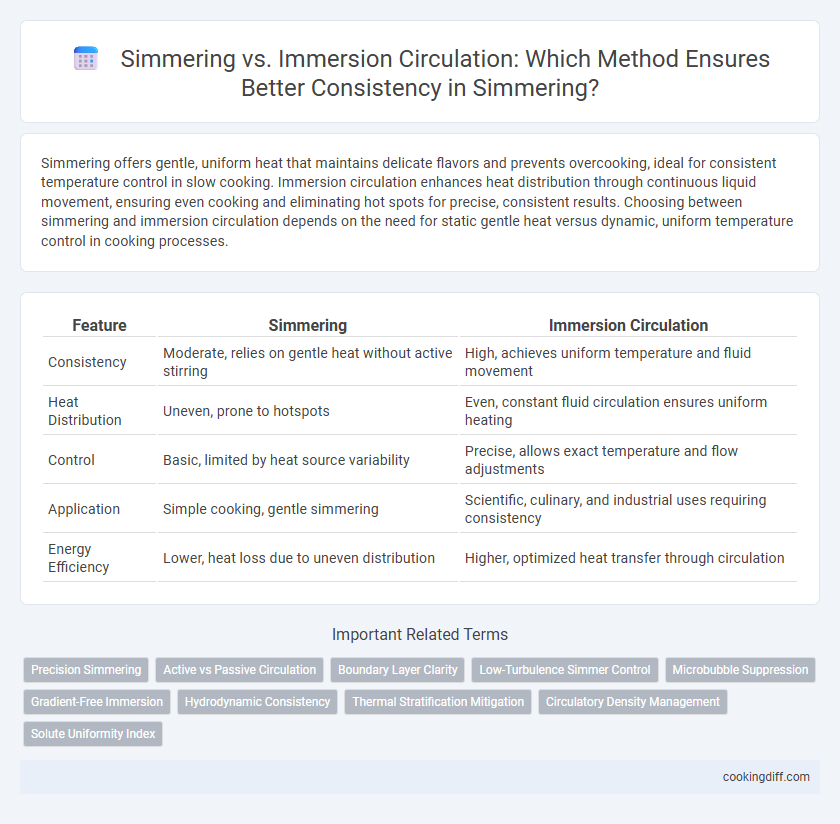
| Feature | Simmering | Immersion Circulation |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Moderate, relies on gentle heat without active stirring | High, achieves uniform temperature and fluid movement |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven, prone to hotspots | Even, constant fluid circulation ensures uniform heating |
| Control | Basic, limited by heat source variability | Precise, allows exact temperature and flow adjustments |
| Application | Simple cooking, gentle simmering | Scientific, culinary, and industrial uses requiring consistency |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, heat loss due to uneven distribution | Higher, optimized heat transfer through circulation |
Understanding Simmering: The Traditional Technique
Simmering is a traditional cooking technique that involves maintaining a liquid at a temperature just below boiling, around 185degF to 205degF (85degC to 96degC), to ensure gentle and consistent heat. This method allows flavors to meld gradually without the turbulence caused by vigorous boiling, preserving texture and taste in delicate dishes. Unlike immersion circulation, simmering relies on natural convection currents instead of mechanical agitation for heat distribution, which can result in subtle variations but enhances depth of flavor through slow, even cooking.
Immersion Circulation: The Science of Precision Cooking
| Cooking Method | Heat Transfer Mechanism | Temperature Consistency | Precision Control |
| Simmering | Gentle convection currents with minimal movement | Moderate fluctuations around 85-95degC (185-203degF) | Limited precision due to uneven heat distribution |
| Immersion Circulation (Sous Vide) | Continuous water circulation for uniform heat distribution | Stable temperature control typically within +-0.1degC | High precision enables consistent and repeatable cooking results |
Temperature Control: Simmering vs Immersion Circulation
Simmering maintains temperature through direct heat, often resulting in fluctuating and uneven heat distribution. Immersion circulation uses a pump to circulate water, ensuring consistent and precise temperature control throughout the vessel.
- Simmering heat variability - Direct heat causes hotspots and temperature swings that affect cooking consistency.
- Immersion circulation stability - Continuous water movement evenly distributes heat, minimizing temperature fluctuations.
- Precision control advantage - Immersion circulators allow accurate digital temperature settings, improving reproducibility in cooking.
Consistency in Cooking Results: Which Method Wins?
Simmering provides steady, gentle heat that helps maintain even cooking without over-agitation, resulting in consistent texture and flavor in delicate dishes. This method controls temperature precisely between 185degF and 205degF, ensuring ingredients cook uniformly without breaking down.
Immersion circulation uses a pump to continuously move liquid, promoting uniform heat distribution and preventing hot spots in larger pots. However, it can sometimes disrupt the texture of fragile foods, making simmering the preferred choice for consistent cooking results in recipes requiring delicate handling.
Impact on Texture and Flavor Development
Simmering provides gentle heat that allows flavors to meld and ingredients to tenderize gradually, enhancing texture complexity without breaking down delicate components. Immersion circulation offers consistent temperature and even heat distribution, promoting uniform texture and intensified flavor extraction throughout the dish.
- Simmering preserves ingredient integrity - Gentle, steady heat prevents overcooking and maintains a tender texture.
- Immersion circulation ensures uniform heat - Constant liquid movement distributes flavor compounds evenly for balanced taste.
- Simmering enhances slow flavor development - Extended cooking time allows gradual melding of subtle aromatic notes.
Choosing between simmering and immersion circulation depends on the desired balance between texture precision and flavor depth in culinary preparation.
Equipment and Setup: What You Need for Each Method
Simmering requires a stovetop or burner with precise temperature control and a pot that can maintain low, consistent heat. Immersion circulation demands specialized equipment like an immersion circulator and a heat-safe container to ensure uniform water temperature.
Simmering setups are straightforward, typically involving just a pot and heat source, suited for gradual temperature changes and easy monitoring. Immersion circulation setups are more complex, needing a water bath and a circulator to maintain precise temperatures and water flow for even cooking. Investing in an immersion circulator provides better consistency for sous vide cooking compared to traditional simmering.
Efficiency and Time Management in the Kitchen
How does simmering compare to immersion circulation in achieving consistent cooking temperatures? Simmering offers a straightforward method but can lead to temperature fluctuations, affecting dish uniformity and increasing cooking time. Immersion circulation ensures precise heat distribution, enhancing efficiency and reducing overall kitchen time.
Versatility Across Recipes: Soups, Stews, and Proteins
Simmering offers precise temperature control ideal for delicate soups and stews, preventing overcooking and preserving flavor nuances. Immersion circulation excels in evenly distributing heat, ensuring consistent texture in dense protein dishes and hearty broths.
Versatility across recipes is enhanced by simmering's gentle heat, which allows gradual flavor development in long-cooked meals. Immersion circulation provides efficient cooking for both liquid-based recipes and solid proteins by maintaining uniform temperature throughout the cooking vessel.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Each Method
Simmering maintains consistent temperature but may cause uneven heat distribution, while immersion circulation ensures uniform heat with occasional flow blockages. Troubleshooting involves adjusting heat levels for simmering and clearing circulation pathways for immersion to optimize consistency.
- Temperature Fluctuations - Adjust burner settings to stabilize simmering temperatures and prevent hotspots.
- Clogged Circulation Pathways - Regularly clean and inspect immersion circulators to ensure unobstructed flow.
- Uneven Heat Distribution - Use proper vessel size and placement to enhance simmering heat consistency.
Related Important Terms
Precision Simmering
Precision simmering ensures uniform temperature control, resulting in consistent heat distribution that prevents overcooking or uneven textures, unlike immersion circulation which may create variable hotspots. This method optimizes the stability of simmering temperatures, enhancing culinary consistency and precision in delicate cooking processes.
Active vs Passive Circulation
Simmering relies on active circulation created by gentle boiling and convection currents, promoting uniform temperature distribution and consistent cooking. In contrast, immersion circulation is passive, depending on natural fluid movement, which can lead to temperature gradients and less consistent heat exposure.
Boundary Layer Clarity
Simmering provides more uniform heat distribution, promoting a stable and clear boundary layer compared to immersion circulation, which can cause localized turbulence and disrupt boundary layer definition. This distinction in flow dynamics ensures better consistency and precision in temperature-sensitive processes requiring sharp thermal gradients.
Low-Turbulence Simmer Control
Low-turbulence simmer control ensures gentle heat application, maintaining consistent temperature and uniform cooking without disturbing delicate ingredients, unlike immersion circulation which can create uneven flow patterns and hot spots. This precise simmering technique optimizes heat distribution by minimizing agitation, resulting in improved texture and flavor consistency throughout the cooking process.
Microbubble Suppression
Simmering provides precise temperature control that minimizes microbubble formation more effectively than immersion circulation, which often introduces turbulence leading to inconsistent bubble suppression. Microbubble suppression during simmering enhances heating uniformity and maintains solution clarity, crucial for sensitive laboratory and culinary processes.
Gradient-Free Immersion
Gradient-Free Immersion offers superior consistency in Simmering processes by eliminating temperature gradients that commonly occur with standard Immersion Circulation methods. This results in uniform heat distribution, enhancing product quality and reducing hot spots during thermal treatment.
Hydrodynamic Consistency
Simmering provides gentle, uniform heat distribution with minimal turbulence, resulting in consistent temperature zones ideal for delicate cooking processes. Immersion circulation enhances hydrodynamic consistency by actively circulating the liquid, reducing hot spots and ensuring more rapid, even heat transfer throughout the vessel.
Thermal Stratification Mitigation
Simmering provides gentle, consistent heat that minimizes thermal stratification by maintaining uniform temperature layers, whereas immersion circulation actively disrupts temperature gradients through continuous fluid movement, enhancing heat distribution and reducing hot spots. Optimizing thermal stratification mitigation requires balancing simmering's stable heat with immersion circulation's dynamic mixing to ensure consistent thermal profiles in various industrial and culinary processes.
Circulatory Density Management
Simmering excels in maintaining consistent temperature gradients, while immersion circulation offers superior circulatory density management by ensuring uniform fluid movement and heat distribution. Effective circulatory density control in immersion systems prevents thermal stratification, enhancing process consistency compared to traditional simmering techniques.
Simmering vs Immersion Circulation for consistency. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com