Steel pots offer superior heat conductivity and durability, making them ideal for consistent simmering without the risk of cracking. Ceramic inserts provide even heat distribution and excellent heat retention, which helps maintain a steady simmer while adding aesthetic appeal. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prioritize rapid heat response or gentle, uniform heat for delicate simmering tasks.
Table of Comparison
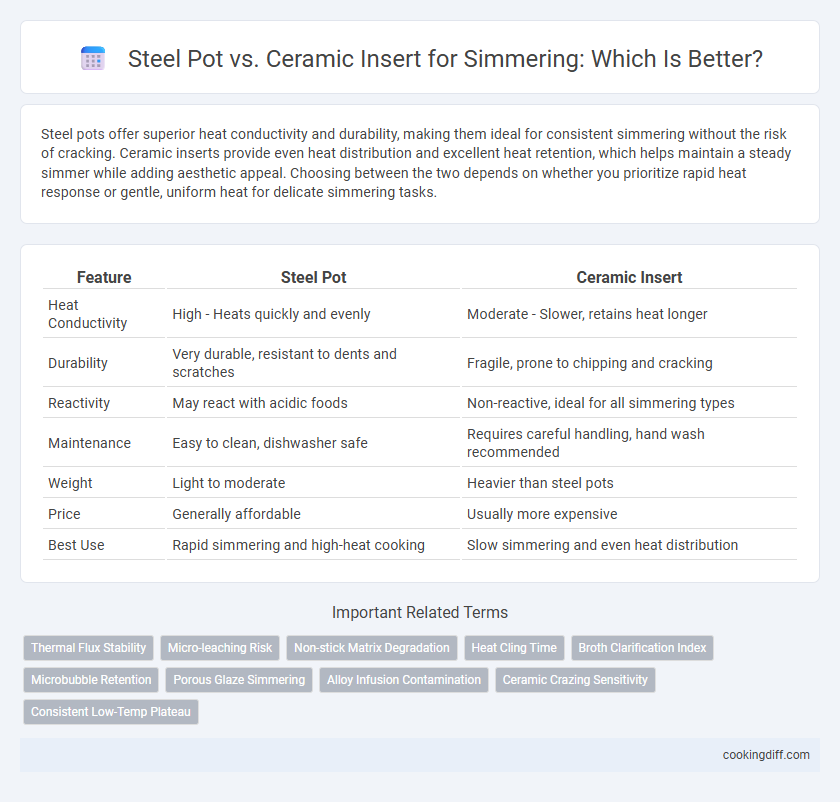
| Feature | Steel Pot | Ceramic Insert |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | High - Heats quickly and evenly | Moderate - Slower, retains heat longer |
| Durability | Very durable, resistant to dents and scratches | Fragile, prone to chipping and cracking |
| Reactivity | May react with acidic foods | Non-reactive, ideal for all simmering types |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires careful handling, hand wash recommended |
| Weight | Light to moderate | Heavier than steel pots |
| Price | Generally affordable | Usually more expensive |
| Best Use | Rapid simmering and high-heat cooking | Slow simmering and even heat distribution |
Introduction: Comparing Steel Pot and Ceramic Insert for Simmering
Choosing between a steel pot and a ceramic insert for simmering affects heat distribution and cooking results. Each material offers unique advantages based on thermal conductivity and food interaction.
- Steel Pot - Provides rapid, even heat distribution allowing precise temperature control during simmering.
- Ceramic Insert - Retains heat longer and offers gentle, consistent warmth ideal for delicate simmering tasks.
- Durability and Maintenance - Steel is highly durable and easy to clean, while ceramic can be more fragile but resists staining and odor absorption.
Selecting the right cookware enhances simmering efficiency and preserves flavor integrity.
Heat Distribution: Steel Pot vs Ceramic Insert
Steel pots offer superior heat distribution due to their metal composition, allowing for quick temperature adjustments essential for precise simmering. Ceramic inserts, while slower to heat, retain heat evenly, providing a consistent temperature ideal for delicate simmering tasks.
Steel's excellent thermal conductivity helps maintain stable simmering temperatures by rapidly dispersing heat across the pot's surface. Ceramic inserts distribute heat more gradually and evenly, reducing hot spots that can cause uneven cooking. Choosing between the two depends on whether quick temperature control or even heat retention is prioritized during simmering.
Temperature Retention: Which Material Excels?
Steel pots excel in temperature retention due to their dense metal composition, allowing consistent simmering without frequent heat adjustments. Ceramic inserts, while providing even heat distribution, tend to lose heat faster because of their porous nature. For recipes requiring steady, long-duration simmering, steel pots are generally more effective in maintaining optimal temperature levels.
Impact on Food Flavor During Simmering
Steel pots provide even heat distribution which helps maintain consistent simmering temperatures, preserving the natural flavors of food without imparting any metallic taste. Ceramic inserts offer non-reactive surfaces that do not alter the flavor, making them ideal for delicate simmered dishes like sauces and soups.
- Steel pots enhance flavor retention - Conductive properties ensure steady heat, preventing flavor breakdown during simmering.
- Ceramic provides non-reactive simmering - Its inert surface avoids chemical reactions that could change the food's taste.
- Flavor neutrality varies by material - Steel may sometimes impart a slight metallic tang, whereas ceramic preserves original flavor profiles.
Durability and Longevity of Both Materials
Which material--steel pot or ceramic insert--offers superior durability and longevity for simmering? Steel pots are highly durable, resistant to chipping, cracking, and thermal shock, making them ideal for long-term use. Ceramic inserts provide excellent heat retention and non-reactive cooking surfaces but are more prone to cracking and require careful handling to ensure longevity.
Ease of Cleaning: Steel Pot vs Ceramic Insert
Steel pots typically offer superior ease of cleaning compared to ceramic inserts due to their non-porous surface and resistance to staining. Ceramic inserts can retain stains and food odors, requiring more careful maintenance and gentle cleaning methods.
- Non-porous Surface - Steel's smooth metal surface prevents food from seeping in, making it easier to scrub off residues.
- Stain Resistance - Steel pots resist discoloration and stains even after prolonged simmering tasks.
- Cleaning Care - Ceramic inserts need mild detergents and avoid abrasive cleaners to maintain their glaze and prevent damage.
Safety and Reactivity with Ingredients
| Material | Safety | Reactivity with Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Pot | Durable, non-porous, and resistant to cracking or chipping, making it safe for long-term cooking. | May react with acidic foods like tomatoes or vinegar, potentially altering flavor and causing metal leaching. |
| Ceramic Insert | Non-toxic, generally free of heavy metals, and safe for cooking with minimal risk of contaminant leaching. | Non-reactive surface preserves the natural taste of acidic and delicate ingredients during simmering. |
Energy Efficiency in Simmering Applications
Steel pots conduct heat quickly and maintain a consistent temperature, making them highly energy efficient for simmering applications. Their ability to respond rapidly to temperature changes reduces overall cooking time and energy consumption.
Ceramic inserts retain heat longer but require more time and energy to reach simmering temperatures initially. This slower heat-up can lead to increased energy use despite excellent heat retention during the simmering process.
Suitability for Different Types of Stovetops
Steel pots are highly suitable for all types of stovetops, including induction, gas, and electric, due to their magnetic properties and excellent heat conductivity. Ceramic inserts perform best on electric and gas stovetops but may not be compatible with induction systems because they lack magnetic responsiveness. Choosing between steel and ceramic depends on the stovetop type and desired heat distribution, with steel offering faster, more even heating and ceramic providing gentle, consistent heat for delicate simmering.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Flux Stability
Steel pots offer superior thermal flux stability during simmering due to their high thermal conductivity and quick heat response, ensuring consistent temperature control. Ceramic inserts, while providing even heat distribution, tend to have slower heat adjustment, which can result in less precise simmering temperature management.
Micro-leaching Risk
Steel pots exhibit minimal micro-leaching due to their inert stainless steel surface, making them safer for prolonged simmering compared to ceramic inserts, which may release trace amounts of heavy metals or toxins when exposed to acidic or high-temperature simmering conditions. Choosing steel over ceramic reduces the risk of contaminating food, ensuring safer and cleaner cooking outcomes during extended simmering processes.
Non-stick Matrix Degradation
Steel pots offer superior resistance to non-stick matrix degradation during simmering due to their durable metal surface, which withstands prolonged low heat without compromising coating integrity. Ceramic inserts, while providing a naturally non-stick surface, are more prone to wear and micro-cracking under extended simmering, leading to faster degradation of their non-stick properties.
Heat Cling Time
Steel pots offer superior heat retention and distribute heat evenly, resulting in consistent simmering with minimal temperature fluctuations. Ceramic inserts, while visually appealing, tend to have longer heat cling time, causing slower cool-down but sometimes uneven heat distribution during simmering.
Broth Clarification Index
Steel pots provide superior heat conductivity and even temperature distribution, which enhances the Broth Clarification Index by preventing impurities from clouding the broth during simmering. Ceramic inserts, while gentle and non-reactive, may retain uneven heat, potentially lowering the clarity and overall quality of the simmered broth.
Microbubble Retention
Steel pots offer superior microbubble retention during simmering due to their excellent heat conductivity and surface texture, promoting even heat distribution and stable microbubble formation. Ceramic inserts, while aesthetically pleasing, typically have lower thermal conductivity and a smoother surface, which can reduce microbubble retention and affect the consistency of gentle simmering.
Porous Glaze Simmering
Porcelain ceramic inserts with a porous glaze enhance simmering by evenly distributing heat and retaining moisture, preventing hot spots and ensuring delicate flavors develop gently. Steel pots lack this porous characteristic, often resulting in uneven heat retention and less controlled simmering for sensitive dishes.
Alloy Infusion Contamination
Steel pots with alloy infusion offer superior durability and resistance to contamination compared to ceramic inserts, which are more prone to leaching minerals into food during simmering. The non-reactive nature of stainless steel alloy ensures consistent heat distribution without compromising the purity of simmered ingredients.
Ceramic Crazing Sensitivity
Ceramic inserts are prone to crazing, a network of fine cracks caused by thermal shock or rapid temperature changes during simmering, which can compromise the pot's durability and food safety. Steel pots offer superior resistance to thermal stress and avoid crazing issues, making them more reliable for consistent low-heat simmering tasks.
Steel Pot vs Ceramic Insert for simmering. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com