Slow cookers provide consistent, even heat with precise temperature control, making them ideal for hands-off cooking and maintaining moisture over long periods. Clay pots enhance slow-cooked dishes by allowing gradual heat absorption and natural moisture retention, infusing food with earthy flavors and a unique texture. Choosing between a slow cooker and a clay pot depends on balancing convenience and the depth of flavor desired in slow-cooked meals.
Table of Comparison
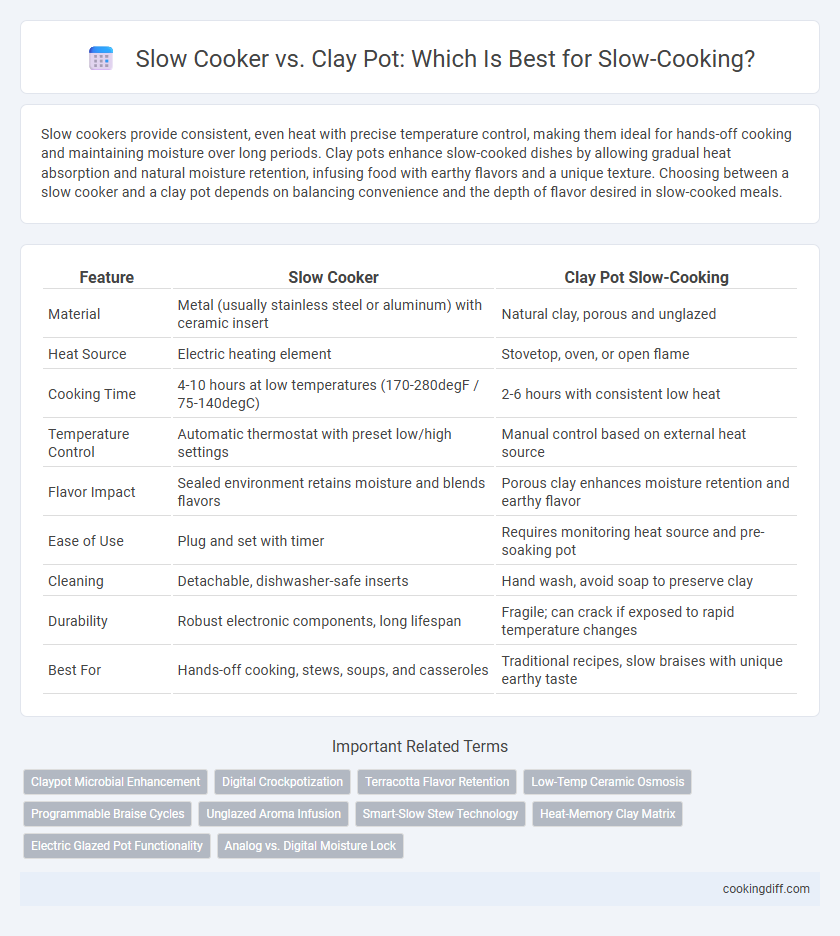
| Feature | Slow Cooker | Clay Pot Slow-Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal (usually stainless steel or aluminum) with ceramic insert | Natural clay, porous and unglazed |
| Heat Source | Electric heating element | Stovetop, oven, or open flame |
| Cooking Time | 4-10 hours at low temperatures (170-280degF / 75-140degC) | 2-6 hours with consistent low heat |
| Temperature Control | Automatic thermostat with preset low/high settings | Manual control based on external heat source |
| Flavor Impact | Sealed environment retains moisture and blends flavors | Porous clay enhances moisture retention and earthy flavor |
| Ease of Use | Plug and set with timer | Requires monitoring heat source and pre-soaking pot |
| Cleaning | Detachable, dishwasher-safe inserts | Hand wash, avoid soap to preserve clay |
| Durability | Robust electronic components, long lifespan | Fragile; can crack if exposed to rapid temperature changes |
| Best For | Hands-off cooking, stews, soups, and casseroles | Traditional recipes, slow braises with unique earthy taste |
Introduction to Slow Cooker and Clay Pot Slow-Cooking
Slow cookers use electric heat to maintain a consistent low temperature, making them ideal for energy-efficient and convenient slow-cooking. Clay pots, traditionally made from natural porous materials, enhance flavor by allowing slow evaporation and even heat distribution. Both methods excel at tenderizing tough cuts of meat and infusing dishes with rich, deep flavors over extended cooking periods.
Key Differences Between Slow Cookers and Clay Pots
Slow cookers and clay pots both excel in slow-cooking but differ significantly in heat distribution and moisture retention. Slow cookers use electric heat with controlled temperature settings, while clay pots rely on radiant heat and porous material to enhance flavor infusion.
- Heat Source - Slow cookers use electric heating elements; clay pots require external heat sources such as stovetops or ovens.
- Material Composition - Slow cookers have ceramic or metal inserts with insulated bases; clay pots are made from porous natural clay that absorbs and releases moisture.
- Temperature Control - Slow cookers provide precise temperature control through built-in thermostats; clay pots depend on manual heat adjustments and cooking experience.
Choosing between slow cookers and clay pots depends on your preference for convenience, flavor development, and cooking control.
How Each Method Preserves Flavors and Nutrients
Slow cookers use a sealed, electric environment that maintains consistent low heat, preserving flavors and nutrients by preventing moisture loss. Clay pots provide a porous structure that allows slow evaporation and circulation of steam, enhancing flavor infusion while retaining nutritional value.
- Slow Cooker Retains Moisture - The sealed lid traps steam, reducing nutrient loss and concentrating flavors within the food.
- Clay Pot Enhances Aroma - Porous material allows gradual evaporation, intensifying the natural aroma and taste of ingredients.
- Temperature Stability - Both methods ensure low, steady heat that prevents overcooking and preserves delicate nutrients.
Cooking Time and Energy Efficiency Comparison
Slow cookers typically have shorter cooking times, averaging 6 to 8 hours on low heat, while clay pot slow-cooking can extend to 8 to 12 hours due to its gradual heat retention properties. The ceramic material in clay pots allows for gentle, even cooking but requires more time to reach optimal temperatures compared to electric slow cookers.
In terms of energy efficiency, slow cookers consume approximately 75 to 150 watts per hour, making them more energy-efficient for long cooking durations. Clay pots, heated on a stovetop or in an oven, often use more energy overall because of longer heating times and less insulation compared to electric slow cookers.
Versatility: What Can You Cook in Each?
Slow cookers offer versatile cooking options, allowing you to prepare soups, stews, roasts, and even desserts with programmable settings for precise temperature control. Clay pots excel in slow-cooking traditional dishes such as tagines, braised meats, and rice-based meals, enhancing flavors through natural moisture retention and heat distribution. While slow cookers provide convenience and consistency, clay pots deliver authentic textures and a rustic cooking experience prized in many cuisines.
Ease of Use and Cleaning: Slow Cooker vs. Clay Pot
Which is easier to use and clean: a slow cooker or a clay pot for slow-cooking? Slow cookers typically offer programmable settings and non-stick inserts, making them more user-friendly and easier to clean. Clay pots require seasoning and careful handling, which can complicate both use and cleaning compared to electric slow cookers.
Safety Considerations for Slow Cooking Methods
Slow cookers are designed with built-in temperature controls that consistently maintain safe cooking temperatures, reducing the risk of bacterial growth. Clay pots require careful monitoring to avoid cracking and ensure food reaches a safe internal temperature during slow cooking.
- Temperature Control - Slow cookers maintain precise heat levels, crucial for food safety by preventing the "danger zone" where bacteria thrive.
- Material Durability - Clay pots can crack under thermal stress if heated too quickly, posing safety hazards and potential contamination.
- Cleaning and Maintenance - Slow cookers typically have removable, dishwasher-safe inserts, while clay pots need gentle hand washing to preserve the material and hygiene.
Texture and Taste: Results from Both Techniques
Slow cookers provide consistent, even heat that tenderizes meat and melds flavors smoothly, resulting in a rich and uniform texture. Clay pots enhance moisture retention and impart an earthy aroma, creating a subtler, delicate taste profile in slow-cooked dishes.
The sealed environment of slow cookers prevents excessive evaporation, maintaining a succulent and juicy texture in stews and braises. Clay pot slow-cooking gradually develops complex flavors and a slightly firmer texture, prized for traditional recipes requiring gentle simmering.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Longevity
Slow cookers generally require a moderate initial investment with prices ranging from $30 to $150 depending on features and brand. Clay pots, while often less expensive initially at around $20 to $60, may require replacement sooner due to fragility and potential cracking over time.
Slow cookers tend to offer greater longevity and durability, often lasting several years with proper care. Clay pots need careful handling to avoid breakage but can provide excellent heat retention and flavor enhancement, adding value beyond cost. Evaluating cost-efficiency involves balancing upfront price with durability and cooking performance unique to each option.
Related Important Terms
Claypot Microbial Enhancement
Clay pot slow-cooking enhances microbial activity by maintaining a stable, moist environment that supports the natural fermentation and breakdown of ingredients, improving flavor complexity and nutritional bioavailability. In contrast, slow cookers often reach higher temperatures that may inhibit beneficial microbial growth, resulting in less pronounced microbial enhancement during the cooking process.
Digital Crockpotization
Slow cookers offer precise temperature control and programmable timers, enabling consistent slow-cooking results through digital crockpotization, while clay pots provide natural heat retention and moisture preservation but lack digital regulation. Digital crockpotization enhances convenience and accuracy compared to traditional clay pot methods, optimizing texture and flavor in slow-cooked meals.
Terracotta Flavor Retention
Clay pot slow-cooking enhances terracotta flavor retention by allowing gradual heat distribution and moisture absorption, resulting in richer, more nuanced taste profiles compared to slow cookers. Slow cookers offer convenience and consistent temperature control but lack the porous nature of terracotta, which uniquely preserves and intensifies flavors during the cooking process.
Low-Temp Ceramic Osmosis
Slow cooker technology utilizes low-temp ceramic osmosis to evenly distribute heat and retain moisture, enhancing flavor infusion and tenderness in slow-cooked dishes. Compared to traditional clay pot slow-cooking, slow cookers offer precise temperature control and consistent heat retention, minimizing the risk of uneven cooking or dryness.
Programmable Braise Cycles
Programmable braise cycles in slow cookers offer precise temperature and timing control, enhancing flavor extraction and texture consistency compared to traditional clay pots, which rely on manual heat adjustment. While clay pots provide natural heat retention and moisture preservation, programmable slow cookers optimize energy efficiency and reduce user intervention for perfect braising results.
Unglazed Aroma Infusion
Unglazed clay pots in slow-cooking retain moisture and enhance aroma infusion by allowing gradual absorption and release of flavors, creating richer and more complex dishes compared to plastic slow cookers. The porous nature of clay pots promotes even heat distribution and natural steam circulation, intensifying the depth of taste and texture.
Smart-Slow Stew Technology
Smart-Slow Stew Technology enhances slow-cooking by optimizing heat distribution and moisture retention, providing consistent results whether using a slow cooker or a traditional clay pot. Slow cookers offer precise temperature control and convenience, while clay pots contribute natural earthy flavors and retain heat longer, benefiting recipes that require uniform simmering over extended periods.
Heat-Memory Clay Matrix
Slow cookers provide consistent, regulated heat through electric coils, ensuring steady cooking temperatures ideal for long, low-temperature meals. In contrast, clay pot slow-cooking leverages the heat-memory clay matrix, which absorbs and radiates heat evenly, enhancing moisture retention and delivering deeper, more flavorful results by maintaining stable internal temperatures naturally.
Electric Glazed Pot Functionality
Electric glazed pots in slow cooking provide consistent heat distribution and precise temperature control, enhancing food flavor extraction and texture. Unlike traditional clay pots, their non-porous surface prevents absorption of odors and stains while offering easy maintenance and durability for long-term use.
Slow cooker vs clay pot slow-cooking for slow-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com