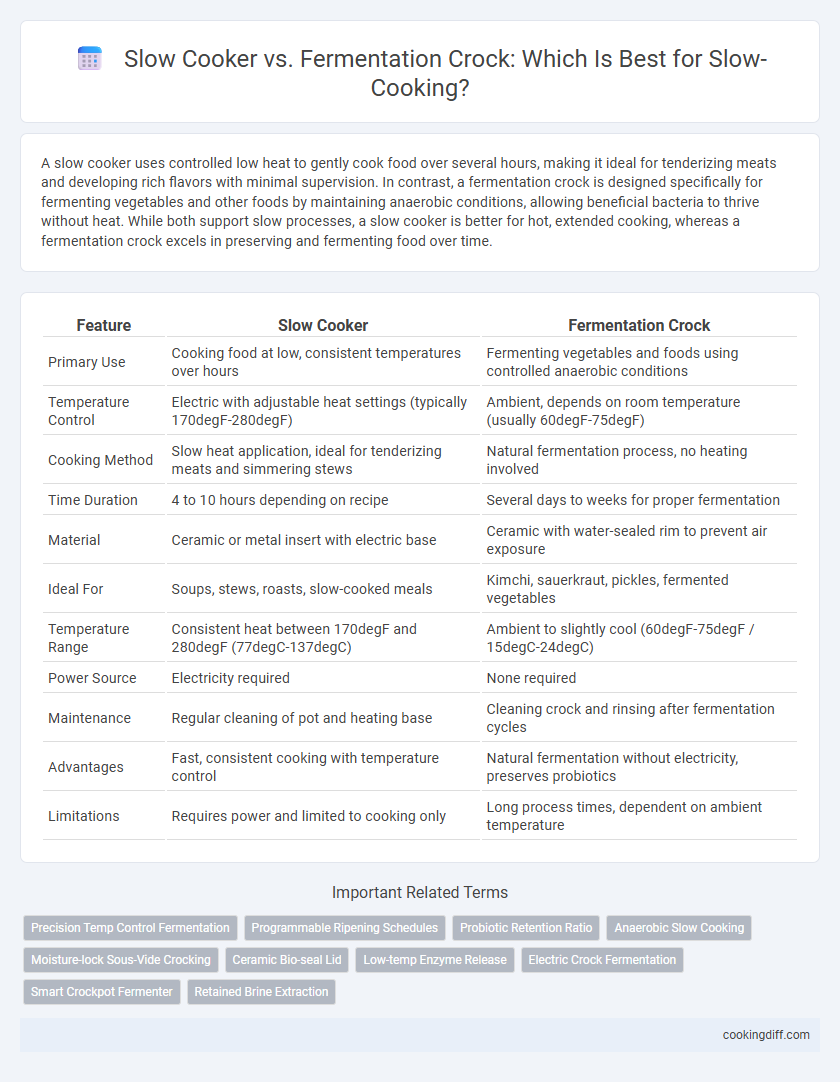
A slow cooker uses controlled low heat to gently cook food over several hours, making it ideal for tenderizing meats and developing rich flavors with minimal supervision. In contrast, a fermentation crock is designed specifically for fermenting vegetables and other foods by maintaining anaerobic conditions, allowing beneficial bacteria to thrive without heat. While both support slow processes, a slow cooker is better for hot, extended cooking, whereas a fermentation crock excels in preserving and fermenting food over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Slow Cooker | Fermentation Crock |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Cooking food at low, consistent temperatures over hours | Fermenting vegetables and foods using controlled anaerobic conditions |
| Temperature Control | Electric with adjustable heat settings (typically 170degF-280degF) | Ambient, depends on room temperature (usually 60degF-75degF) |
| Cooking Method | Slow heat application, ideal for tenderizing meats and simmering stews | Natural fermentation process, no heating involved |
| Time Duration | 4 to 10 hours depending on recipe | Several days to weeks for proper fermentation |
| Material | Ceramic or metal insert with electric base | Ceramic with water-sealed rim to prevent air exposure |
| Ideal For | Soups, stews, roasts, slow-cooked meals | Kimchi, sauerkraut, pickles, fermented vegetables |
| Temperature Range | Consistent heat between 170degF and 280degF (77degC-137degC) | Ambient to slightly cool (60degF-75degF / 15degC-24degC) |
| Power Source | Electricity required | None required |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning of pot and heating base | Cleaning crock and rinsing after fermentation cycles |
| Advantages | Fast, consistent cooking with temperature control | Natural fermentation without electricity, preserves probiotics |
| Limitations | Requires power and limited to cooking only | Long process times, dependent on ambient temperature |
Introduction to Slow Cookers and Fermentation Crocks
Slow cookers use consistent low heat over extended periods to tenderize ingredients and develop deep flavors, making them ideal for soups, stews, and braised dishes. Fermentation crocks maintain a controlled anaerobic environment suitable for fermenting vegetables like sauerkraut and kimchi by promoting beneficial bacterial growth.
Slow cookers feature electric heating elements and temperature controls to ensure steady cooking temperatures between 170degF and 280degF. Fermentation crocks are typically ceramic vessels with water-sealed rims that prevent air exposure while allowing gases to escape during fermentation.
How Slow Cookers Work: Modern Convenience
| Slow cookers use an electric heating element to maintain a consistent low temperature, typically between 170degF and 280degF, enabling the gradual cooking of food over several hours. Their insulated ceramic or metal pots retain heat efficiently, ensuring even cooking without the need for constant monitoring. This modern convenience allows users to start meals in the morning and enjoy tender, flavorful dishes by dinner time with minimal effort. |
Traditional Fermentation Crocks: Timeless Technique
Traditional fermentation crocks provide a natural, anaerobic environment crucial for slow-cooking fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi. These crocks maintain consistent temperatures and moisture levels, enhancing flavor development over time.
- Natural fermentation environment - The crocks are designed to create airtight conditions that prevent spoilage and promote beneficial bacterial growth.
- Temperature regulation - Thick ceramic walls help maintain a stable, cool temperature ideal for slow fermentation.
- Durability and reusability - These crocks are made from durable materials that support long-term, repeated use without affecting food quality.
Key Differences in Cooking Methods
What are the key differences between a Slow Cooker and a Fermentation Crock for slow-cooking? A Slow Cooker uses consistent low heat to gently cook food over several hours, ideal for tenderizing meats and developing complex flavors. In contrast, a Fermentation Crock relies on anaerobic fermentation at room temperature, promoting probiotic growth rather than applying heat to cook the ingredients.
Flavor Development: Which Yields Better Taste?
Slow cookers use consistent low heat to tenderize food, enhancing flavor through gradual chemical reactions. Fermentation crocks develop complex, tangy tastes by promoting beneficial microbial activity over time.
- Slow Cooker - Maintains steady temperatures around 170-280degF to break down fibers and intensify savory flavors.
- Fermentation Crock - Creates an anaerobic environment ideal for lactic acid bacteria, producing rich depth and natural sourness.
- Flavor Complexity - Fermentation yields more layered and probiotic-rich flavors, while slow cookers emphasize savory, hearty profiles.
Choosing between a slow cooker and fermentation crock depends on whether you prefer cooked richness or fermented tang in your dishes.
Nutritional Impact: Slow Cooker vs Fermentation Crock
Slow cookers preserve nutrients by cooking food at low temperatures over extended periods, minimizing nutrient loss compared to high-heat methods. Fermentation crocks enhance nutritional value by promoting probiotic growth, which improves gut health and digestion. While slow cookers focus on nutrient retention, fermentation crocks add beneficial live cultures, offering distinct nutritional benefits.
Versatility in Recipes and Ingredients
Slow cookers offer exceptional versatility by accommodating a wide range of recipes, from soups and stews to roasts and desserts, using varied ingredients with consistent temperature control. Fermentation crocks specialize in creating fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, and pickles, relying on anaerobic conditions rather than heat.
Slow cookers allow for multi-ingredient combinations and extended cooking times that tenderize tough cuts of meat and infuse flavors deeply. Fermentation crocks promote probiotic development by facilitating natural bacterial growth over days or weeks without cooking, enhancing digestive benefits.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Slow cookers offer simple, user-friendly controls and require minimal monitoring, making them ideal for effortless meal preparation. Their non-porous surfaces are easy to clean, ensuring low maintenance compared to fermentation crocks.
Fermentation crocks demand more attention due to the need for controlled temperature and humidity during the slow-cooking process. Cleaning can be more involved because of their porous ceramic material that may retain odors or residues. Choosing between the two depends on convenience priorities and the specific slow-cooking method desired.
Cost Comparison and Accessibility
Slow cookers typically offer a more affordable entry point compared to fermentation crocks, making them accessible for most home cooks. Fermentation crocks often require a higher initial investment but provide specialized functionality for fermenting foods.
- Cost efficiency - Slow cookers generally range from $30 to $100, whereas fermentation crocks can cost between $50 and $150 depending on size and material.
- Accessibility - Slow cookers are widely available in supermarkets and online, while fermentation crocks may require purchase from specialty kitchenware stores or online retailers.
- Multi-functionality - Slow cookers serve dual purposes for both cooking and warming food, whereas fermentation crocks are dedicated primarily to fermenting processes.
Related Important Terms
Precision Temp Control Fermentation
Slow cookers offer precise temperature control settings ideal for maintaining steady heat during extended cooking processes, whereas fermentation crocks rely on ambient conditions and natural temperature variations, making them less suitable for precision fermentation tasks. For slow-cooking that demands exact temperature regulation, such as yogurt or kimchi fermentation, slow cookers with digital thermostats provide consistent results compared to traditional fermentation crocks.
Programmable Ripening Schedules
Programmable ripening schedules in fermentation crocks enable precise control over temperature and timing, optimizing the slow-cooking fermentation process for enhanced flavor development. Unlike slow cookers, which primarily rely on consistent heat application, fermentation crocks use customizable settings to guide microbial activity, ensuring ideal conditions for fermenting vegetables and other foods.
Probiotic Retention Ratio
Slow cookers operate at steady low temperatures typically between 170degF and 280degF, which can significantly reduce probiotic retention due to heat-sensitive bacteria dying above 115degF. In contrast, fermentation crocks maintain a cooler, controlled environment around 68degF to 72degF, allowing optimal probiotic development and preservation, resulting in a significantly higher probiotic retention ratio for fermented foods.
Anaerobic Slow Cooking
Slow cookers maintain a consistent low temperature between 170degF and 280degF, ideal for anaerobic slow cooking by tightly sealing in moisture and preventing oxygen exposure, which tenderizes meats and preserves flavors. Fermentation crocks create an oxygen-free environment through water-sealed airlocks, enabling anaerobic fermentation of foods like sauerkraut but lack temperature control for traditional slow cooking methods.
Moisture-lock Sous-Vide Crocking
Slow Cooker and Fermentation Crock both provide effective slow-cooking methods, but the Moisture-lock Sous-Vide Crocking in fermentation crocks ensures consistent hydration and temperature control, preserving flavors and textures more efficiently. Slow Cookers rely on sealed heat and steam, while Sous-Vide Crocking enhances moisture retention through immersion, delivering tender, evenly cooked results with enhanced nutrient preservation.
Ceramic Bio-seal Lid
A Slow Cooker utilizes a ceramic bio-seal lid that maintains an airtight environment, enhancing heat retention and moisture preservation during extended cooking times. This sealed ceramic design contrasts with fermentation crocks, which focus on microbial activity but lack the controlled heat and moisture regulation essential for slow-cooking.
Low-temp Enzyme Release
Slow cookers maintain consistent low temperatures around 170degF to 200degF, optimizing enzyme activity for tenderizing meats and breaking down complex fibers over extended periods. Fermentation crocks operate at ambient temperatures between 60degF and 75degF, facilitating natural enzyme release primarily for fermenting vegetables without sustained heat application.
Electric Crock Fermentation
Electric crock fermentation offers precise temperature control ideal for consistent slow-cooking and fermentation processes, enhancing flavor development and microbial activity. Unlike traditional slow cookers, electric fermentation crocks maintain specific warmth ranges critical for probiotic growth and safety in fermented foods.
Smart Crockpot Fermenter
The Smart Crockpot Fermenter combines precise temperature control with slow-cooking versatility, allowing for both fermentation and extended cooking processes in one device. Its advanced sensor technology ensures consistent heat distribution, making it ideal for achieving optimal flavors in slow-cooked meals and fermented foods alike.
Slow Cooker vs Fermentation Crock for slow-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com