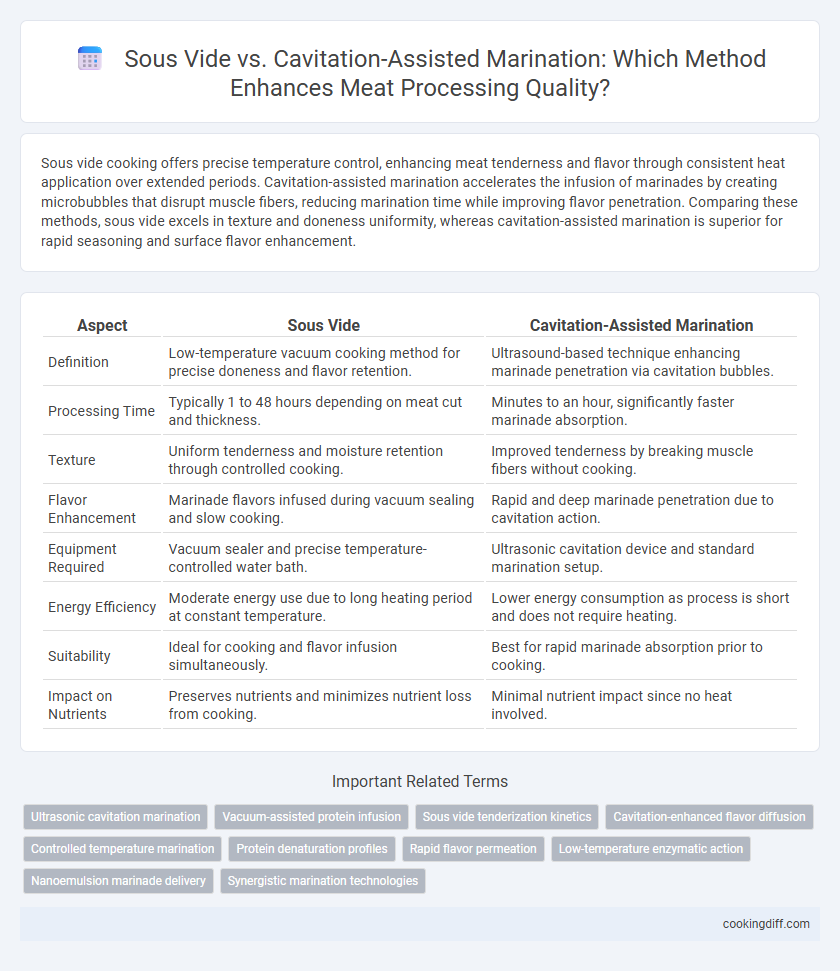
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, enhancing meat tenderness and flavor through consistent heat application over extended periods. Cavitation-assisted marination accelerates the infusion of marinades by creating microbubbles that disrupt muscle fibers, reducing marination time while improving flavor penetration. Comparing these methods, sous vide excels in texture and doneness uniformity, whereas cavitation-assisted marination is superior for rapid seasoning and surface flavor enhancement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Cavitation-Assisted Marination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Low-temperature vacuum cooking method for precise doneness and flavor retention. | Ultrasound-based technique enhancing marinade penetration via cavitation bubbles. |
| Processing Time | Typically 1 to 48 hours depending on meat cut and thickness. | Minutes to an hour, significantly faster marinade absorption. |
| Texture | Uniform tenderness and moisture retention through controlled cooking. | Improved tenderness by breaking muscle fibers without cooking. |
| Flavor Enhancement | Marinade flavors infused during vacuum sealing and slow cooking. | Rapid and deep marinade penetration due to cavitation action. |
| Equipment Required | Vacuum sealer and precise temperature-controlled water bath. | Ultrasonic cavitation device and standard marination setup. |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy use due to long heating period at constant temperature. | Lower energy consumption as process is short and does not require heating. |
| Suitability | Ideal for cooking and flavor infusion simultaneously. | Best for rapid marinade absorption prior to cooking. |
| Impact on Nutrients | Preserves nutrients and minimizes nutrient loss from cooking. | Minimal nutrient impact since no heat involved. |
Understanding Sous Vide Cooking
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it at a precise, consistent low temperature in a water bath, ensuring even doneness and enhanced flavor retention. This method contrasts with cavitation-assisted marination, which uses ultrasonic waves to accelerate marinade absorption without heat application.
- Temperature Control - Sous vide maintains exact temperature settings to achieve uniform cooking, which is critical for texture and safety.
- Flavor Development - The vacuum seal in sous vide traps moisture and flavors, intensifying the taste profile of meat.
- Processing Time - Sous vide typically requires longer cooking durations than cavitation-assisted marination, which is faster but does not cook the meat.
What is Cavitation-Assisted Marination?
Cavitation-assisted marination utilizes ultrasonic waves to create microscopic bubbles that enhance marinade penetration and accelerate the tenderizing process. This technique contrasts with sous vide by focusing on mechanical disruption to improve flavor infusion rather than precise temperature control.
- Ultrasonic cavitation - Generates microbubbles that implode, breaking down meat fibers for better marinade absorption.
- Enhanced marination speed - Reduces marination time significantly compared to traditional soaking methods.
- Improved texture and flavor - Results in uniformly tenderized meat with deeper and more consistent flavor profiles.
Key Differences in Meat Tenderization
Sous vide uses precise temperature control to break down collagen in meat gently over extended cooking times, resulting in consistent tenderness and moisture retention. Cavitation-assisted marination leverages ultrasonic waves to create microbubbles that disrupt muscle fibers, accelerating marinade absorption and enhancing tenderization more rapidly than conventional methods. While sous vide excels in uniform texture and juiciness, cavitation offers faster processing, making it ideal for high-throughput meat tenderization in industrial settings.
Flavor Infusion: Sous Vide vs Cavitation
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control to evenly infuse flavors over extended cooking times, enhancing meat tenderness and flavor absorption. Cavitation-assisted marination accelerates flavor penetration through ultrasonic waves that create microbubbles, disrupting meat fibers and allowing marinade to deeply permeate in minutes.
Flavor infusion via sous vide results in a more subtle, uniform taste due to gradual diffusion at low temperatures. Cavitation delivers intense, rapid marinade uptake that can produce more pronounced flavors without the need for lengthy cooking periods.
Time Efficiency in Meat Processing
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control but generally requires longer cooking times compared to cavitation-assisted marination, which accelerates marinade absorption and reduces pre-cooking preparation. Cavitation-assisted marination enhances time efficiency by disrupting meat fibers, allowing marination in minutes rather than hours.
- Sous vide requires extended cooking durations - Typically, sous vide meat processing ranges from 1 to 48 hours depending on the cut and desired doneness.
- Cavitation-assisted marination shortens marination time - Ultrasonic cavitation can reduce marination time from several hours to under 30 minutes.
- Combined techniques optimize total processing time - Using cavitation-assisted marination prior to sous vide can minimize overall meat preparation time while maintaining quality.
Time efficiency in meat processing increases significantly when cavitation-assisted marination complements sous vide cooking.
Equipment and Technology Requirements
What are the key differences in equipment and technology requirements between sous vide and cavitation-assisted marination for meat processing? Sous vide requires precise temperature-controlled water baths and vacuum-sealed bags to ensure consistent cooking and flavor infusion, while cavitation-assisted marination relies on ultrasonic devices that generate high-frequency sound waves to enhance marinade absorption. Both methods demand specialized technology, but sous vide focuses on thermal precision whereas cavitation emphasizes ultrasonic energy application.
Effect on Meat Texture and Juiciness
Sous vide cooking enhances meat texture by maintaining precise temperature control, resulting in tender and evenly cooked meat with superior juiciness retention. Cavitation-assisted marination uses ultrasonic waves to accelerate marinade penetration, improving flavor absorption and slightly altering meat fibers, but its impact on tenderness is less consistent compared to sous vide. Combining cavitation with sous vide can optimize both texture and juiciness by ensuring deep marinade infusion without compromising the precise cooking benefits of sous vide.
Food Safety Considerations
| Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control, effectively eliminating pathogens by maintaining meat at safe, consistent temperatures for extended periods. Cavitation-assisted marination enhances flavor penetration but requires careful monitoring as it does not inherently guarantee microbial safety without subsequent cooking. Proper integration of sous vide after cavitation marination offers an optimized balance of safety and quality in meat processing workflows. |
Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
Sous vide cooking typically consumes moderate energy due to precise temperature control over extended periods, often resulting in consistent energy efficiency. Cavitation-assisted marination uses ultrasonic waves that generate localized energy, leading to shorter processing times and potentially lower overall energy consumption.
The initial investment cost for sous vide equipment ranges from $200 to $1,000 for commercial setups, with relatively low operational costs due to stable temperature maintenance. Cavitation-assisted marination systems generally involve higher upfront costs between $1,000 and $5,000, but offer cost savings through reduced marinade usage and faster processing cycles.
Related Important Terms
Ultrasonic cavitation marination
Ultrasonic cavitation marination enhances meat processing by creating microscopic bubbles that disrupt muscle fibers, significantly accelerating marinade absorption and improving tenderness compared to traditional sous vide techniques. This method leverages high-frequency sound waves to intensify flavor penetration and reduce marination time while maintaining meat quality and juiciness.
Vacuum-assisted protein infusion
Sous vide cooking enhances vacuum-assisted protein infusion by maintaining precise temperature control, which preserves meat texture and allows uniform flavor penetration. In contrast, cavitation-assisted marination uses ultrasonic waves to create microscopic pores in the meat, accelerating infusion but may affect protein integrity, making sous vide more reliable for consistent vacuum-based protein uptake.
Sous vide tenderization kinetics
Sous vide tenderization kinetics rely on precise temperature control over extended times, allowing collagen breakdown and enzyme activity to enhance meat texture uniformly. This method contrasts with cavitation-assisted marination, which accelerates flavor infusion but lacks the controlled protein denaturation and moisture retention critical to optimizing tenderness in sous vide processing.
Cavitation-enhanced flavor diffusion
Cavitation-assisted marination enhances flavor diffusion by generating microscopic bubbles that rapidly disrupt meat fibers, allowing marinades to penetrate deeper and faster compared to traditional sous vide techniques. This process significantly improves aroma retention and taste uniformity, making it superior for achieving intense, consistent flavor profiles in meat processing.
Controlled temperature marination
Sous vide marination offers precise control over temperature, ensuring uniform flavor infusion and tenderization throughout the meat by maintaining consistent heat during the process. Cavitation-assisted marination accelerates marinade penetration through ultrasonic waves, but lacks the same level of thermal regulation critical for optimal enzymatic activity and texture development.
Protein denaturation profiles
Sous vide cooking achieves precise protein denaturation by maintaining uniform low temperatures, resulting in tender textures and consistent moisture retention, whereas cavitation-assisted marination induces rapid protein unfolding through ultrasonic waves, enhancing marinade penetration but potentially causing uneven denaturation. Optimizing protein denaturation profiles in meat processing depends on balancing sous vide's thermal precision with cavitation's mechanical effects to achieve desired tenderness and flavor absorption.
Rapid flavor permeation
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control, allowing gradual and uniform flavor permeation through extended low-temperature cooking, while cavitation-assisted marination uses ultrasonic waves to rapidly create microscopic channels in meat fibers, accelerating marinade absorption within minutes. This innovative cavitation technique significantly reduces marination time compared to traditional sous vide methods, enhancing flavor depth without sacrificing texture or moisture retention.
Low-temperature enzymatic action
Sous vide cooking enhances low-temperature enzymatic action by maintaining precise heat levels that activate natural tenderizing enzymes in meat, improving texture without overcooking. In contrast, cavitation-assisted marination accelerates enzyme penetration through ultrasonic waves but may lack the temperature control necessary to optimize enzymatic activity for consistent low-temperature tenderization.
Nanoemulsion marinade delivery
Sous vide ensures precise temperature control for even cooking, while cavitation-assisted marination enhances nanoemulsion penetration, improving flavor absorption and tenderness at the molecular level. Nanoemulsion delivery systems in cavitation-assisted techniques enable uniform dispersion of marinade particles, accelerating infusion compared to traditional sous vide marination.
Sous vide vs Cavitation-assisted marination for meat processing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com