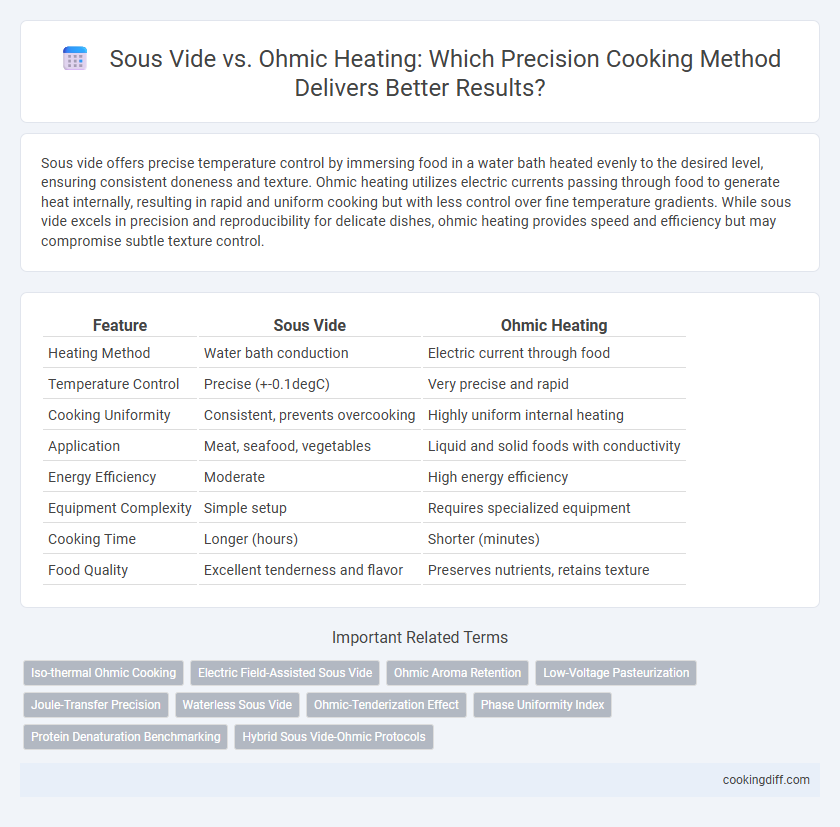
Sous vide offers precise temperature control by immersing food in a water bath heated evenly to the desired level, ensuring consistent doneness and texture. Ohmic heating utilizes electric currents passing through food to generate heat internally, resulting in rapid and uniform cooking but with less control over fine temperature gradients. While sous vide excels in precision and reproducibility for delicate dishes, ohmic heating provides speed and efficiency but may compromise subtle texture control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sous Vide | Ohmic Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Water bath conduction | Electric current through food |
| Temperature Control | Precise (+-0.1degC) | Very precise and rapid |
| Cooking Uniformity | Consistent, prevents overcooking | Highly uniform internal heating |
| Application | Meat, seafood, vegetables | Liquid and solid foods with conductivity |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High energy efficiency |
| Equipment Complexity | Simple setup | Requires specialized equipment |
| Cooking Time | Longer (hours) | Shorter (minutes) |
| Food Quality | Excellent tenderness and flavor | Preserves nutrients, retains texture |
Introduction to Precision Cooking Techniques
Sous vide employs precise temperature control by immersing vacuum-sealed food in a water bath, ensuring uniform cooking with minimal nutrient loss. Ohmic heating uses electrical currents passing through food to generate heat internally for rapid and even cooking, reducing thermal gradients.
Both techniques optimize precision cooking by improving temperature accuracy and consistency, critical for achieving desired textures and flavors. Sous vide excels in low-temperature, long-duration cooking, while ohmic heating offers faster processing suitable for industrial applications.
What is Sous Vide Cooking?
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and immersing it in a water bath maintained at a precise, consistent temperature, ensuring even cooking and enhanced flavor retention. Ohmic heating uses electrical currents passing through the food to generate heat internally, offering rapid and uniform temperature control but less common in home kitchens. Sous vide is preferred for its ability to maintain exact temperatures over long durations, resulting in tender and perfectly cooked dishes.
Understanding Ohmic Heating in the Kitchen
Ohmic heating uses electrical currents passed directly through food to generate heat internally, resulting in rapid and uniform cooking. This method contrasts with traditional sous vide, which relies on circulating water baths to maintain precise temperature control externally.
In the kitchen, ohmic heating offers enhanced energy efficiency and faster cooking times while preserving food texture and nutrients. Understanding its integration with sous vide principles can revolutionize precision cooking by combining consistent heat distribution with quick thermal response.
Temperature Control: Sous Vide vs Ohmic Heating
Sous vide offers exceptional temperature stability by circulating water at a precise and consistent temperature, ensuring uniform cooking. Ohmic heating uses electrical currents to heat food directly, achieving rapid temperature changes but with less precise control over gradual temperature adjustments.
- Sous vide maintains temperature within +-0.1degC - precision is achieved through continuous water circulation and feedback controls.
- Ohmic heating delivers faster heating rates - electrical resistance rapidly converts energy into heat inside the food.
- Sous vide ensures even cooking throughout - gentle temperature control minimizes overcooking and texture degradation.
Temperature control with sous vide excels in consistency, while ohmic heating prioritizes speed, influencing the choice for precise culinary applications.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Sous vide cooking utilizes a water bath heated by an external source, resulting in moderate energy consumption due to heat loss during water circulation. Ohmic heating directly passes electrical current through the food, converting electrical energy into heat internally, which enhances energy efficiency by minimizing transfer losses.
- Sous Vide Energy Use - Requires continuous heating of a large water volume, leading to higher energy expenditure over extended cooking periods.
- Ohmic Heating Efficiency - Converts electrical energy directly into heat within the food matrix, significantly reducing energy waste.
- Comparative Advantage - Ohmic heating offers faster temperature ramp-up and reduced energy consumption, making it more efficient for precision cooking than traditional sous vide methods.
Impact on Food Texture and Flavor
How do sous vide and ohmic heating compare in their impact on food texture and flavor? Sous vide cooking ensures uniform temperature control, resulting in tender textures and enhanced natural flavors due to slow and precise heat application. Ohmic heating rapidly heats food through electrical resistance, which can preserve moisture but may cause uneven texture development compared to sous vide.
Safety Considerations for Home Cooks
Both sous vide and ohmic heating offer precise temperature control, but sous vide is generally safer for home cooks due to its low-temperature water bath that reduces the risk of burns and uneven cooking. Ohmic heating involves electrical currents passing through food, requiring careful equipment handling to prevent electric shock and ensure food safety. Proper sealing of sous vide bags and maintaining consistent temperatures are critical safety practices for preventing bacterial growth during cooking.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Sous vide cooking requires a water bath with precise temperature control, usually maintained by an immersion circulator, whereas ohmic heating utilizes electrical currents passing through the food for rapid and uniform heating. The equipment for sous vide is more accessible and compact, while ohmic heating systems are typically larger and used in industrial food processing.
- Sous vide equipment - Consists mainly of an immersion circulator and a water bath container for controlled, low-temperature cooking.
- Ohmic heating setup - Involves electrodes and power supply to pass current directly through food, requiring specialized industrial-grade machinery.
- Precision and scalability - Sous vide offers home-friendly precision cooking; ohmic heating provides rapid heating for large-scale food production with consistent results.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Maintenance
Sous vide equipment typically requires a moderate initial investment, with precision water baths ranging from $200 to $1,000, while Ohmic heating systems demand higher upfront costs due to advanced electrical components and control systems. Maintenance expenses for sous vide machines are generally lower, focusing mainly on water circulation and temperature control parts, whereas Ohmic systems involve more complex electrode upkeep and calibration.
The cost analysis reveals that sous vide is more accessible for small-scale and home cooks due to affordable equipment and minimal maintenance needs. Ohmic heating, despite its higher investment and upkeep costs, offers superior energy efficiency and faster cooking times, which may offset expenses in commercial or industrial settings. Choosing between the two methods depends significantly on the scale of operation and budget allocation for both initial purchase and ongoing maintenance.
Related Important Terms
Iso-thermal Ohmic Cooking
Iso-thermal Ohmic Cooking provides rapid and uniform heating by passing electric current directly through food, maintaining precise temperature control similar to sous vide but with significantly shorter cooking times. This method enhances nutrient retention and texture by minimizing thermal gradients and allows scalable, energy-efficient precision cooking in commercial applications.
Electric Field-Assisted Sous Vide
Electric field-assisted sous vide utilizes ohmic heating to deliver rapid, uniform cooking by passing an electric current through the food, enhancing temperature control and reducing cooking time compared to traditional sous vide methods. This technique improves nutrient retention and texture precision by minimizing thermal gradients and ensuring consistent heat distribution at the molecular level.
Ohmic Aroma Retention
Ohmic heating enhances aroma retention in precision cooking by heating food through electrical currents, resulting in uniform temperature distribution that prevents volatile aroma loss compared to traditional sous vide methods. This technology preserves the natural flavors and aromatic compounds more effectively, delivering a superior sensory experience in cooked dishes.
Low-Voltage Pasteurization
Sous vide provides precise temperature control ideal for low-voltage pasteurization, maintaining food safety and quality by evenly cooking at consistent low temperatures. Ohmic heating offers rapid, uniform heating through electrical currents, but sous vide ensures superior precision in delicate pasteurization processes with minimal thermal degradation.
Joule-Transfer Precision
Sous vide offers precise temperature control through water immersion and even heat distribution, while ohmic heating leverages Joule-transfer precision by directly passing electrical current through food, enabling rapid and uniform internal heating. Joule-transfer in ohmic heating minimizes temperature gradients and enhances cooking accuracy, outperforming conventional sous vide methods in consistency and speed.
Waterless Sous Vide
Waterless sous vide uses ohmic heating to achieve precise temperature control by directly heating the food through electrical resistance, eliminating the need for water as a heat transfer medium. This method enhances cooking accuracy and speed while reducing energy consumption and preventing water contamination commonly associated with traditional water-based sous vide techniques.
Ohmic-Tenderization Effect
Ohmic heating offers superior precision in cooking by utilizing electrical resistance within food to generate uniform heat, resulting in enhanced Tenderization Effect compared to sous vide methods. This technique allows faster heat penetration and improved texture retention, making it ideal for achieving consistent, high-quality results in precision cooking.
Phase Uniformity Index
Sous vide offers a high Phase Uniformity Index (PUI) by maintaining consistent temperature throughout the cooking vessel, ensuring even heat transfer and precise control over food texture and doneness. In contrast, ohmic heating typically exhibits lower PUI due to localized heating effects, which can result in uneven temperature distribution and less predictable cooking outcomes.
Protein Denaturation Benchmarking
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control for consistent protein denaturation, maintaining optimal texture and juiciness by holding food at exact temperatures often between 55degC and 65degC. Ohmic heating achieves rapid and uniform heating through electrical resistance, but its impact on protein denaturation varies with voltage and conductivity, requiring careful benchmarking to match sous vide's precise control over protein structure transformation.
Sous vide vs Ohmic heating for precision cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com