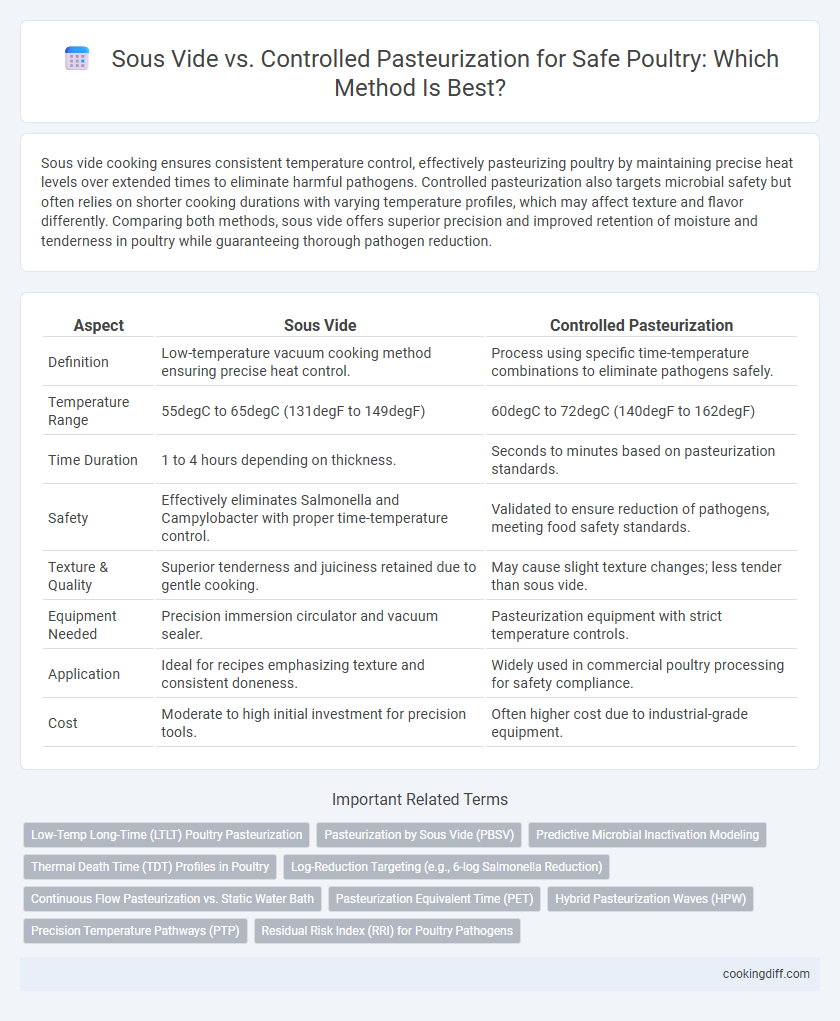
Sous vide cooking ensures consistent temperature control, effectively pasteurizing poultry by maintaining precise heat levels over extended times to eliminate harmful pathogens. Controlled pasteurization also targets microbial safety but often relies on shorter cooking durations with varying temperature profiles, which may affect texture and flavor differently. Comparing both methods, sous vide offers superior precision and improved retention of moisture and tenderness in poultry while guaranteeing thorough pathogen reduction.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Controlled Pasteurization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Low-temperature vacuum cooking method ensuring precise heat control. | Process using specific time-temperature combinations to eliminate pathogens safely. |
| Temperature Range | 55degC to 65degC (131degF to 149degF) | 60degC to 72degC (140degF to 162degF) |
| Time Duration | 1 to 4 hours depending on thickness. | Seconds to minutes based on pasteurization standards. |
| Safety | Effectively eliminates Salmonella and Campylobacter with proper time-temperature control. | Validated to ensure reduction of pathogens, meeting food safety standards. |
| Texture & Quality | Superior tenderness and juiciness retained due to gentle cooking. | May cause slight texture changes; less tender than sous vide. |
| Equipment Needed | Precision immersion circulator and vacuum sealer. | Pasteurization equipment with strict temperature controls. |
| Application | Ideal for recipes emphasizing texture and consistent doneness. | Widely used in commercial poultry processing for safety compliance. |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment for precision tools. | Often higher cost due to industrial-grade equipment. |
Understanding Sous Vide: Precision Cooking Explained
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing poultry and cooking it at precise, consistent temperatures, typically between 130degF and 165degF, to ensure safety and optimal texture. This method allows for even heat distribution, which effectively reduces pathogens while preserving moisture and flavor for tender, juicy results.
Controlled pasteurization in sous vide relies on maintaining specific time-temperature combinations, such as 145degF for 9.2 minutes, to achieve safe levels of bacterial reduction in poultry. This precision cooking technique surpasses traditional methods by minimizing overcooking risks and enhancing food safety through scientifically validated guidelines.
What is Controlled Pasteurization in Poultry Preparation?
Controlled pasteurization in poultry preparation involves heating the meat to a specific temperature for a precise duration to eliminate harmful bacteria while preserving texture and juiciness. This method ensures food safety by targeting pathogens without overcooking, contrasting with standard high-heat cooking techniques.
- Precise Temperature Control - Poultry is cooked at temperatures typically between 130degF and 160degF to achieve pasteurization without compromising quality.
- Time-Temperature Relationship - The safety is ensured by maintaining the temperature for a set time, often several minutes, sufficient to reduce bacterial load effectively.
- Texture and Flavor Preservation - Controlled pasteurization minimizes moisture loss, resulting in tender, juicy poultry unlike traditional cooking that may cause dryness.
Key Differences: Sous Vide vs. Controlled Pasteurization
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control, typically between 54degC to 65degC, allowing poultry to cook evenly while preserving moisture and texture. Controlled pasteurization involves holding poultry at specific temperatures for designated times to eliminate pathogens, with regulatory standards often requiring minimum temperatures such as 60degC for 27.5 minutes. Sous vide offers flexibility in doneness and texture, whereas controlled pasteurization prioritizes stringent safety thresholds validated by scientific time-temperature kill curves.
Food Safety Science: Pathogen Reduction in Poultry
Sous vide cooking provides precise temperature control crucial for effective pathogen reduction in poultry, ensuring consistent pasteurization while preserving moisture and texture. Controlled pasteurization relies on established time-temperature combinations to inactivate harmful bacteria such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, central to food safety science in poultry processing.
- Sous vide temperature accuracy - Maintains steady temperatures typically between 55degC and 65degC to effectively reduce pathogens over extended cooking times.
- Controlled pasteurization protocols - Utilize validated time-temperature profiles to guarantee microbial safety without overcooking poultry meat.
- Pathogen reduction efficacy - Both methods achieve significant log reductions of Salmonella and Campylobacter when applied under recommended conditions.
Temperature and Time: Critical Factors for Safe Poultry
| Method | Temperature Range | Time Required | Safety Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sous Vide | 55degC to 65degC (131degF to 149degF) | 1 to 4 hours depending on thickness | Achieves pasteurization by holding consistent temperature for extended time, ensuring pathogen destruction and meat quality preservation |
| Controlled Pasteurization | 70degC to 75degC (158degF to 167degF) | 15 to 30 minutes | Kills harmful bacteria quickly through higher heat, potentially affecting texture but guaranteeing food safety |
Texture and Flavor: Culinary Outcomes Compared
Sous vide cooking enhances poultry texture by maintaining consistent low temperatures, resulting in tender, evenly cooked meat. Controlled pasteurization ensures safety but often leads to firmer texture and less pronounced natural flavors.
- Sous vide texture - Produces juicier, more tender poultry by gently breaking down muscle fibers over extended cooking times.
- Controlled pasteurization texture - Can cause meat to become denser and less moist due to higher heat exposure.
- Flavor profile - Sous vide preserves the natural juices and delicate flavors, while pasteurization often diminishes subtle taste nuances.
Choosing sous vide maximizes culinary quality by balancing food safety with superior texture and flavor retention.
Equipment and Accessibility: What Home Cooks Need
Sous vide requires precise immersion circulators that maintain consistent temperatures, making it accessible for home cooks with moderate investment. Controlled pasteurization often relies on commercial-grade equipment, limiting its practicality for everyday kitchen use. Basic sous vide devices are widely available and user-friendly, offering a safer poultry cooking method through accurate temperature control.
Regulatory Standards: Guidelines for Poultry Safety
How do regulatory standards compare between sous vide and controlled pasteurization for ensuring poultry safety? Regulatory guidelines from the USDA and FDA specify precise time-temperature combinations for both methods to effectively eliminate pathogens like Salmonella and Campylobacter. Sous vide requires strict adherence to these standards, often involving lower temperatures held for longer periods, while controlled pasteurization typically uses higher temperatures for shorter durations to achieve safe poultry consumption.
Common Myths About Sous Vide and Pasteurization
Common myths suggest that sous vide cooking is less effective than controlled pasteurization for ensuring poultry safety, but both methods rely on precise temperature control to eliminate harmful pathogens like Salmonella. Sous vide achieves pasteurization by maintaining poultry at a specific low temperature over an extended period, which can be as safe as traditional methods when done correctly.
Misconceptions often arise from the belief that sous vide's low temperatures are insufficient to kill bacteria; however, time and temperature combinations are scientifically validated to achieve pasteurization. Controlled pasteurization involves heating poultry at higher temperatures for shorter times, whereas sous vide uses lower temperatures for longer periods to reach the same microbial safety standards. Both techniques must follow stringent guidelines to prevent foodborne illness and ensure safe poultry consumption.
Related Important Terms
Low-Temp Long-Time (LTLT) Poultry Pasteurization
Low-Temp Long-Time (LTLT) poultry pasteurization using sous vide ensures precise temperature control, effectively eliminating pathogens like Salmonella while preserving meat texture and juiciness. Compared to traditional controlled pasteurization, sous vide LTLT offers enhanced safety by maintaining consistent heat penetration throughout the poultry, reducing the risk of undercooked areas.
Pasteurization by Sous Vide (PBSV)
Pasteurization by Sous Vide (PBSV) ensures safe poultry by precisely controlling temperature and time, effectively eliminating harmful pathogens while retaining moisture and texture. This method offers superior uniformity compared to traditional controlled pasteurization, reducing the risk of undercooked areas and enhancing food safety standards in poultry processing.
Predictive Microbial Inactivation Modeling
Predictive microbial inactivation modeling in sous vide cooking allows precise time-temperature control to achieve safe poultry by targeting specific pathogen reduction levels, often outperforming traditional controlled pasteurization methods in consistency. These models integrate thermal death kinetics data to optimize pasteurization parameters, ensuring poultry safety while preserving texture and flavor.
Thermal Death Time (TDT) Profiles in Poultry
Thermal Death Time (TDT) profiles are critical for ensuring the safety of poultry in both sous vide and controlled pasteurization methods, with sous vide relying on precise temperature control and extended cooking times to achieve pathogen reduction without compromising texture. Controlled pasteurization typically uses higher temperatures for shorter durations, while sous vide protocols optimize lower temperatures maintained longer to inactivate Salmonella and Campylobacter based on validated TDT data.
Log-Reduction Targeting (e.g., 6-log Salmonella Reduction)
Sous vide cooking achieves precise temperature control to meet specific log-reduction targets, such as a 6-log reduction of Salmonella in poultry, ensuring microbial safety without overcooking. Controlled pasteurization similarly targets bacterial inactivation but relies on established thermal death time parameters, with sous vide offering enhanced consistency through uniform heat distribution.
Continuous Flow Pasteurization vs. Static Water Bath
Continuous flow pasteurization offers faster processing and consistent temperature control for safe poultry by rapidly heating and cooling meat in a sealed environment, whereas static water bath sous vide relies on prolonged, precise low-temperature cooking for even heat distribution and tender texture. Continuous flow systems enhance microbial safety through rapid temperature elevation, while static water baths optimize flavor and moisture retention during sous vide cooking.
Pasteurization Equivalent Time (PET)
Sous vide cooking achieves precise Pasteurization Equivalent Time (PET) control, ensuring poultry reaches the exact temperature and duration required to eliminate pathogens without overcooking. Controlled pasteurization relies on standardized PET values to guarantee safety, but sous vide's exact temperature management enhances both microbial inactivation and meat texture retention.
Hybrid Pasteurization Waves (HPW)
Hybrid Pasteurization Waves (HPW) combine sous vide precision with controlled pasteurization techniques to ensure safe poultry by optimizing time-temperature profiles that effectively eliminate pathogens without compromising texture. This method enhances microbial safety by integrating low-temperature long-time cooking with targeted thermal pulses, reducing the risk of overcooking while maintaining the poultry's juiciness and tenderness.
Precision Temperature Pathways (PTP)
Precision Temperature Pathways (PTP) in sous vide cooking enable exact control of temperature and time, resulting in thorough pasteurization of poultry while preserving texture and moisture. This method ensures safe poultry by achieving microbial inactivation standards more consistently than conventional controlled pasteurization techniques.
Sous vide vs controlled pasteurization for safe poultry. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com