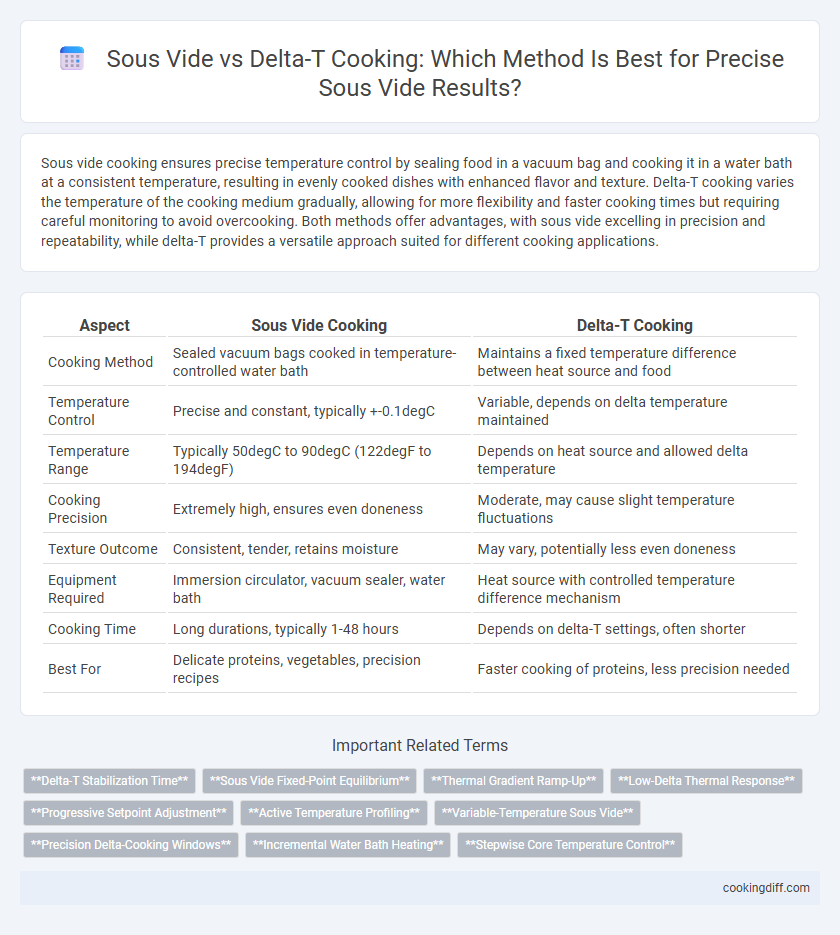
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control by sealing food in a vacuum bag and cooking it in a water bath at a consistent temperature, resulting in evenly cooked dishes with enhanced flavor and texture. Delta-T cooking varies the temperature of the cooking medium gradually, allowing for more flexibility and faster cooking times but requiring careful monitoring to avoid overcooking. Both methods offer advantages, with sous vide excelling in precision and repeatability, while delta-T provides a versatile approach suited for different cooking applications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide Cooking | Delta-T Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Sealed vacuum bags cooked in temperature-controlled water bath | Maintains a fixed temperature difference between heat source and food |
| Temperature Control | Precise and constant, typically +-0.1degC | Variable, depends on delta temperature maintained |
| Temperature Range | Typically 50degC to 90degC (122degF to 194degF) | Depends on heat source and allowed delta temperature |
| Cooking Precision | Extremely high, ensures even doneness | Moderate, may cause slight temperature fluctuations |
| Texture Outcome | Consistent, tender, retains moisture | May vary, potentially less even doneness |
| Equipment Required | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, water bath | Heat source with controlled temperature difference mechanism |
| Cooking Time | Long durations, typically 1-48 hours | Depends on delta-T settings, often shorter |
| Best For | Delicate proteins, vegetables, precision recipes | Faster cooking of proteins, less precision needed |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Delta-T Cooking
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a temperature-controlled water bath, ensuring even and precise heat distribution. This method preserves moisture and enhances flavor by cooking food slowly at low temperatures.
Delta-T cooking differs by focusing on maintaining a consistent temperature difference between the cooking medium and the food, which allows for faster heating and improved texture control. Unlike traditional sous vide, Delta-T adjusts the heat dynamically based on the core and water temperatures, resulting in more efficient cooking. This technique is particularly advantageous for chefs seeking precise temperature management with reduced cooking times.
How Sous Vide Works: Precision Temperature Control
| Sous Vide Precision | Sous vide uses immersion circulators to maintain water at a consistent target temperature, ensuring even and precise cooking by controlling heat within +-0.1degC. This exact temperature control cooks food evenly, preventing overcooking and preserving juiciness. |
| Delta-T Cooking | Delta-T cooking regulates the temperature difference between the cooking medium and the food, cooking at a fixed gradient to avoid overcooking but with less temperature precision than sous vide. |
| Comparison | Sous vide offers superior control for delicate textures by immersing food in a precisely heated water bath, while delta-T relies on temperature differentials for gradual heat transfer, making sous vide more reliable for consistent doneness. |
The Delta-T Cooking Method Explained
Delta-T cooking is a precision technique that relies on maintaining a constant temperature difference between the cooking medium and the core of the food, optimizing heat transfer for even cooking. Unlike traditional sous vide, which cooks food at a fixed temperature, Delta-T dynamically adjusts to prevent overcooking and retains better texture and moisture.
- Temperature Differential Control - Delta-T method controls the temperature gradient to gently cook food from the outside in.
- Enhanced Texture Preservation - It minimizes overcooking by adapting heat delivery according to the food's core temperature.
- Energy Efficiency - Delta-T cooking often uses less energy by avoiding constant high temperatures typical in sous vide baths.
This method offers a sophisticated alternative to sous vide, improving cooking precision and food quality.
Comparing Temperature Stability: Sous Vide vs Delta-T
Sous vide cooking maintains a precise, constant temperature by immersing food in a water bath controlled by a digital thermostat, ensuring even cooking with minimal temperature fluctuations. Delta-T cooking, in contrast, uses a temperature gradient method where the food's internal temperature gradually rises at a constant difference from the water temperature, requiring continuous temperature adjustment.
Temperature stability in sous vide leads to highly consistent results, ideal for delicate proteins and precise doneness levels. Delta-T offers flexibility and faster cooking times but demands careful monitoring to avoid exceeding desired temperatures, impacting texture and moisture retention.
Cooking Time and Efficiency Differences
Sous vide cooking maintains a precise water bath temperature, ensuring consistent results but often requires longer cooking times compared to delta-T cooking. Delta-T cooking utilizes a temperature gradient to speed up heat transfer, reducing overall cooking time while balancing efficiency and texture preservation.
- Consistent Temperature Control - Sous vide uses a stable water bath temperature for even cooking throughout.
- Faster Heat Transfer - Delta-T cooking leverages a temperature difference to accelerate cooking processes.
- Efficiency in Time - Delta-T methods typically reduce cooking time by optimizing thermal gradients without sacrificing quality.
Impact on Food Texture and Flavor
How does sous vide compare to delta-T cooking in terms of impact on food texture and flavor? Sous vide offers precise temperature control, resulting in evenly cooked food with enhanced moisture retention and tender texture. Delta-T cooking gradually applies heat, which can create more complex Maillard reactions and layered flavors but may produce less consistent texture.
Safety Considerations for Each Technique
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control, maintaining food at safe levels to minimize bacterial growth during extended cooking times. The vacuum-sealed environment further reduces contamination risk by limiting exposure to oxygen and airborne pathogens.
Delta-T cooking, utilizing a controlled temperature difference, requires careful monitoring to prevent unsafe temperature fluctuations that might allow harmful bacteria to develop. Proper calibration of equipment and adherence to USDA guidelines are essential to ensure food safety with this method.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Sous vide cooking requires precise temperature-controlled water baths often using immersion circulators, ensuring consistent heat distribution. Delta-T cooking relies on maintaining a specific temperature difference between the cooking medium and the food, necessitating precise monitoring tools but less specialized equipment. Sous vide setups typically involve sealed vacuum bags and immersion devices, whereas delta-T methods may use conventional ovens or water baths with added temperature probes for control.
Ideal Foods for Sous Vide vs Delta-T Cooking
Sous vide excels in cooking delicate proteins like fish and eggs by maintaining precise temperature control, ensuring even doneness without overcooking. Delta-T cooking is better suited for tougher cuts such as beef brisket or pork shoulder, where gradual temperature increases optimize collagen breakdown for tender results.
- Fish and seafood - Sous vide preserves texture and moisture by cooking at low, stable temperatures.
- Tough meats - Delta-T cooking slowly raises temperature, enhancing tenderness through controlled collagen melting.
- Eggs and custards - Sous vide enables precise temperature control crucial for perfect consistency and safety.
Related Important Terms
Delta-T Stabilization Time
Delta-T cooking offers faster delta-T stabilization time compared to traditional sous vide by adjusting the temperature difference between the water bath and the food, resulting in more efficient heat penetration and reduced overall cooking duration. This method optimizes cooking gradients, enhancing precision for delicate proteins while maintaining food safety standards.
Sous Vide Fixed-Point Equilibrium
Sous vide fixed-point equilibrium maintains a precise, constant temperature by submerging food in a water bath, ensuring even doneness and optimal texture through controlled heat transfer. In contrast, Delta-T cooking allows temperature gradients between the heat source and food, resulting in less uniform cooking and potential over- or under-cooked areas.
Thermal Gradient Ramp-Up
Sous vide cooking ensures precise Thermal Gradient Ramp-Up by maintaining a constant, low-temperature water bath that evenly heats food from edge to center, minimizing overcooking. In contrast, delta-T cooking uses a controlled temperature difference to accelerate heat transfer, resulting in a faster but less uniform thermal gradient that can risk uneven doneness.
Low-Delta Thermal Response
Sous vide cooking maintains a precise, low-delta thermal response by holding food at a consistent temperature within +-0.1degC, ensuring even heat distribution and optimal texture. In contrast, delta-T cooking involves a controlled temperature difference between the cooking medium and food, which can result in less stable temperature regulation and variable cooking outcomes due to fluctuating thermal gradients.
Progressive Setpoint Adjustment
Progressive setpoint adjustment in sous vide cooking involves gradually raising the water temperature in controlled increments to ensure even heat distribution and precise doneness. Unlike delta-T cooking, which maintains a constant temperature differential between the food and the water, this method minimizes thermal gradients, enhancing texture and moisture retention.
Active Temperature Profiling
Sous vide cooking maintains a precise, consistent water bath temperature to ensure even doneness, while delta-T cooking actively adjusts the temperature based on the food's core temperature, optimizing heat transfer for faster and more uniform cooking. Active temperature profiling in delta-T cooking reduces overcooking risk by dynamically modulating heat input, unlike the static temperature control in sous vide methods.
Variable-Temperature Sous Vide
Variable-Temperature Sous Vide offers precise control over cooking by adjusting water temperature in response to real-time thermal gradients, optimizing heat transfer and reducing cooking times compared to traditional delta-T methods. This dynamic approach enhances texture and flavor by maintaining ideal temperatures that adapt to the specific thermal properties of each ingredient.
Precision Delta-Cooking Windows
Sous vide offers unparalleled precision delta-cooking windows by maintaining a consistent water bath temperature, ensuring exact food doneness through minimal temperature variance. Delta-T cooking uses a temperature differential between the food and cooking environment, providing a controlled but less stable heat transfer that can lead to wider temperature fluctuations compared to sous vide.
Incremental Water Bath Heating
Incremental water bath heating in sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control by gradually raising the water temperature, maintaining consistent heat transfer to the food. In contrast, delta-T cooking relies on a constant temperature difference, which can result in uneven cooking and less accurate temperature management.
Sous vide vs delta-T cooking for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com