Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control by immersing vacuum-sealed food in a water bath maintained at a consistent temperature, ensuring even cooking throughout. Delta-T cooking adjusts the temperature difference between the cooking medium and the food, allowing for gentle and gradual heat transfer that prevents overcooking and preserves texture. Comparing both methods, sous vide provides unmatched accuracy for time-sensitive recipes, while Delta-T is preferred for its ability to maintain quality in thicker cuts by controlling the temperature gradient.
Table of Comparison
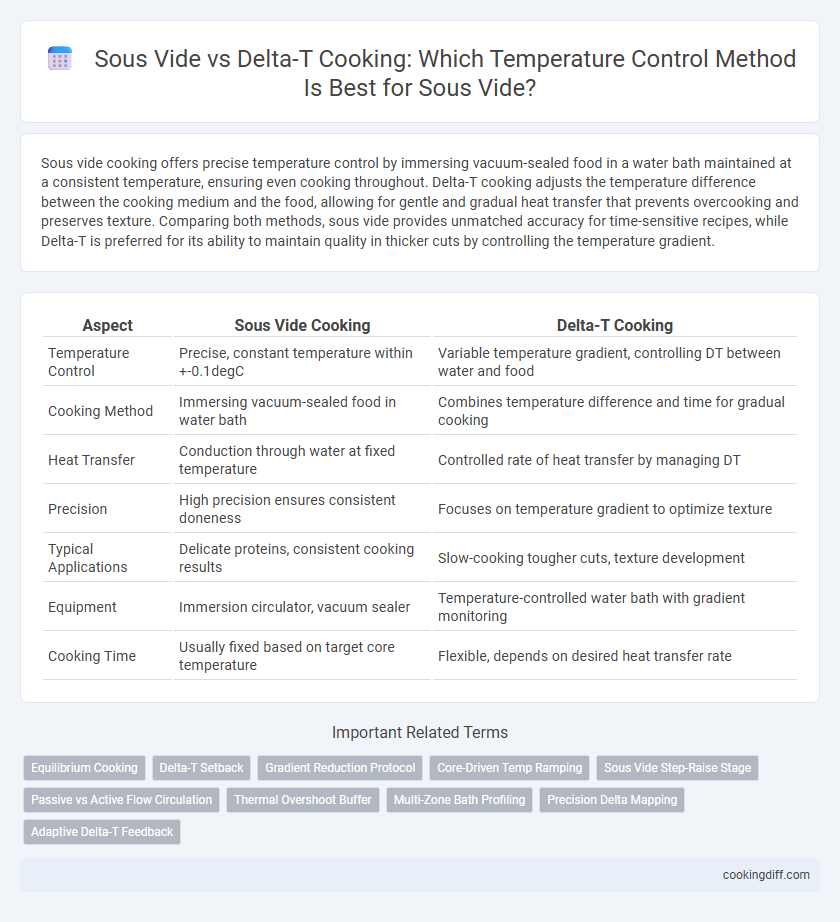
| Aspect | Sous Vide Cooking | Delta-T Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Precise, constant temperature within +-0.1degC | Variable temperature gradient, controlling DT between water and food |
| Cooking Method | Immersing vacuum-sealed food in water bath | Combines temperature difference and time for gradual cooking |
| Heat Transfer | Conduction through water at fixed temperature | Controlled rate of heat transfer by managing DT |
| Precision | High precision ensures consistent doneness | Focuses on temperature gradient to optimize texture |
| Typical Applications | Delicate proteins, consistent cooking results | Slow-cooking tougher cuts, texture development |
| Equipment | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer | Temperature-controlled water bath with gradient monitoring |
| Cooking Time | Usually fixed based on target core temperature | Flexible, depends on desired heat transfer rate |
Introduction: Understanding Sous Vide and Delta-T Cooking
| Sous vide | A cooking method involving vacuum-sealed food submerged in a water bath with precise temperature control, typically held constant throughout the cooking process. |
| Delta-T cooking | A temperature control technique where the difference between the water bath temperature and the core food temperature is maintained at a set value, allowing slower, more even heat transfer. |
| Temperature control comparison | Sous vide uses fixed temperature settings focused on exact doneness, while Delta-T applies a gradual heating approach based on temperature gradients to optimize texture and moisture retention. |
What is Sous Vide Cooking?
Sous vide cooking is a precise temperature-controlled method where food is vacuum-sealed in a bag and submerged in a water bath to cook evenly. This technique ensures consistent doneness by maintaining a stable temperature throughout the cooking process.
Compared to Delta-T cooking, which gradually raises the temperature allowing for slow heat transfer, sous vide offers exact temperature control, preventing overcooking. The sous vide method perfectly retains moisture, texture, and flavor by cooking food at a precise and constant temperature. Professional chefs and home cooks use sous vide to achieve restaurant-quality results with minimal effort.
What is Delta-T Cooking?
Delta-T cooking is a precise temperature control method where the difference between the food's core temperature and the cooking environment is carefully regulated. This technique ensures even cooking and optimal texture by gradually bringing food to the desired doneness.
- Temperature Differential - Delta-T cooking maintains a fixed temperature difference, typically a few degrees, between the food's internal temperature and the cooking medium.
- Even Heat Transfer - By controlling the temperature gradient, Delta-T cooking promotes uniform heat distribution, avoiding overcooking or undercooking.
- Comparison with Sous Vide - Unlike traditional sous vide, which holds a constant water bath temperature, Delta-T dynamically adjusts to the food's thermal response for precise doneness.
Key Differences in Temperature Control
Sous vide cooking maintains a constant, precise water temperature by circulating water around a sealed bag, ensuring even cooking throughout. Delta-T cooking uses a controlled temperature gradient where the cooking medium gradually increases to the target temperature, reducing overcooking risks for delicate proteins. The key difference in temperature control lies in sous vide's stable environment versus Delta-T's gradual, dynamic temperature adjustment.
Precision and Consistency: Sous Vide vs Delta-T
How does temperature control precision compare between Sous Vide and Delta-T cooking methods? Sous vide cooking maintains a constant water bath temperature, ensuring highly precise and consistent cooking results by eliminating temperature fluctuations. In contrast, Delta-T cooking adjusts temperature gradually, which can lead to less exact control but allows for gentle cooking transitions and reduced thermal stress on food.
Equipment Required for Each Method
Sous vide cooking requires a precision immersion circulator to maintain consistent temperature within a water bath, ensuring exact heat control around the food. This method typically utilizes vacuum-sealed bags to enhance heat transfer and flavor retention.
Delta-T cooking relies on a temperature differential between the cooking environment and the food's core temperature, often using a standard oven or water bath with precise temperature monitoring devices. Advanced thermometers or probes are essential in Delta-T to continually measure and adjust cooking parameters for optimal results.
Cooking Times and Temperature Ranges
Sous vide cooking maintains a precise and consistent temperature, typically ranging from 120degF to 190degF, allowing for extended cooking times that evenly tenderize food without overcooking. Delta-T cooking uses a temperature differential approach, usually involving a difference of 10-20degF between the cooking medium and the target food temperature, resulting in faster cook times but less precise control.
Cooking times for sous vide can extend from one hour up to 72 hours, making it ideal for tough cuts of meat requiring long, low-temperature cooking. Delta-T achieves quicker results, often within 1 to 3 hours, but may sacrifice some texture uniformity due to variable temperature gradients during the process.
Food Safety Considerations
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control to minimize harmful bacterial growth, ensuring food safety through consistent pasteurization. Delta-T cooking adjusts temperature gradually, which may increase the risk of pathogen survival if not carefully monitored.
- Sous vide's stable low-temperature environment - ensures uniform heat penetration, reducing the chance of bacterial contamination.
- Delta-T's variable temperature approach - can create temperature zones that allow pathogens to survive if the cooking process is not tightly controlled.
- Accurate temperature monitoring is critical - for both methods to guarantee food is held long enough at safe temperatures for pathogen destruction.
Best Use Cases for Sous Vide and Delta-T Cooking
Sous vide cooking excels in precise temperature control for delicate proteins such as fish and eggs, ensuring even doneness and retention of moisture. Delta-T cooking is ideal for tougher cuts of meat, enabling gradual temperature increases that break down connective tissues without overcooking. Both methods optimize culinary results by targeting temperature management tailored to specific food textures and cooking goals.
Related Important Terms
Equilibrium Cooking
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control by holding food at a constant equilibrium temperature, ensuring even doneness throughout. In contrast, Delta-T cooking uses a dynamic temperature differential between the food and water bath to accelerate cooking while still preventing overcooking by monitoring this gradient.
Delta-T Setback
Delta-T cooking enhances temperature control by gradually adjusting the cooking water temperature in relation to the food's core temperature, allowing precise heat penetration without overcooking. The Delta-T Setback technique minimizes thermal gradients, ensuring consistent doneness and improved texture compared to traditional sous vide, which maintains a constant bath temperature.
Gradient Reduction Protocol
Sous vide cooking maintains a constant water bath temperature for precise temperature control, while Delta-T cooking employs the Gradient Reduction Protocol to gradually decrease the temperature difference between the cooking medium and the food, minimizing thermal stress and preserving texture. The Gradient Reduction Protocol in Delta-T ensures even heat penetration by controlling temperature gradients, improving tenderness and consistency compared to the static environment of sous vide.
Core-Driven Temp Ramping
Sous vide cooking maintains a precise, constant temperature by immersing food in a water bath, ensuring uniform doneness with core-driven temperature control. In contrast, Delta-T cooking gradually increases the temperature difference between the core and environment, promoting gentle heat transfer and minimizing moisture loss while allowing for controlled temperature ramping.
Sous Vide Step-Raise Stage
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control by gradually increasing water temperature in the step-raise stage, ensuring even heat distribution and tender results. This contrasts with Delta-T cooking, which adjusts temperature dynamically but may risk uneven cooking due to less consistent heat application.
Passive vs Active Flow Circulation
Sous vide employs active flow circulation using a precision immersion circulator to maintain consistent temperature and evenly distribute heat throughout the water bath, ensuring precise cooking results. In contrast, Delta-T cooking relies on passive flow circulation by gradually raising the internal food temperature within a narrow differential, reducing thermal stress but requiring careful monitoring to avoid uneven heat distribution.
Thermal Overshoot Buffer
Sous vide cooking excels in precise temperature control by maintaining a constant set temperature, minimizing thermal overshoot through an advanced feedback loop that stabilizes water bath heat. In contrast, Delta-T cooking uses a temperature differential approach, which inherently requires a thermal overshoot buffer to prevent food surface temperatures from exceeding target levels, leading to less exact thermal regulation.
Multi-Zone Bath Profiling
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control by maintaining a consistent water bath temperature, while Delta-T cooking optimizes heat transfer through a controlled temperature gradient between the bath and the food. Multi-Zone Bath Profiling enhances Delta-T cooking efficiency by creating distinct temperature zones within the bath, allowing customized cooking profiles that improve texture and doneness accuracy for complex dishes.
Precision Delta Mapping
Sous vide cooking offers consistent temperature control by immersing food in a water bath set to a precise temperature, whereas Delta-T cooking relies on the temperature difference between the cooking medium and the food, adjusting heat based on dynamic changes. Precision Delta Mapping enhances Delta-T cooking by continuously monitoring the exact temperature gradient, resulting in more accurate thermal regulation and uniform cooking outcomes.
Sous vide vs Delta-T cooking for temperature control. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com