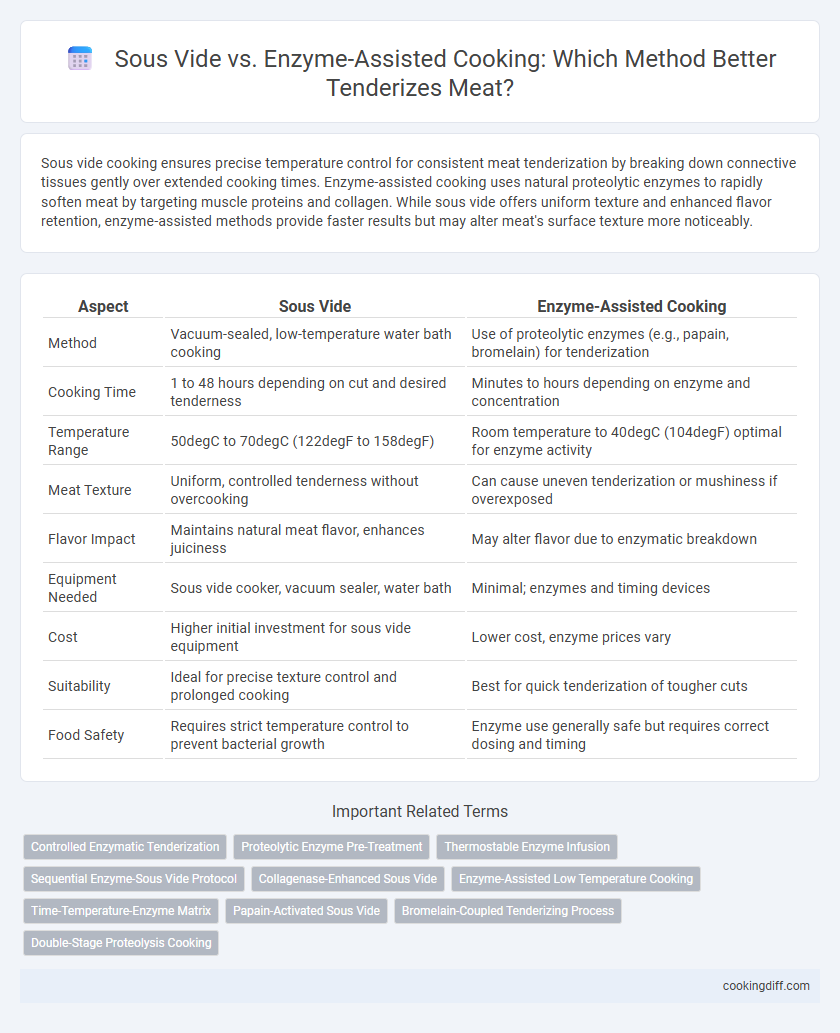
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control for consistent meat tenderization by breaking down connective tissues gently over extended cooking times. Enzyme-assisted cooking uses natural proteolytic enzymes to rapidly soften meat by targeting muscle proteins and collagen. While sous vide offers uniform texture and enhanced flavor retention, enzyme-assisted methods provide faster results but may alter meat's surface texture more noticeably.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Enzyme-Assisted Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Vacuum-sealed, low-temperature water bath cooking | Use of proteolytic enzymes (e.g., papain, bromelain) for tenderization |
| Cooking Time | 1 to 48 hours depending on cut and desired tenderness | Minutes to hours depending on enzyme and concentration |
| Temperature Range | 50degC to 70degC (122degF to 158degF) | Room temperature to 40degC (104degF) optimal for enzyme activity |
| Meat Texture | Uniform, controlled tenderness without overcooking | Can cause uneven tenderization or mushiness if overexposed |
| Flavor Impact | Maintains natural meat flavor, enhances juiciness | May alter flavor due to enzymatic breakdown |
| Equipment Needed | Sous vide cooker, vacuum sealer, water bath | Minimal; enzymes and timing devices |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for sous vide equipment | Lower cost, enzyme prices vary |
| Suitability | Ideal for precise texture control and prolonged cooking | Best for quick tenderization of tougher cuts |
| Food Safety | Requires strict temperature control to prevent bacterial growth | Enzyme use generally safe but requires correct dosing and timing |
Introduction to Meat Tenderization Techniques
Meat tenderization techniques enhance texture and flavor by breaking down muscle fibers and connective tissues. Sous vide and enzyme-assisted methods offer distinct approaches to achieving optimal tenderness.
- Sous Vide Cooking - Utilizes precise temperature control over extended cooking times to gently break down collagen without overcooking the meat.
- Enzyme-Assisted Tenderization - Employs natural proteolytic enzymes like papain and bromelain to chemically degrade muscle proteins for faster tenderizing.
- Comparison of Methods - Sous vide provides consistent texture and moisture retention, while enzymes accelerate tenderization but may alter flavor and texture if not managed carefully.
These techniques represent innovative strategies in modern culinary science to improve meat palatability.
Understanding Sous Vide: Process and Benefits
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing meat and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath at low temperatures for extended periods, ensuring even heat distribution and moisture retention. This method preserves the meat's natural flavors and texture while enhancing tenderness without the risk of overcooking.
Enzyme-assisted cooking uses proteolytic enzymes like papain or bromelain to break down muscle fibers, accelerating tenderization chemically. Sous vide offers greater consistency and control over texture by maintaining steady temperatures, unlike enzyme treatments which can result in uneven softness or mushiness. Combining sous vide with enzyme treatments can optimize tenderness while preserving meat integrity, but sous vide alone is prized for its gentle, uniform cooking process and flavor enhancement.
What is Enzyme-Assisted Cooking?
Enzyme-assisted cooking involves the use of natural enzymes such as papain, bromelain, or ficin to break down muscle fibers and connective tissues in meat, enhancing tenderness and flavor. These enzymes are typically applied as marinades or injected into the meat before cooking to accelerate the tenderization process.
Unlike sous vide, which relies on precise temperature control over extended periods to achieve tenderness, enzyme-assisted cooking offers a biochemical approach by directly altering protein structures. This method can be combined with sous vide techniques for improved texture and accelerated cooking times in meat preparation.
Key Differences Between Sous Vide and Enzyme-Assisted Methods
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Enzyme-Assisted Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Low-temperature water bath cooking with precise time control | Use of proteolytic enzymes like papain or bromelain to break down proteins |
| Tenderization Mechanism | Gradual collagen breakdown and muscle fiber softening through heat | Direct enzymatic degradation of muscle proteins for rapid tenderization |
| Timeframe | Typically requires 1 to 48 hours depending on cut | Shorter duration of minutes to a few hours due to enzyme activity |
| Flavor and Texture Impact | Preserves natural flavors and yields uniform texture | May alter flavor due to enzyme residues and can result in uneven texture |
Meat Tenderization Results: Texture and Flavor Comparison
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, resulting in consistently tender meat with enhanced natural flavors. Enzyme-assisted cooking uses proteolytic enzymes to break down muscle fibers, which can improve tenderness but may alter texture and introduce enzymatic flavors.
- Texture Consistency - Sous vide produces uniform tenderness throughout the meat, while enzyme-assisted methods can create variable textures depending on enzyme concentration and application time.
- Flavor Retention - Sous vide preserves the meat's intrinsic flavors by avoiding high-heat cooking, whereas enzymes may impact flavor by generating slight enzymatic notes.
- Cooking Time - Sous vide requires longer cooking durations at controlled temperatures, while enzyme-assisted tenderization is typically faster but may require precise control to avoid over-tenderizing.
Time and Temperature Considerations
Sous vide cooking precisely controls temperature, typically between 55degC and 65degC for several hours, allowing collagen to break down gently and evenly in meat. Enzyme-assisted tenderization relies on proteolytic enzymes like papain or bromelain that act quickly at moderate temperatures, generally below 50degC, to prevent enzyme denaturation. Time and temperature synergy in sous vide ensures consistent texture, while enzyme methods require careful monitoring to avoid over-tenderization or mushy meat.
Food Safety: Pasteurization and Microbial Control
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control that achieves effective pasteurization, significantly reducing microbial load and enhancing food safety in meat tenderization. Enzyme-assisted cooking relies on proteolytic enzymes to break down muscle fibers but does not inherently provide microbial control, necessitating additional safety measures. Combining sous vide with enzyme treatment can optimize tenderness while maintaining strict pasteurization standards to prevent foodborne pathogens.
Suitability for Different Cuts of Meat
Sous vide is highly effective for tenderizing tougher cuts by precise temperature control without overcooking, while enzyme-assisted cooking excels in breaking down muscle fibers quickly, suitable for both tough and delicate cuts. Each method offers unique benefits depending on the meat's texture and desired tenderness level.
- Sous vide suits tough cuts - It gradually tenderizes and maintains moisture in cuts like brisket and chuck through controlled low-temperature cooking.
- Enzyme-assisted cooking is versatile - It can tenderize both tough and tender cuts by enzymatically breaking down proteins, ideal for short cooking times.
- Sous vide preserves texture - It retains the natural structure of delicate cuts, preventing mushiness common with enzymatic methods.
Equipment and Cost Analysis
How do the equipment and cost demands of sous vide compare to enzyme-assisted cooking for meat tenderization? Sous vide requires precise immersion circulators and vacuum sealers, which represent a higher initial investment but offer consistent temperature control for tenderization. Enzyme-assisted cooking, relying on marinades and minimal equipment, presents a lower upfront cost but may lack the precise control that sous vide systems provide.
Related Important Terms
Controlled Enzymatic Tenderization
Controlled enzymatic tenderization in sous vide cooking enhances meat texture by precisely regulating temperature and time to activate endogenous enzymes like calpains and cathepsins, promoting collagen breakdown and muscle fiber relaxation. This method prevents over-tenderization and preserves juiciness, offering superior consistency compared to traditional enzyme-assisted techniques with exogenous proteases.
Proteolytic Enzyme Pre-Treatment
Proteolytic enzyme pre-treatment in meat tenderization enhances the effectiveness of sous vide cooking by breaking down muscle proteins before precise low-temperature cooking, resulting in superior texture and juiciness. Combining enzyme-assisted marination with sous vide immersion optimizes collagen degradation and maintains moisture retention compared to sous vide alone.
Thermostable Enzyme Infusion
Thermostable enzyme infusion in sous vide cooking enhances meat tenderization by maintaining enzyme activity at precise low temperatures, allowing deeper protein breakdown compared to conventional enzyme-assisted methods that denature enzymes at higher heat. This technique improves texture and juiciness by combining controlled heat and enzymatic hydrolysis within vacuum-sealed bags, optimizing tenderness without overcooking.
Sequential Enzyme-Sous Vide Protocol
The Sequential Enzyme-Sous Vide Protocol combines targeted enzyme-assisted marination with precise sous vide cooking to enhance meat tenderization by breaking down connective tissues before gentle heat application, resulting in improved texture and juiciness. This method leverages proteolytic enzymes like papain or bromelain followed by controlled low-temperature immersion, optimizing protein denaturation and maintaining meat quality.
Collagenase-Enhanced Sous Vide
Collagenase-enhanced sous vide cooking significantly accelerates meat tenderization by breaking down collagen fibers more efficiently than traditional sous vide alone, resulting in improved texture and reduced cooking time. Combining enzyme-assisted collagen degradation with precise temperature control optimizes tenderness while maintaining juiciness and flavor integrity.
Enzyme-Assisted Low Temperature Cooking
Enzyme-assisted low temperature cooking combines sous vide precision with natural proteolytic enzymes like papain or bromelain to enhance meat tenderness by breaking down collagen and muscle fibers at controlled temperatures. This method preserves juiciness and flavor while achieving consistent, efficient tenderization compared to traditional sous vide alone.
Time-Temperature-Enzyme Matrix
Sous vide leverages precise time-temperature control to achieve consistent meat tenderization by denaturing proteins slowly, while enzyme-assisted cooking employs proteolytic enzymes like papain or bromelain to break down connective tissues more rapidly. Optimizing the time-temperature-enzyme matrix enhances tenderness by balancing enzymatic activity with controlled heat exposure to prevent over-tenderization and maintain desirable texture.
Papain-Activated Sous Vide
Papain-activated sous vide enhances meat tenderization by combining the precise temperature control of sous vide with the proteolytic action of the papain enzyme, breaking down connective tissues more efficiently than traditional methods. This hybrid technique preserves meat juiciness and texture while accelerating tenderization compared to enzyme-assisted cooking alone.
Bromelain-Coupled Tenderizing Process
The Bromelain-Coupled Tenderizing Process in enzyme-assisted cooking utilizes the proteolytic enzyme bromelain to break down muscle fibers, significantly enhancing meat tenderness more rapidly than traditional sous vide methods. While sous vide relies on precise temperature control over extended periods to achieve consistent texture, bromelain integration accelerates protein degradation, offering a combined approach for superior meat tenderness and flavor retention.
Sous vide vs enzyme-assisted cooking for meat tenderization. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com