Sous vide offers precise temperature control to evenly cook desserts, preserving delicate textures and flavors without overcooking. Hydrocolloid gel cooking excels at creating unique textures and visually striking presentations by manipulating gelling agents like agar or gelatin. While sous vide emphasizes consistency and subtlety, hydrocolloid gels allow for innovative culinary artistry in dessert preparation.
Table of Comparison
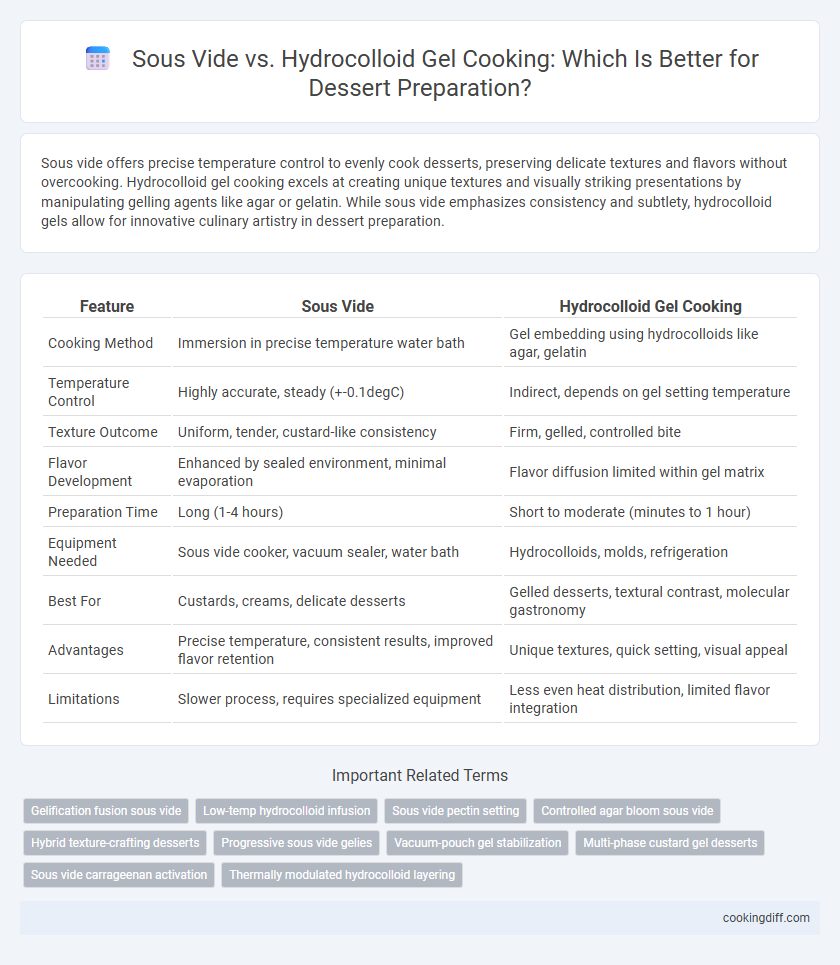
| Feature | Sous Vide | Hydrocolloid Gel Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Immersion in precise temperature water bath | Gel embedding using hydrocolloids like agar, gelatin |
| Temperature Control | Highly accurate, steady (+-0.1degC) | Indirect, depends on gel setting temperature |
| Texture Outcome | Uniform, tender, custard-like consistency | Firm, gelled, controlled bite |
| Flavor Development | Enhanced by sealed environment, minimal evaporation | Flavor diffusion limited within gel matrix |
| Preparation Time | Long (1-4 hours) | Short to moderate (minutes to 1 hour) |
| Equipment Needed | Sous vide cooker, vacuum sealer, water bath | Hydrocolloids, molds, refrigeration |
| Best For | Custards, creams, delicate desserts | Gelled desserts, textural contrast, molecular gastronomy |
| Advantages | Precise temperature, consistent results, improved flavor retention | Unique textures, quick setting, visual appeal |
| Limitations | Slower process, requires specialized equipment | Less even heat distribution, limited flavor integration |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Hydrocolloid Gel Techniques for Desserts
Sous vide cooking utilizes precise temperature control by sealing food in vacuum bags and immersing them in a water bath, ensuring even cooking and retaining moisture for delicate desserts. Hydrocolloid gel techniques employ natural gelling agents like agar, gelatin, or xanthan gum to create unique textures and stabilize dessert components without heat. Both methods enable innovative dessert preparation but differ in process and textural outcomes, offering chefs versatile options for modern pastry creations.
Key Differences: Sous Vide vs Hydrocolloid Gel Cooking
| Key Differences | Sous Vide | Hydrocolloid Gel Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Technique | Precision temperature control with water bath for even cooking. | Use of gelling agents like agar or xanthan for texture and structure. |
| Texture Control | Consistent moisture retention resulting in tender, smooth desserts. | Creates firm, gelled desserts with customizable elasticity and firmness. |
| Applications | Ideal for custards, creams, and slow-cooked flavor development. | Best for mousse, jelly, and layered desserts requiring precise shapes. |
| Equipment Needs | Immersion circulator and vacuum-sealed bags required. | No specialized equipment needed beyond mixers and molds. |
Temperature Precision and Texture Control in Dessert Preparation
Sous vide cooking offers unmatched temperature precision, maintaining water baths typically between 50degC to 90degC, ensuring consistent texture in delicate desserts like custards and mousses. Hydrocolloid gel cooking relies on chemical setting agents but lacks the exact thermal control that sous vide provides, affecting texture consistency.
The precise temperature regulation in sous vide allows chefs to achieve optimal gelatinization and protein denaturation, directly influencing dessert smoothness and creaminess. Hydrocolloid gels, such as agar or carrageenan, offer texture control through concentration adjustments but can produce varying firmness and mouthfeel without precise thermal modulation. Sous vide's ability to hold constant temperatures enhances reproducibility and refinement in dessert preparation compared to hydrocolloid gel methods.
Flavor Infusion: Sous Vide vs Hydrocolloid Gels
Sous vide cooking allows precise temperature control for consistent flavor infusion in desserts by gently extracting and melding ingredients' essences over time. Hydrocolloid gels, such as agar or gelatin, trap flavors within a gel matrix, releasing them upon melting, which creates a burst of taste concentrated in each bite.
The slow, even heat of sous vide enhances the depth and subtlety of flavors by preventing volatile compounds from evaporating during cooking. Hydrocolloid gels excel in texture innovation and targeted flavor delivery but may lack the gradual flavor development achieved through sous vide's extended infusion process.
Application of Hydrocolloid Gels in Modern Dessert Making
Hydrocolloid gels are extensively used in modern dessert making due to their ability to create unique textures and stable emulsions that sous vide techniques cannot easily achieve. These gels, derived from natural gums and polysaccharides, enable precise control over viscosity and gelation, allowing chefs to design innovative layered desserts and mousse-like consistencies. While sous vide excels in temperature-controlled cooking for infusions and custards, hydrocolloid gels offer versatile applications in textural modification and visual presentation within high-end pastry creations.
Equipment and Setup: What You Need for Each Method
What equipment is essential for sous vide compared to hydrocolloid gel cooking in desserts? Sous vide requires an immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, and heat-resistant bags to maintain precise temperature control for even cooking. Hydrocolloid gel cooking utilizes specialized powders like agar or carrageenan and molds or containers for shaping, with no need for temperature-maintaining devices.
Popular Sous Vide Dessert Recipes Compared to Hydrocolloid Gel Recipes
Sous vide desserts like custards and cheesecakes offer precise temperature control for consistent texture. Hydrocolloid gel recipes excel in creating unique textures through gelling agents like agar or carrageenan.
- Smooth Texture - Sous vide cooking ensures even heat distribution, resulting in creamy and silky dessert textures.
- Innovative Textures - Hydrocolloid gels allow chefs to experiment with firmness and elasticity in dessert presentations.
- Recipe Versatility - Sous vide supports classic desserts while hydrocolloid gels expand options for molecular gastronomy techniques.
Choosing between sous vide and hydrocolloid gels depends on desired texture and culinary creativity in dessert making.
Food Safety and Shelf Life Considerations
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control, significantly reducing the risk of microbial growth and enhancing food safety in dessert preparation. Controlled low-temperature cooking also extends shelf life by maintaining consistent pasteurization levels without overcooking delicate ingredients.
Hydrocolloid gel cooking relies on gelation properties rather than heat, which may limit its effectiveness against pathogens if not combined with proper thermal processing. Shelf life of desserts using hydrocolloid gels depends heavily on refrigeration and preservative methods, as microbial stability is less predictable compared to sous vide techniques.
Creative Plating and Presentation: Visual Impact of Each Method
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, resulting in smooth, consistent textures that elevate the elegance of plated desserts, while hydrocolloid gel cooking enables innovative shapes and translucent layers that captivate visually. Both methods provide unique aesthetic advantages that enhance the creative presentation and make desserts visually striking.
- Sous vide enhances texture uniformity - This method ensures even cooking that produces velvety, refined dessert bases perfect for sophisticated plating.
- Hydrocolloid gels allow artistic freedom - Chefs can mold gels into intricate forms and vibrant layers, expanding visual creativity and modernist plating styles.
- Combining techniques maximizes impact - Utilizing sous vide for base preparations and hydrocolloid gels for decorative elements creates multi-dimensional presentations with strong visual appeal.
Related Important Terms
Gelification fusion sous vide
Sous vide cooking enables precise temperature control to achieve consistent gelification, enhancing texture and flavor fusion in desserts, while hydrocolloid gel cooking relies on chemical interactions for structure but lacks the temperature uniformity of sous vide. Gelification fusion sous vide maximizes ingredient synergy by slowly combining flavors and textures under controlled heat, resulting in superior dessert quality compared to traditional hydrocolloid methods.
Low-temp hydrocolloid infusion
Low-temp hydrocolloid infusion in sous vide cooking enables precise flavor and texture control in desserts by maintaining consistent temperatures that optimize gelation and infusion. Hydrocolloid gels formed under these conditions offer uniform viscosity and enhanced mouthfeel, surpassing traditional methods in achieving delicate, stable dessert structures.
Sous vide pectin setting
Sous vide pectin setting allows precise temperature control for consistent gelation in desserts, resulting in superior texture and flavor retention compared to hydrocolloid gel cooking. This method enhances pectin network formation by maintaining steady heat, which optimizes the setting process and improves dessert quality.
Controlled agar bloom sous vide
Controlled agar bloom sous vide creates precise gel textures by maintaining stable temperatures during agar hydration, ensuring consistent dessert quality unlike hydrocolloid gel cooking which can vary with temperature fluctuations. This method enhances flavor infusion and texture uniformity, making it ideal for professional dessert preparation using agar-based gels.
Hybrid texture-crafting desserts
Sous vide and hydrocolloid gel cooking complement each other in crafting hybrid texture desserts by offering precise temperature control and versatile gelation properties, respectively. Combining sous vide's ability to maintain exact heat with hydrocolloid gels like agar or carrageenan creates innovative desserts featuring smooth, creamy interiors and structured, gelled exteriors.
Progressive sous vide gelies
Progressive sous vide gelies offer precise temperature control and consistent texture, outperforming traditional hydrocolloid gel cooking by enabling smoother, more stable dessert gels with enhanced flavor infusion. Sous vide's precise thermal regulation enhances gel-setting processes, ensuring superior mouthfeel and visual appeal in delicate dessert preparations compared to the variable results from hydrocolloid gels.
Vacuum-pouch gel stabilization
Sous vide technique achieves precise temperature control for desserts by vacuum-pouch gel stabilization, enhancing texture consistency and flavor infusion. Hydrocolloid gel cooking, while effective for gel structure, lacks the vacuum-sealed environment that sous vide provides, limiting moisture retention and uniform heat transfer.
Multi-phase custard gel desserts
Sous vide provides precise temperature control ideal for achieving uniform texture in multi-phase custard gel desserts, while hydrocolloid gel cooking offers rapid setting and textural versatility through tailored gelling agents like agar or carrageenan. Combining sous vide's stable heat with hydrocolloid gels' phase separation enhances custard layers with smooth consistency and defined gel boundaries, optimizing both flavor integration and mouthfeel.
Sous vide carrageenan activation
Sous vide cooking enables precise temperature control essential for activating carrageenan in hydrocolloid gels, ensuring consistent gelation and texture in desserts. This method enhances the carrageenan's ability to form stable, smooth gels by maintaining uniform heat, resulting in superior mouthfeel and presentation compared to traditional hydrocolloid gel cooking techniques.
Sous vide vs hydrocolloid gel cooking for desserts. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com