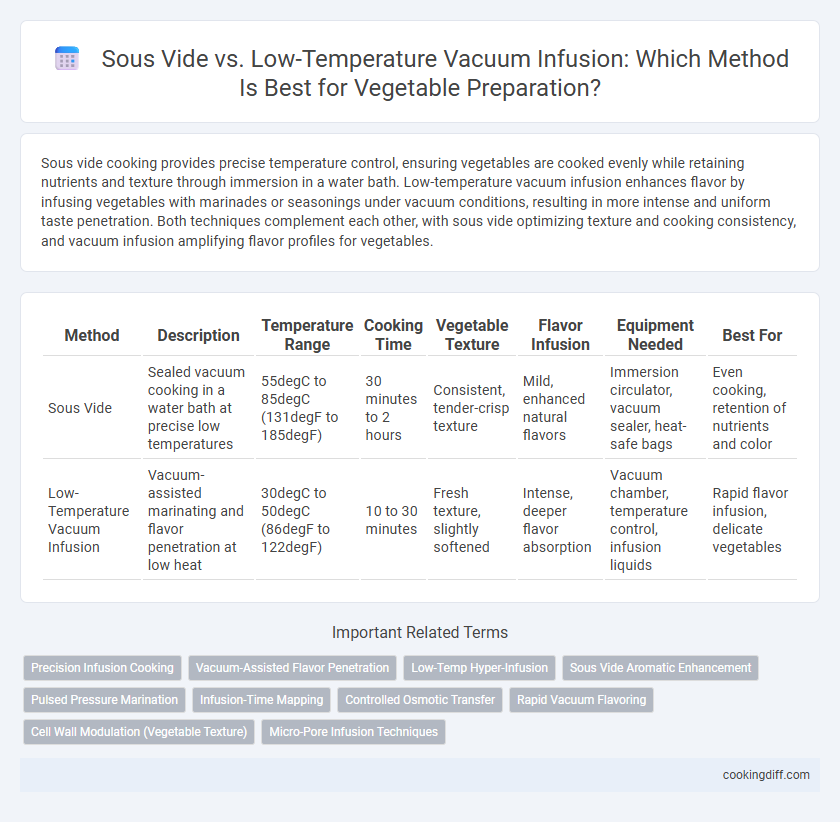
Sous vide cooking provides precise temperature control, ensuring vegetables are cooked evenly while retaining nutrients and texture through immersion in a water bath. Low-temperature vacuum infusion enhances flavor by infusing vegetables with marinades or seasonings under vacuum conditions, resulting in more intense and uniform taste penetration. Both techniques complement each other, with sous vide optimizing texture and cooking consistency, and vacuum infusion amplifying flavor profiles for vegetables.
Table of Comparison
| Method | Description | Temperature Range | Cooking Time | Vegetable Texture | Flavor Infusion | Equipment Needed | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sous Vide | Sealed vacuum cooking in a water bath at precise low temperatures | 55degC to 85degC (131degF to 185degF) | 30 minutes to 2 hours | Consistent, tender-crisp texture | Mild, enhanced natural flavors | Immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, heat-safe bags | Even cooking, retention of nutrients and color |
| Low-Temperature Vacuum Infusion | Vacuum-assisted marinating and flavor penetration at low heat | 30degC to 50degC (86degF to 122degF) | 10 to 30 minutes | Fresh texture, slightly softened | Intense, deeper flavor absorption | Vacuum chamber, temperature control, infusion liquids | Rapid flavor infusion, delicate vegetables |
Introduction: Comparing Sous Vide and Low-Temperature Vacuum Infusion
Sous vide involves cooking vegetables in a precisely controlled water bath to maintain consistent low temperatures, preserving texture and nutrients. Low-temperature vacuum infusion enhances flavor absorption by applying vacuum pressure to infuse liquids into vegetable tissues at controlled temperatures. Both methods utilize precise temperature control but differ in their approach to flavor development and texture preservation in vegetable preparation.
Understanding Sous Vide Cooking for Vegetables
Sous vide cooking for vegetables involves sealing produce in vacuum bags and immersing them in precisely controlled water baths at temperatures typically between 85degF to 185degF. This method ensures even cooking, retains nutrients, and enhances texture while preserving natural flavors compared to traditional methods.
Low-temperature vacuum infusion uses vacuum pressure to infuse flavors or marinades deeply into vegetables before cooking, but it lacks the precise temperature control of sous vide. Understanding sous vide's exact temperature regulation helps achieve consistent texture and doneness, making it superior for delicate vegetable preparation.
What is Low-Temperature Vacuum Infusion?
Low-temperature vacuum infusion is a culinary technique that uses controlled vacuum pressure to infuse flavors into vegetables at precise, low temperatures. Unlike traditional sous vide, which primarily cooks food evenly in a water bath, vacuum infusion enhances taste penetration by extracting air from vegetable tissues and allowing marinades to penetrate deeply. This method preserves texture and color while intensifying flavor profiles in delicate vegetables.
Key Differences Between Sous Vide and Vacuum Infusion
What are the key differences between sous vide and low-temperature vacuum infusion for vegetable preparation? Sous vide involves precise temperature control by cooking vegetables sealed in vacuum bags in a water bath, ensuring even heat distribution and retention of nutrients. Low-temperature vacuum infusion uses vacuum pressure to rapidly infuse flavors into vegetables without prolonged cooking, preserving texture and enhancing taste profiles.
Effects on Vegetable Texture and Color
Sous vide cooking provides precise temperature control that preserves vegetable texture by preventing cell wall breakdown, resulting in a tender yet firm bite. Low-temperature vacuum infusion, while also gentle on texture, can cause slight softening due to the infusion process but enhances color retention through reduced oxidation.
- Sous vide texture preservation - Maintains firmness by slow, even heating without exposure to air.
- Vacuum infusion softening - Infusion may mildly soften vegetables by disrupting cell structure during vacuum treatment.
- Color retention differences - Vacuum infusion limits oxidation better than sous vide, preserving vibrant colors longer.
Both methods significantly improve vegetable quality, with sous vide excelling in texture and vacuum infusion enhancing color vibrancy.
Flavor Enhancement: Infusion vs Traditional Sous Vide
Low-temperature vacuum infusion intensifies vegetable flavor by allowing marinades and seasonings to penetrate deeper and faster compared to traditional sous vide cooking, which primarily relies on slow heat transfer. This method enhances aroma and taste retention without altering texture, making it ideal for delicate vegetables.
Sous vide preserves natural vegetable flavors by sealing food in vacuum bags and cooking at precise temperatures, but infusion techniques offer superior flavor complexity through active ingredient absorption. Combining both methods can optimize taste and nutrient preservation in vegetable preparation.
Nutrient Retention in Both Methods
Sous vide cooking preserves nutrients in vegetables by using precise temperature control that minimizes nutrient loss. Low-temperature vacuum infusion enhances nutrient retention by infusing flavors and nutrients without extensive heat exposure.
- Sous Vide Nutrient Preservation - Maintains vitamins and antioxidants by cooking at consistent temperatures between 55degC and 85degC, reducing oxidation and leaching.
- Vacuum Infusion Efficiency - Uses low-pressure vacuum cycles to infuse water-soluble nutrients and flavors directly into vegetable tissue without thermal degradation.
- Comparative Advantage - Sous vide excels in preserving heat-sensitive nutrients, while vacuum infusion better retains water-soluble compounds through minimal heat application.
Equipment and Setup Required
Sous vide requires precise temperature-controlled water baths and vacuum-sealed bags to ensure even cooking and flavor infusion in vegetables. Low-temperature vacuum infusion combines vacuum technology and marination but needs specialized infusion chambers alongside basic sous vide equipment.
- Sous vide equipment - Includes immersion circulators and vacuum sealers to maintain consistent cooking temperatures and airtight conditions.
- Vacuum infusion setup - Utilizes vacuum chambers to infuse flavors under low pressure, requiring more complex machinery than standard sous vide.
- Complexity and cost - Vacuum infusion setups are generally more expensive and intricate, limiting their use to professional kitchens compared to sous vide's simpler setup.
Common Culinary Applications for Each Method
| Method | Common Culinary Applications |
|---|---|
| Sous Vide | Precision cooking of vegetables such as carrots, asparagus, and potatoes to achieve consistent texture and enhanced flavor retention through controlled low-temperature water bath cooking. |
| Low-Temperature Vacuum Infusion | Flavor enhancement and marination of vegetables by infusing liquids, oils, or seasonings under vacuum conditions, commonly used for preparation of salads, pickles, and infused vegetable dishes with intensified taste profiles. |
Related Important Terms
Precision Infusion Cooking
Sous vide offers precise temperature control for even cooking, preserving vegetable texture and nutrients, while low-temperature vacuum infusion enhances flavor penetration by using vacuum pressure to infuse liquids into vegetables more rapidly. Precision infusion cooking combines these methods to achieve both uniform doneness and intensified taste profiles in vegetable preparation.
Vacuum-Assisted Flavor Penetration
Sous vide cooking combined with low-temperature vacuum infusion enhances vegetable preparation by promoting deeper and faster vacuum-assisted flavor penetration, ensuring uniform seasoning without overcooking. Vacuum infusion accelerates marinade absorption compared to traditional sous vide, resulting in intensified flavors and improved texture retention.
Low-Temp Hyper-Infusion
Low-temperature hyper-infusion enhances vegetable preparation by combining precise sous vide cooking with vacuum infusion techniques, resulting in deeper flavor penetration and improved texture retention. This method excels in maintaining nutrient density and achieving uniform seasoning compared to traditional sous vide cooking alone.
Sous Vide Aromatic Enhancement
Sous vide technique enhances vegetable flavors by precisely controlling temperature to extract and preserve aromatic compounds, offering a consistent infusion of natural essences. Compared to low-temperature vacuum infusion, sous vide maintains optimal nutrient retention while intensifying taste profiles through extended cooking periods in sealed environments.
Pulsed Pressure Marination
Sous vide ensures precise temperature control for consistent vegetable texture, while low-temperature vacuum infusion with pulsed pressure marination enhances flavor absorption by alternating pressure cycles to open plant cell structures. Pulsed pressure marination significantly accelerates infusion rates and intensifies seasoning penetration compared to traditional sous vide cooking methods.
Infusion-Time Mapping
Sous vide maintains precise temperature control for consistent vegetable texture while low-temperature vacuum infusion accelerates flavor absorption by using pressure differentials, optimizing infusion-time mapping based on cell structure permeability. Infusion-time mapping reveals that vacuum infusion achieves uniform flavor penetration in minutes compared to the extended hours required in sous vide, making it highly efficient for rapid vegetable preparation.
Controlled Osmotic Transfer
Sous vide cooking utilizes precise temperature control to achieve even heat distribution and consistent texture in vegetables, optimizing enzymatic activity for flavor development. Low-temperature vacuum infusion enhances Controlled Osmotic Transfer by using vacuum pressure to accelerate the absorption of marinades or brines, intensifying flavor penetration while maintaining vegetable integrity and moisture.
Rapid Vacuum Flavoring
Rapid Vacuum Flavoring intensifies vegetable infusion by using precise low-pressure cycles to accelerate flavor absorption compared to traditional sous vide, which relies on extended cooking times at controlled temperatures. This method enhances texture retention while delivering deeper flavor penetration, optimizing both cooking efficiency and taste quality.
Cell Wall Modulation (Vegetable Texture)
Sous vide preserves vegetable texture by gently heating at precise low temperatures, maintaining cell wall integrity and preventing over-softening. Low-temperature vacuum infusion enhances flavor absorption but can disrupt cell walls more aggressively, leading to a softer, less crisp texture compared to sous vide.
Sous vide vs low-temperature vacuum infusion for vegetable preparation. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com