Sous vide offers precise temperature control by cooking food in a vacuum-sealed bag submerged in a water bath, ensuring even doneness and enhanced flavor retention. Cryo-cooking, in contrast, involves rapid freezing techniques that preserve texture and nutrients before final preparation but do not cook food directly. Comparing both methods, sous vide excels in consistent cooking results, while cryo-cooking is ideal for preservation and pre-processing stages.
Table of Comparison
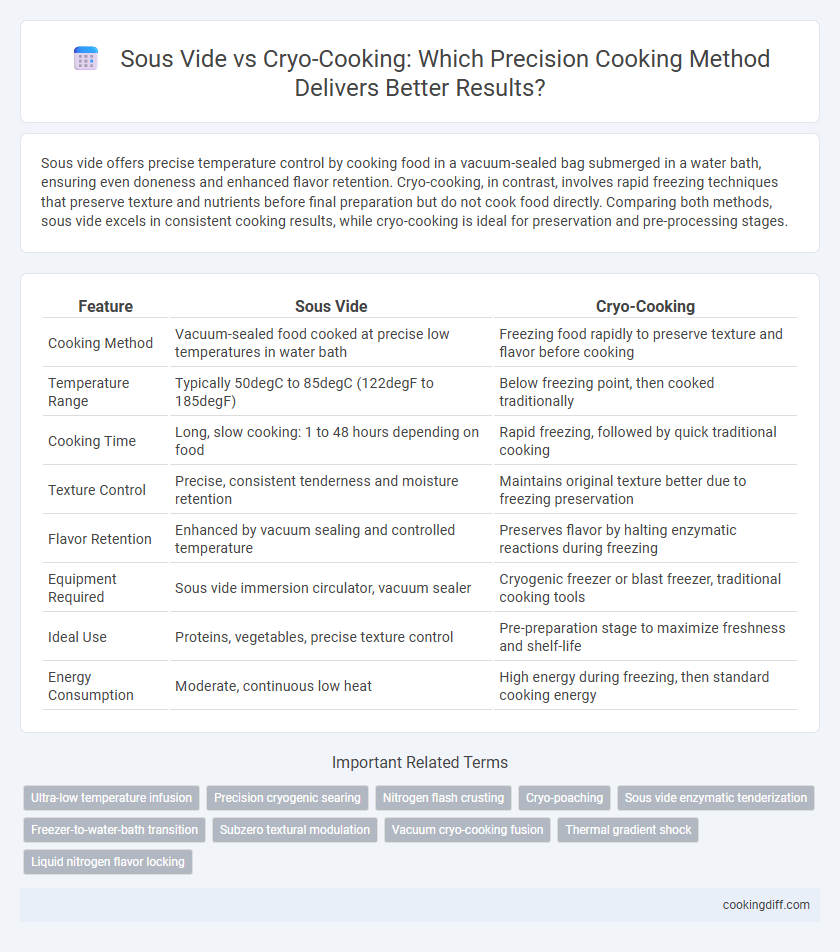
| Feature | Sous Vide | Cryo-Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vacuum-sealed food cooked at precise low temperatures in water bath | Freezing food rapidly to preserve texture and flavor before cooking |
| Temperature Range | Typically 50degC to 85degC (122degF to 185degF) | Below freezing point, then cooked traditionally |
| Cooking Time | Long, slow cooking: 1 to 48 hours depending on food | Rapid freezing, followed by quick traditional cooking |
| Texture Control | Precise, consistent tenderness and moisture retention | Maintains original texture better due to freezing preservation |
| Flavor Retention | Enhanced by vacuum sealing and controlled temperature | Preserves flavor by halting enzymatic reactions during freezing |
| Equipment Required | Sous vide immersion circulator, vacuum sealer | Cryogenic freezer or blast freezer, traditional cooking tools |
| Ideal Use | Proteins, vegetables, precise texture control | Pre-preparation stage to maximize freshness and shelf-life |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate, continuous low heat | High energy during freezing, then standard cooking energy |
Introduction: Understanding Sous Vide and Cryo-Cooking
Sous vide is a precision cooking technique that uses vacuum-sealed bags and controlled temperature water baths to cook food evenly. Cryo-cooking involves freezing food rapidly to preserve texture and flavor before a secondary cooking process.
Understanding the temperature control in sous vide allows for consistent doneness, whereas cryo-cooking emphasizes preservation and flavor retention through freezing techniques. Sous vide cooks food slowly at lower temperatures, enhancing tenderness and moisture. Cryo-cooking requires specialized equipment to maintain ultra-low temperatures, often complementing traditional cooking methods for unique culinary results.
Key Differences Between Sous Vide and Cryo-Cooking
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control in a water bath to evenly cook food over extended periods, preserving texture and flavor. Cryo-cooking involves freezing food rapidly to manipulate texture and enhance flavor before traditional cooking methods. The key difference lies in sous vide's focus on gentle, consistent heat versus cryo-cooking's emphasis on freezing techniques for texture modification.
Temperature Control: Precision in Both Methods
Sous vide and cryo-cooking both rely on meticulous temperature control to achieve optimal cooking results. Sous vide maintains precise temperatures typically between 50degC and 85degC, while cryo-cooking operates near freezing points using subzero techniques for unique culinary effects.
- Sous vide temperature stability - Utilizes water baths regulated within +-0.1degC for consistent heat exposure.
- Cryo-cooking temperature management - Employs cryogenic liquids or refrigeration systems to maintain temperatures around -20degC to 0degC.
- Precision impact on food texture - Both methods manipulate temperature to enhance texture and flavor by controlling protein denaturation and enzymatic reactions.
Mastering temperature control in sous vide and cryo-cooking ensures reproducible and high-quality culinary outcomes.
Equipment Required for Sous Vide vs Cryo-Cooking
| Cooking Method | Required Equipment |
|---|---|
| Sous vide | Precision immersion circulator, vacuum sealer, heat-proof water container |
| Cryo-cooking | Cryogenic freezer or liquid nitrogen setup, vacuum sealer, insulated storage |
Flavor and Texture Outcomes: A Comparison
How do flavor and texture outcomes differ between sous vide and cryo-cooking methods? Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, preserving moisture and enhancing natural flavors by slowly cooking food in vacuum-sealed bags. Cryo-cooking, involving freezing techniques, primarily impacts texture by preventing ice crystal formation but may dilute flavors compared to the concentrated taste achieved through sous vide.
Food Safety Considerations of Each Technique
Sous vide cooking ensures food safety by maintaining precise low temperatures that effectively eliminate harmful bacteria over time. Cryo-cooking, which involves very low temperatures, primarily focuses on preservation but requires additional measures to ensure complete pathogen control during thawing and cooking.
- Sous vide reduces pathogens - Cooking at temperatures typically between 130degF and 160degF for extended periods destroys bacteria like Salmonella and Listeria.
- Cryo-cooking relies on freezing - Freezing slows bacterial growth but does not kill all pathogens, necessitating careful handling post-thaw.
- Cross-contamination risk - Both techniques require strict vacuum sealing to prevent exposure to contaminants during processing.
Cooking Times: Speed vs Consistency
Sous vide cooking typically requires longer cooking times, ranging from 1 to 48 hours, to ensure precise temperature control and consistent results by slowly tenderizing food. Cryo-cooking, on the other hand, uses rapid freezing techniques that significantly reduce preparation time but may compromise uniformity in texture and doneness throughout the dish. Chefs prioritize sous vide for consistent, evenly cooked meals, while cryo-cooking is favored for speed in commercial settings where rapid turnaround is essential.
Versatility: What Foods Can Each Method Cook?
Sous vide offers exceptional versatility by precisely cooking a wide range of foods such as meats, vegetables, and seafood with consistent texture and flavor. Cryo-cooking, or flash freezing combined with cooking, is more limited, primarily used to preserve food quality before traditional cooking methods.
- Sous vide excels with proteins - It evenly cooks beef, chicken, fish, and eggs to exact doneness levels without overcooking.
- Vegetables retain nutrients better sous vide - The low-temperature water bath preserves texture and vitamins more effectively than conventional methods.
- Cryo-cooking focuses on preservation - It rapidly freezes foods to maintain freshness before final preparation rather than serving as a standalone cooking technique.
Costs and Accessibility of Sous Vide and Cryo-Cooking
Sous vide equipment, including immersion circulators and vacuum sealers, is generally more affordable and widely accessible to home cooks compared to the specialized machinery required for cryo-cooking, which involves ultra-low temperature freezers and advanced handling tools. The initial investment for sous vide setups can start as low as $100, making it a popular choice for enthusiasts and professional kitchens alike.
Cryo-cooking typically demands higher costs due to the need for expensive cryogenic materials such as liquid nitrogen or dry ice, and the maintenance of specialized storage units. This limits its accessibility mainly to experimental chefs and high-end restaurants with budgets to support such technology.
Related Important Terms
Ultra-low temperature infusion
Sous vide and cryo-cooking both utilize precise temperature control, but ultra-low temperature infusion in cryo-cooking allows flavors and marinades to penetrate foods at temperatures below traditional sous vide ranges, typically under 0degC. This technique enhances texture retention and intensifies taste profiles by combining slow infusion with freezing, distinguishing it from the typical 50-85degC cooking bands of sous vide.
Precision cryogenic searing
Sous vide ensures precise temperature control for consistent cooking, while cryo-cooking incorporates rapid freezing to enhance texture and flavor retention. Precision cryogenic searing uses liquid nitrogen or dry ice to rapidly caramelize surfaces, creating a distinct crust without overcooking the interior, making it a complementary technique to sous vide for high-quality culinary results.
Nitrogen flash crusting
Sous vide offers precise temperature control for even cooking, while cryo-cooking leverages rapid cooling with liquid nitrogen for nitrogen flash crusting, creating an instant, ultra-crisp exterior without overcooking the interior. Nitrogen flash crusting enhances texture and flavor contrasts, making cryo-cooking ideal for innovative culinary presentations combined with sous vide's tender, consistent results.
Cryo-poaching
Cryo-poaching, a precision cooking technique involving immersion of food in ultra-cold nutrient-rich liquids, offers unique benefits compared to traditional sous vide by preserving delicate textures and flavors through controlled low-temperature environments below freezing. This method enhances moisture retention and nutrient density, making it ideal for delicate proteins and extended shelf life applications where sous vide's vacuum-sealed, moderate-temperature water bath may fall short.
Sous vide enzymatic tenderization
Sous vide utilizes precise temperature control to activate enzymatic tenderization, preserving natural enzymes like proteases that break down muscle fibers gently over time. This method contrasts with cryo-cooking, which relies on low temperatures to halt enzyme activity, making sous vide more effective for enhancing meat tenderness through controlled enzymatic processes.
Freezer-to-water-bath transition
Sous vide offers precise temperature control by cooking food sealed in vacuum bags directly in a water bath, ensuring uniform doneness from freezer to table without thawing. Cryo-cooking involves freezing the food first and then cooking it, which can create challenges in maintaining consistent heat transfer during the freezer-to-water-bath transition, potentially affecting texture and safety.
Subzero textural modulation
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control to achieve uniform doneness and tender textures, while cryo-cooking uses subzero temperatures to induce unique textural modulation by altering muscle fiber structures and enhancing food firmness. The subzero process in cryo-cooking preserves moisture and freshness, creating distinctive mouthfeel contrasts that sous vide cannot replicate.
Vacuum cryo-cooking fusion
Vacuum cryo-cooking fusion combines sous vide precision with cryogenic temperature control to enhance food texture and nutrient retention by freezing vacuum-sealed ingredients before gradual cooking. This method optimizes flavor infusion and extends shelf life beyond traditional sous vide, leveraging low-temperature preservation and controlled cooking for superior culinary results.
Thermal gradient shock
Sous vide cooking maintains a stable temperature that prevents thermal gradient shock by evenly heating food in a water bath, while cryo-cooking subjects ingredients to rapid freezing and thawing cycles that can cause cellular damage and texture loss. This thermal gradient stability in sous vide ensures precise doneness and moisture retention without compromising structural integrity.
Sous vide vs cryo-cooking for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com