Sous vide offers precise temperature control by cooking food in vacuum-sealed bags submerged in a water bath, ensuring even cooking and enhanced flavor retention. In contrast, thermal bain-marie relies on indirect heat with less accuracy, often resulting in uneven cooking and potential nutrient loss. The controlled environment of sous vide makes it superior for consistent texture and tenderness compared to the traditional thermal bain-marie method.
Table of Comparison
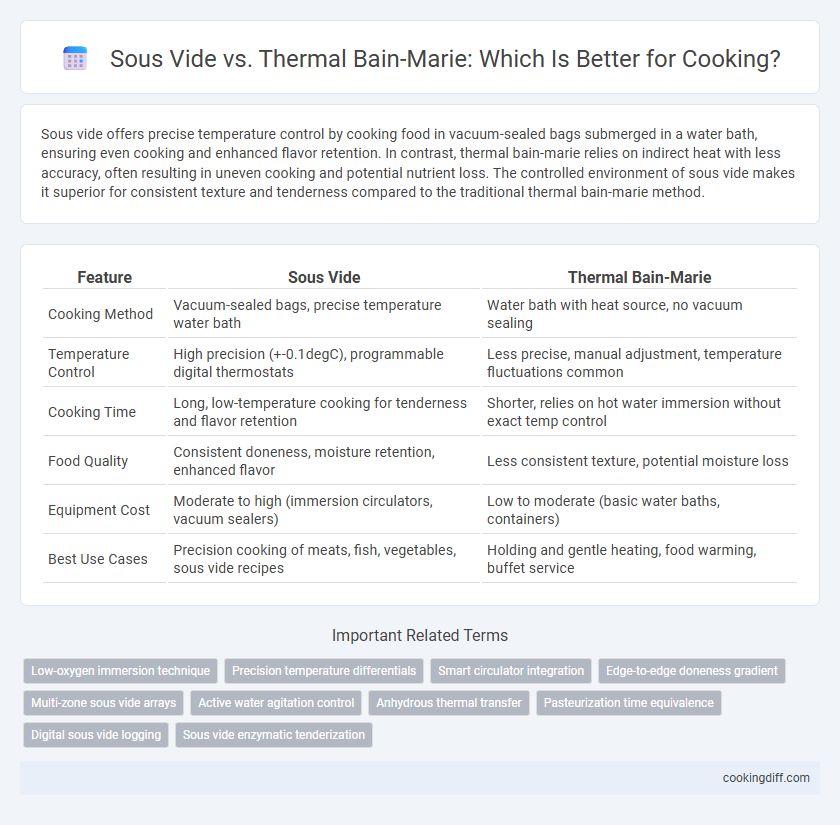
| Feature | Sous Vide | Thermal Bain-Marie |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vacuum-sealed bags, precise temperature water bath | Water bath with heat source, no vacuum sealing |
| Temperature Control | High precision (+-0.1degC), programmable digital thermostats | Less precise, manual adjustment, temperature fluctuations common |
| Cooking Time | Long, low-temperature cooking for tenderness and flavor retention | Shorter, relies on hot water immersion without exact temp control |
| Food Quality | Consistent doneness, moisture retention, enhanced flavor | Less consistent texture, potential moisture loss |
| Equipment Cost | Moderate to high (immersion circulators, vacuum sealers) | Low to moderate (basic water baths, containers) |
| Best Use Cases | Precision cooking of meats, fish, vegetables, sous vide recipes | Holding and gentle heating, food warming, buffet service |
Introduction: Comparing Sous Vide and Thermal Bain-Marie
Sous vide cooking involves sealing food in vacuum bags and immersing them in a precisely temperature-controlled water bath, ensuring consistent doneness and flavor retention. Thermal bain-marie relies on indirect heat by placing containers in hot water, commonly used for gentle warming or slow cooking without exact temperature control.
While sous vide offers precise temperature regulation typically between 50degC and 90degC for extended cooking times, thermal bain-marie temperatures often fluctuate around 60degC to 85degC, limiting culinary precision. The sous vide method enhances texture and nutrient preservation through vacuum sealing, contrasting with the bain-marie's simpler, less controlled approach suited for sauces and delicate dishes.
Technology Overview: How Sous Vide Works
How does sous vide technology differ from a traditional thermal bain-marie in cooking precision? Sous vide uses a vacuum-sealed bag immersed in a water bath with a digitally controlled temperature, ensuring consistent and uniform heat distribution. In contrast, a thermal bain-marie relies on indirect heating with less precise temperature control, often causing uneven cooking results.
Understanding the Thermal Bain-Marie Method
The thermal bain-marie method involves cooking food in a container placed in hot water maintained at a consistent temperature, typically between 60degC and 90degC. This technique ensures gentle, even heating, preventing food from burning or overcooking while preserving moisture and texture.
Unlike sous vide, which uses precise temperature control through immersion circulators, the bain-marie method relies on the water bath's thermal capacity to maintain heat. This can result in less exact temperature regulation, potentially causing fluctuations that affect cooking consistency. Despite this, the bain-marie is widely used for delicate preparations such as custards, terrines, and melting chocolate due to its simplicity and reliability in providing steady heat.
Temperature Control: Precision and Consistency
Sous vide cooking offers unparalleled temperature control, maintaining water baths within +-0.1degC to ensure precise and consistent cooking results. Thermal bain-marie systems typically have larger temperature fluctuations, often within +-1-2degC, which can affect the uniformity of food preparation. This precision in sous vide technology enhances texture and flavor by evenly cooking food at exact temperatures over extended periods.
Cooking Results: Taste, Texture, and Moisture Retention
Sous vide cooking consistently delivers superior moisture retention, resulting in juicier and more tender dishes compared to thermal bain-marie methods. The precise temperature control of sous vide enhances flavor development and achieves even texture throughout the food.
- Enhanced Moisture Retention - Sous vide seals in natural juices by cooking food in a vacuum-sealed bag, preventing water loss.
- Consistent Texture - Precise temperature regulation ensures uniform doneness without overcooking any part of the food.
- Improved Flavor Infusion - Flavor compounds are better preserved and intensified due to low-temperature, slow cooking in sealed environments.
Versatility: Food Types and Recipe Compatibility
Sous vide offers superior versatility by precisely controlling temperature, making it ideal for cooking a wide range of food types including meats, vegetables, and eggs with consistent results. Unlike thermal bain-marie, which is limited to gentle heating primarily for sauces and delicate items, sous vide can handle complex recipes that require precise doneness and texture. This precision expands recipe compatibility, allowing chefs to experiment with innovative cooking techniques and ingredients that are difficult to achieve through traditional bain-marie methods.
Equipment Requirements and Costs
Sous vide cooking requires specialized immersion circulators or water ovens to maintain precise temperature control, often resulting in higher initial equipment costs. Thermal bain-marie setups use simpler, less expensive equipment like steam tables or heated water baths but lack the fine temperature accuracy of sous vide devices.
- Sous vide equipment - Typically involves digital immersion circulators costing between $100 and $300.
- Thermal bain-marie equipment - Basic models are priced under $100 and are easier to source.
- Operational cost - Sous vide devices may consume more electricity due to longer cooking times at stable temperatures.
Choosing between the two depends on the balance between cost constraints and the desired precision in cooking results.
Energy Efficiency: Power Consumption Compared
Sous vide cooking generally uses less power due to precise temperature control and insulation, leading to reduced energy waste compared to thermal bain-marie methods. Thermal bain-marie systems often consume more energy as they maintain larger water volumes at target temperatures without the same level of efficiency.
- Lower power consumption - Sous vide immersion circulators typically use 800-1200 watts, optimizing energy by maintaining exact temperatures and reducing heat loss.
- Higher energy usage - Thermal bain-marie units require continuous heating of extensive water baths, often exceeding 1500 watts to maintain stable heat across larger volumes.
- Improved insulation - Sous vide devices usually incorporate sealed containers and lids that minimize heat escape, enhancing overall energy efficiency during long cooking cycles.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Sous vide devices offer precise temperature control with simple digital interfaces, making them easier to use than traditional thermal bain-marie setups. Users can set exact cooking times and temperatures without constant monitoring, ensuring consistent results.
Maintenance of sous vide equipment is straightforward, typically requiring only occasional cleaning of the immersion circulator and sealing bags. In contrast, bain-marie systems often demand frequent water changes and can be prone to mineral buildup, increasing upkeep efforts.
Related Important Terms
Low-oxygen immersion technique
Sous vide offers precise temperature control and a low-oxygen immersion environment that prevents oxidation and preserves food quality better than traditional thermal bain-marie methods. Its vacuum-sealed bags create an anaerobic atmosphere that enhances flavor retention and texture by minimizing oxygen exposure during cooking.
Precision temperature differentials
Sous vide cooking maintains water temperature with precision often within +-0.1degC, ensuring consistent doneness and texture by evenly transferring heat throughout the food. Thermal bain-marie systems typically have larger temperature fluctuations, around +-1-2degC, which can lead to uneven cooking and less control over delicate temperature-sensitive recipes.
Smart circulator integration
Sous vide cooking with a smart circulator offers precise temperature control and consistent water flow, ensuring even heat distribution compared to a traditional thermal bain-marie. The smart circulator's connectivity features enable remote monitoring and adjustments, enhancing cooking accuracy and convenience that bain-marie methods lack.
Edge-to-edge doneness gradient
Sous vide cooking ensures a precise edge-to-edge doneness gradient by maintaining a constant, uniform water bath temperature, whereas a thermal bain-marie often results in uneven cooking due to temperature fluctuations and less precise heat control. The controlled environment of sous vide minimizes overcooking at the edges and undercooking in the center, delivering consistent texture and optimal flavor throughout the entire food item.
Multi-zone sous vide arrays
Multi-zone sous vide arrays provide precise temperature control across different cooking zones, ensuring consistent results compared to traditional thermal bain-marie systems that often struggle with uneven heat distribution. These advanced sous vide setups enhance cooking accuracy for various proteins simultaneously, maintaining optimal doneness and texture throughout.
Active water agitation control
Sous vide employs precise active water agitation control to maintain consistent temperature and even heat distribution, ensuring perfect cooking results by preventing hot or cold spots. Thermal bain-marie lacks this level of agitation, leading to uneven temperature zones that can affect the uniformity and quality of the cooked food.
Anhydrous thermal transfer
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control through water bath immersion, ensuring uniform heat distribution via anhydrous thermal transfer in sealed vacuum bags, which prevents oxidation and flavor loss. Thermal bain-marie relies on direct water contact and less effective heat conduction, often resulting in uneven cooking due to varying thermal conductivity and evaporation.
Pasteurization time equivalence
Sous vide cooking ensures precise pasteurization by maintaining consistent, low temperatures over specific times, allowing for safer and more uniform bacterial reduction compared to thermal bain-marie methods. Thermal bain-marie often requires longer pasteurization times due to temperature fluctuations, making sous vide more efficient in achieving food safety standards.
Digital sous vide logging
Digital sous vide devices offer precise temperature control and continuous logging, enabling consistent cooking results that surpass traditional thermal bain-marie methods prone to temperature variation. The integration of digital temperature data tracking ensures repeatability and food safety, essential for professional kitchens and culinary enthusiasts seeking exact doneness and texture.
Sous vide vs thermal bain-marie for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com