Sous vide cooking relies on precise temperature control by sealing food in a vacuum bag, preserving flavor and moisture. Low-oxygen immersion for vacuum sealing removes most oxygen, reducing oxidation and spoilage, which also enhances shelf life and food safety. Both methods optimize preservation, but sous vide emphasizes controlled cooking temperatures while low-oxygen immersion focuses on prolonging freshness before cooking.
Table of Comparison
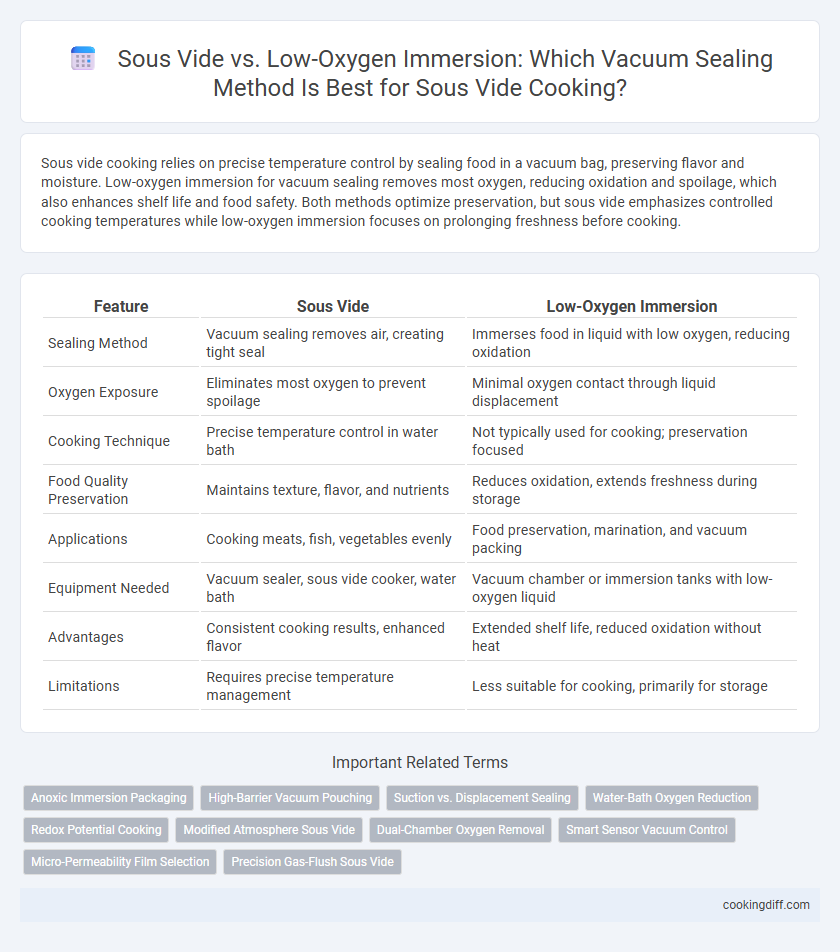
| Feature | Sous Vide | Low-Oxygen Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Method | Vacuum sealing removes air, creating tight seal | Immerses food in liquid with low oxygen, reducing oxidation |
| Oxygen Exposure | Eliminates most oxygen to prevent spoilage | Minimal oxygen contact through liquid displacement |
| Cooking Technique | Precise temperature control in water bath | Not typically used for cooking; preservation focused |
| Food Quality Preservation | Maintains texture, flavor, and nutrients | Reduces oxidation, extends freshness during storage |
| Applications | Cooking meats, fish, vegetables evenly | Food preservation, marination, and vacuum packing |
| Equipment Needed | Vacuum sealer, sous vide cooker, water bath | Vacuum chamber or immersion tanks with low-oxygen liquid |
| Advantages | Consistent cooking results, enhanced flavor | Extended shelf life, reduced oxidation without heat |
| Limitations | Requires precise temperature management | Less suitable for cooking, primarily for storage |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Low-Oxygen Immersion
Sous vide is a precise cooking technique that uses vacuum-sealed bags to cook food at controlled low temperatures in a water bath, preserving flavor and texture. Low-oxygen immersion involves sealing food in an environment with reduced oxygen levels to prevent oxidation and extend shelf life while maintaining quality. Both methods utilize vacuum sealing but differ in their approach to oxygen control and cooking application.
Understanding Sous Vide Vacuum Sealing
Sous vide cooking relies on precise vacuum sealing to create a low-oxygen environment that ensures even heat distribution and flavor retention. Low-oxygen immersion techniques also reduce oxygen exposure but differ in sealing methods and impact on texture and shelf life.
- Sous Vide Vacuum Sealing - Uses specialized vacuum sealers to remove air, preserving food integrity during long, controlled temperature cooking.
- Low-Oxygen Immersion - Involves submerging food in liquid to limit oxygen but may not achieve the same airtight seal as vacuum sealing.
- Oxygen Removal Efficiency - Vacuum sealing provides a stronger oxygen barrier, preventing spoilage and oxidation more effectively than immersion.
Proper vacuum sealing is essential for maximizing the benefits of sous vide cooking while maintaining food safety and quality.
What is Low-Oxygen Immersion Sealing?
Low-oxygen immersion sealing is a vacuum packaging technique that removes oxygen by submerging food in liquid before sealing, minimizing oxidation and spoilage. This method enhances the preservation of fresh flavors and textures, especially in delicate foods.
- Oxygen Removal - Oxygen is displaced by immersing food in water or other liquids to create an anaerobic environment.
- Improved Preservation - Reduced oxygen slows down enzyme activity and microbial growth, extending shelf life.
- Texture and Flavor Retention - Maintaining low oxygen levels prevents oxidation, preserving food quality during sous vide cooking.
Key Differences: Sous Vide vs Low-Oxygen Immersion
What are the key differences between sous vide and low-oxygen immersion for vacuum sealing? Sous vide cooking involves precise temperature control in a water bath to cook food evenly, while low-oxygen immersion focuses on removing oxygen to preserve freshness and extend shelf life. Sous vide methods optimize texture and flavor through controlled heat, whereas low-oxygen immersion mainly aims to prevent oxidation and bacterial growth during storage.
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Sous vide cooking typically requires a precision immersion circulator, a vacuum sealer, and BPA-free vacuum bags to ensure consistent temperature control and airtight sealing. The immersion circulator maintains the water bath at a precise temperature while the vacuum sealer removes air from the food bag, preventing oxidation.
Low-oxygen immersion for vacuum sealing involves an airtight container or chamber vacuum sealer designed to reduce oxygen levels without fully submerging the food. This method often uses specialized oxygen-absorbing bags or barriers, but does not require the precise temperature control equipment needed for sous vide.
Impact on Food Flavor and Texture
Sous vide cooking uses precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed bag, preserving natural flavors and enhancing tenderness by preventing moisture loss. Low-oxygen immersion for vacuum sealing reduces oxidation but may slightly compress delicate textures, subtly altering mouthfeel.
The sous vide method ensures even heat distribution, maintaining consistent texture and intensifying taste by locking in aromatic compounds. Low-oxygen immersion minimizes spoilage, but its impact on food flavor is less pronounced compared to the controlled environment sous vide provides.
Safety and Shelf Life Comparison
Sous vide employs precise temperature control to ensure food safety by eliminating harmful pathogens during cooking. Low-oxygen immersion vacuum sealing reduces oxygen exposure, extending shelf life but requires strict monitoring to prevent anaerobic bacterial growth.
- Sous vide enhances food safety - It maintains consistent temperatures that destroy harmful bacteria, ensuring safe consumption.
- Low-oxygen immersion prolongs shelf life - By minimizing oxygen, it slows oxidation and spoilage, keeping food fresh longer.
- Risk management differs - Sous vide relies on heat for safety, while low-oxygen immersion needs careful oxygen and temperature control to avoid anaerobic contamination.
Cost and Accessibility Factors
Sous vide equipment generally incurs higher initial costs compared to low-oxygen immersion vacuum sealers, which are often more affordable and accessible for home cooks. The sous vide method requires precise temperature control devices, increasing investment and maintenance expenses.
Low-oxygen immersion vacuum sealing systems are simpler and widely available at lower price points, making them suitable for budget-conscious consumers. Sous vide devices, including immersion circulators, tend to be more specialized and less accessible in some regions. For those prioritizing cost and ease of use, low-oxygen vacuum sealers present a practical alternative without sacrificing essential food preservation benefits.
Best Practices for Each Technique
| Sous Vide | Optimal vacuum sealing involves removing nearly all air to ensure even heat transfer and prevent package floatation, essential for precise temperature control during cooking. |
| Low-Oxygen Immersion | Maintaining minimal oxygen levels in the vacuum bag slows oxidation and microbial growth, with the recommended practice being a gentle vacuum to avoid damaging delicate foods. |
| Best Practices | Use high-quality vacuum seal bags designed for high heat, verify seal integrity before immersion, and monitor pressure levels to balance oxygen removal without compromising food texture or bag integrity. |
Related Important Terms
Anoxic Immersion Packaging
Anoxic Immersion Packaging utilizes a low-oxygen environment by displacing air with inert gases, effectively preserving food quality and extending shelf life by preventing oxidation and microbial growth. Unlike traditional sous vide vacuum sealing, which removes air to create a vacuum, anoxic immersion enhances preservation by maintaining an oxygen-free state while allowing for precise temperature control during cooking.
High-Barrier Vacuum Pouching
High-barrier vacuum pouches used in sous vide cooking provide superior oxygen and moisture protection compared to low-oxygen immersion methods, ensuring optimal food preservation and flavor retention. These pouches maintain an airtight environment that significantly reduces oxidation, extending shelf life and enhancing cooking precision.
Suction vs. Displacement Sealing
Suction sealing in sous vide uses vacuum pumps to extract air, preserving food by creating a low-oxygen environment that slows oxidation and microbial growth. Displacement sealing, often used in low-oxygen immersion, relies on water pressure to push air out of bags during sealing, offering a more cost-effective method but potentially less precise air removal compared to suction vacuum sealing.
Water-Bath Oxygen Reduction
Sous vide cooking relies on vacuum sealing to minimize oxygen exposure, enhancing flavor and texture preservation through precise water-bath oxygen reduction. Low-oxygen immersion employs controlled environments to further reduce dissolved oxygen in the water, preventing oxidation and improving the shelf life and quality of vacuum-sealed foods during sous vide processes.
Redox Potential Cooking
Sous vide cooking maintains a controlled temperature environment that stabilizes redox potential, enhancing food texture and flavor through precise low-oxygen immersion. Low-oxygen vacuum sealing reduces oxidative reactions by minimizing oxygen exposure, but combining it with sous vide optimizes redox balance for superior preservation and taste development.
Modified Atmosphere Sous Vide
Modified Atmosphere Sous Vide (MASV) enhances vacuum sealing by replacing oxygen with inert gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide, minimizing oxidation and microbial growth during cooking. Compared to traditional low-oxygen immersion techniques, MASV ensures prolonged shelf life and improved flavor retention by stabilizing the food's environment under precise atmospheric conditions.
Dual-Chamber Oxygen Removal
Sous vide cooking benefits from Dual-Chamber Oxygen Removal technology in vacuum sealers, which ensures enhanced preservation by effectively eliminating oxygen, reducing oxidation, and extending food freshness compared to standard low-oxygen immersion methods. This advanced vacuum sealing method maintains optimal texture and flavor by preventing microbial growth and preserving nutrient integrity during precision temperature cooking.
Smart Sensor Vacuum Control
Smart Sensor Vacuum Control enhances sous vide precision by actively monitoring and adjusting vacuum levels to maintain optimal low-oxygen conditions, preventing oxidation and preserving flavor integrity. This technology surpasses traditional low-oxygen immersion vacuum sealing by ensuring consistent seal quality and reducing the risk of package collapse during cooking.
Micro-Permeability Film Selection
Micro-permeability film selection for sous vide vs low-oxygen immersion vacuum sealing significantly affects oxygen transmission rates, impacting food preservation and texture. Sous vide optimizes low permeability films to maintain an anaerobic environment, while low-oxygen immersion often uses films with controlled gas exchange to balance spoilage prevention and product respiration.
Sous vide vs Low-oxygen immersion for vacuum sealing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com