Steaming rice ensures even cooking by using direct steam heat, preserving its texture and nutrients without added fats. Bamboo steaming offers a natural, eco-friendly alternative that imparts a subtle woody aroma to the rice while allowing excess moisture to escape, preventing sogginess. Both methods produce fluffy, perfectly cooked rice, but bamboo steaming adds a unique flavor and traditional aesthetic often preferred in Asian cuisine.
Table of Comparison
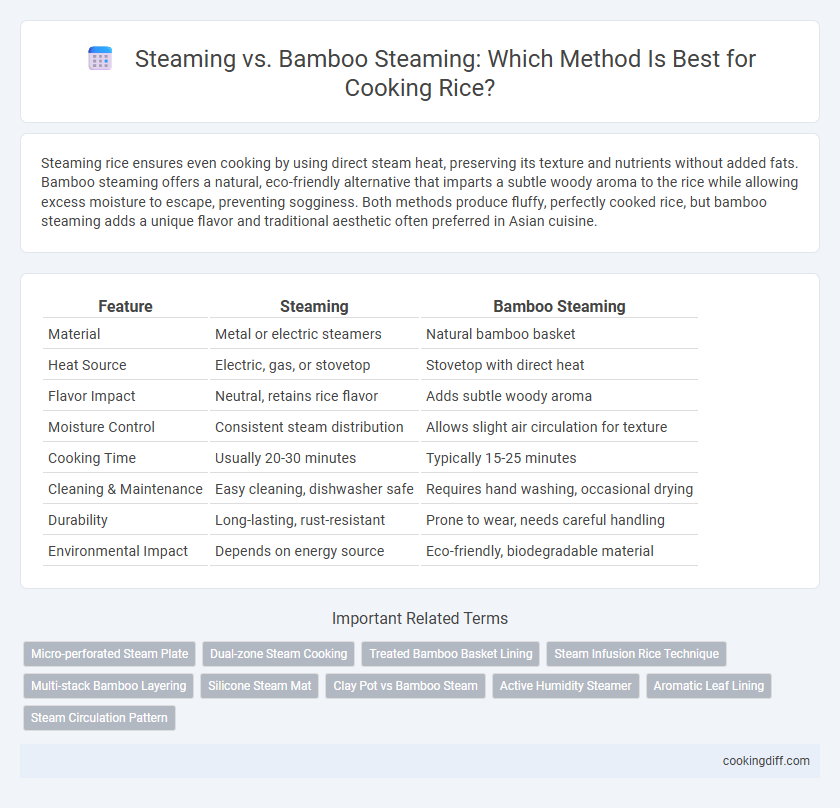
| Feature | Steaming | Bamboo Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Metal or electric steamers | Natural bamboo basket |
| Heat Source | Electric, gas, or stovetop | Stovetop with direct heat |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, retains rice flavor | Adds subtle woody aroma |
| Moisture Control | Consistent steam distribution | Allows slight air circulation for texture |
| Cooking Time | Usually 20-30 minutes | Typically 15-25 minutes |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy cleaning, dishwasher safe | Requires hand washing, occasional drying |
| Durability | Long-lasting, rust-resistant | Prone to wear, needs careful handling |
| Environmental Impact | Depends on energy source | Eco-friendly, biodegradable material |
Introduction to Steaming Methods for Rice
What are the differences between traditional steaming and bamboo steaming for rice? Traditional steaming uses a metal or electric steamer that delivers consistent heat and moisture, ensuring even cooking. Bamboo steaming incorporates natural bamboo baskets that add subtle aroma and texture, enhancing the overall flavor and presentation of the rice.
What Is Bamboo Steaming?
Bamboo steaming involves using a traditional bamboo steamer basket, which allows steam to circulate evenly around the rice, enhancing texture and flavor. This method naturally absorbs excess moisture, preventing sogginess commonly encountered in metal steamers.
Made from woven bamboo strips, the steamer is placed over boiling water, allowing steam to cook the rice gently and uniformly. The porous material also imparts a subtle, aromatic quality to the rice while maintaining its natural nutrients. Bamboo steaming is favored for delicate grains and Asian culinary dishes due to its ability to create fluffy, non-sticky results.
Traditional Steaming Techniques Explained
Traditional steaming techniques involve cooking rice by surrounding it with steam to ensure even heat distribution and moisture retention. Bamboo steaming utilizes a woven bamboo basket that allows excess steam to escape, enhancing flavor and texture.
- Even Heat Distribution - Traditional steaming maintains consistent temperature through enclosed steam circulation.
- Natural Material Use - Bamboo baskets are eco-friendly and impart a subtle aroma to the rice.
- Textural Difference - Bamboo steaming often results in fluffier rice with distinct grain separation.
Benefits of Steaming Rice
Steaming rice preserves essential nutrients like vitamins B and E more effectively than boiling, enhancing its nutritional value. Bamboo steaming offers gentle, even heat circulation which helps retain the natural texture and aroma of rice. Both steaming methods reduce oil usage, contributing to a healthier, low-fat meal option.
Advantages of Bamboo Steamers
Bamboo steamers offer natural breathability that prevents condensation from dripping back onto rice, ensuring a fluffy texture. Their multi-tiered design allows simultaneous steaming of different dishes, saving time and energy.
Unlike metal steamers, bamboo steamers absorb excess moisture, preserving the delicate flavor and aroma of rice. They are eco-friendly, lightweight, and add a subtle woody fragrance that enhances the overall dining experience.
Comparing Flavor and Texture: Standard vs. Bamboo
Steaming rice using a bamboo steamer imparts a subtle earthy aroma that enhances the natural flavor, while standard steaming maintains a more neutral taste. Texture-wise, bamboo steaming allows for a slightly firmer and fluffier grain compared to the uniformly soft texture achieved with standard steamers.
- Flavor Enhancement - Bamboo steaming adds a mild woody fragrance that enriches the rice's flavor profile.
- Texture Variation - Rice steamed in bamboo tends to have a drier, fluffier texture versus the moist consistency from standard steaming.
- Heat Distribution - Bamboo steamers provide gentler, more even heat, preserving the rice's structural integrity better than metal steamers.
Choosing between standard and bamboo steaming depends on the desired balance of flavor nuance and rice texture.
Health Aspects: Bamboo vs. Metal/Plastic Steamers
| Health Safety | Bamboo steamers release no harmful chemicals and are less likely to leach toxins, making them a safer choice compared to some metal or plastic steamers which can contain harmful BPA or heavy metals. |
| Material Impact | Bamboo is a natural, biodegradable material that avoids chemical contamination during steaming, whereas metal steamers may sometimes corrode or react with acidic foods, and plastic steamers can release microplastics under heat. |
| Flavor and Nutrient Retention | Bamboo steamers allow gentle, even steaming that preserves rice nutrients and enhances natural flavor, while metal or plastic steamers may conduct excessive heat, potentially affecting nutrient levels and taste. |
Ease of Use and Cleaning Differences
Traditional steaming involves using metal or electric steamers that are often easier to assemble and clean due to removable parts and dishwasher-safe materials. Bamboo steamers, made from natural bamboo, require more delicate handling and thorough drying to prevent mold, making cleaning less convenient. While bamboo steamers add a subtle aroma to rice, metal steamers score higher in ease of cleaning and maintenance.
Environmental Impact of Bamboo Steamers
Bamboo steamers offer a sustainable alternative to metal or plastic steamers due to their biodegradable and renewable materials. Their production has a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional steaming equipment, making them more eco-friendly for rice preparation.
- Renewable Resource - Bamboo grows quickly and can be harvested without causing deforestation, reducing environmental degradation.
- Biodegradability - Bamboo steamers decompose naturally, minimizing waste and pollution compared to metal or plastic alternatives.
- Lower Energy Consumption - Manufacturing bamboo steamers requires less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases than the production of metal steamers.
Related Important Terms
Micro-perforated Steam Plate
Micro-perforated steam plates enhance steaming efficiency by evenly distributing steam and preventing water droplets from falling onto the rice, which preserves texture and flavor better than traditional bamboo steaming. This advanced method reduces cooking time and absorption of excess moisture, resulting in fluffier, well-cooked rice with consistent heat penetration.
Dual-zone Steam Cooking
Dual-zone steam cooking offers precise temperature control, enabling simultaneous steaming of rice with optimal moisture retention and texture. Bamboo steaming, while traditional and aromatic, lacks the consistent heat distribution of dual-zone systems, often leading to uneven rice cooking and variable results.
Treated Bamboo Basket Lining
Treated bamboo basket linings enhance bamboo steaming by providing natural breathability and moisture regulation, resulting in evenly cooked rice with a subtle fragrance. This eco-friendly method prevents sticking and excess condensation, preserving rice texture better than conventional metal steaming.
Steam Infusion Rice Technique
The Steam Infusion Rice Technique utilizes precise steam pressure and temperature to evenly cook rice kernels, resulting in enhanced texture and flavor compared to traditional bamboo steaming methods. Unlike bamboo steaming, which relies on indirect heat and can yield inconsistent results, steam infusion ensures uniform hydration and optimum starch gelatinization for perfectly cooked rice every time.
Multi-stack Bamboo Layering
Multi-stack bamboo steaming enhances rice texture by allowing even heat and steam distribution through its layered design, preserving aroma and nutrients more efficiently than traditional steaming methods. This technique prevents sogginess by enabling excess moisture to escape between bamboo layers, resulting in perfectly cooked, fluffy rice.
Silicone Steam Mat
Silicone steam mats enhance traditional bamboo steaming by providing a non-stick surface that prevents rice from sticking and allows even heat distribution for perfectly cooked grains. Their heat-resistant and flexible properties make silicone mats a reusable and hygienic alternative to bamboo steamers, ensuring easy cleanup and durability during rice steaming.
Clay Pot vs Bamboo Steam
Steaming rice in a clay pot ensures even heat distribution and moisture retention, resulting in a tender, fluffy texture with a slight smoky aroma, while bamboo steaming provides gentle airflow and prevents condensation from dripping onto the rice, preserving its delicate grains. Clay pots offer durability and enhanced heat retention, whereas bamboo steamers excel in maintaining natural flavors and are ideal for layered steaming of multiple dishes simultaneously.
Active Humidity Steamer
Active Humidity Steamers provide consistent moisture and precise temperature control, resulting in perfectly cooked rice with a fluffy texture compared to traditional bamboo steaming. Unlike bamboo steamers, which rely on natural ventilation, Active Humidity Steamers actively regulate humidity levels to prevent rice from drying out or becoming soggy.
Aromatic Leaf Lining
Steaming rice using an aromatic leaf lining, such as banana or lotus leaves, imparts subtle floral and herbal notes that enhance the flavor and fragrance, unlike bamboo steaming which primarily relies on the natural sweetness and slightly woody aroma of the bamboo basket itself. The leaf lining technique also helps retain moisture and prevent rice from sticking, resulting in a more evenly cooked and aromatic dish.
Steaming vs Bamboo Steaming for rice Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com