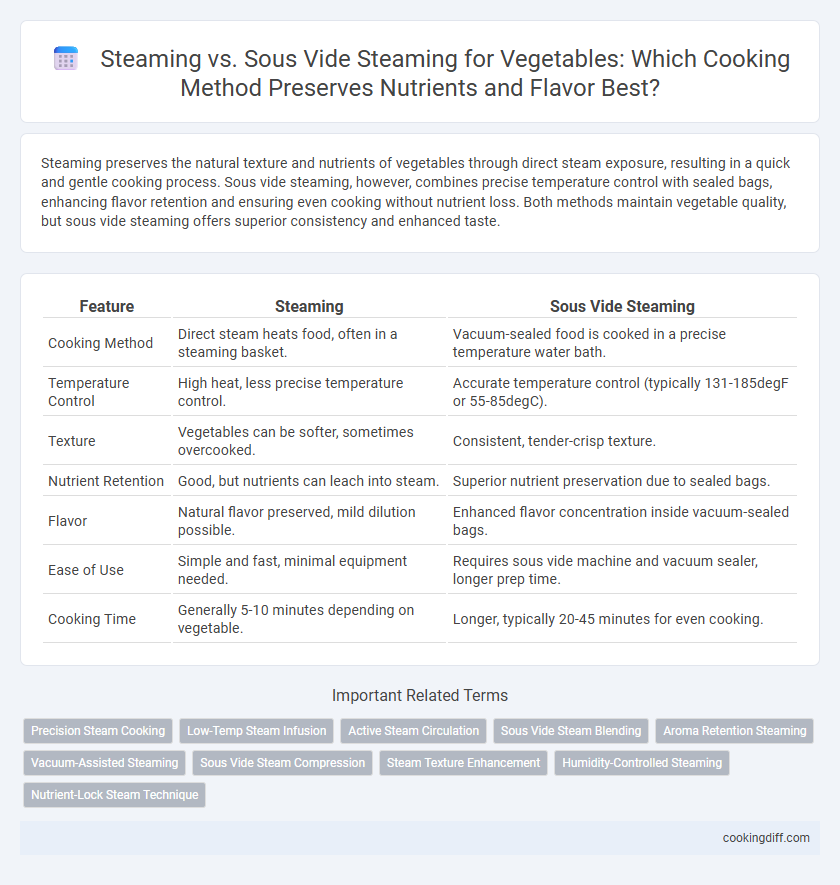
Steaming preserves the natural texture and nutrients of vegetables through direct steam exposure, resulting in a quick and gentle cooking process. Sous vide steaming, however, combines precise temperature control with sealed bags, enhancing flavor retention and ensuring even cooking without nutrient loss. Both methods maintain vegetable quality, but sous vide steaming offers superior consistency and enhanced taste.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Steaming | Sous Vide Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Direct steam heats food, often in a steaming basket. | Vacuum-sealed food is cooked in a precise temperature water bath. |
| Temperature Control | High heat, less precise temperature control. | Accurate temperature control (typically 131-185degF or 55-85degC). |
| Texture | Vegetables can be softer, sometimes overcooked. | Consistent, tender-crisp texture. |
| Nutrient Retention | Good, but nutrients can leach into steam. | Superior nutrient preservation due to sealed bags. |
| Flavor | Natural flavor preserved, mild dilution possible. | Enhanced flavor concentration inside vacuum-sealed bags. |
| Ease of Use | Simple and fast, minimal equipment needed. | Requires sous vide machine and vacuum sealer, longer prep time. |
| Cooking Time | Generally 5-10 minutes depending on vegetable. | Longer, typically 20-45 minutes for even cooking. |
Introduction to Steaming and Sous Vide Steaming
Steaming is a traditional cooking method that uses hot steam to gently cook vegetables, preserving their nutrients, color, and texture. It requires a steamer basket placed over boiling water, allowing steam to circulate and evenly cook the food.
Sous vide steaming combines vacuum-sealed bags with precise temperature control through water baths, ensuring consistent cooking results. This technique enhances flavor retention and texture by cooking vegetables at lower temperatures for extended periods.
How Traditional Steaming Works
Traditional steaming cooks vegetables by exposing them to boiling water vapor, which gently penetrates the food without direct contact with water. This method preserves nutrients and texture by maintaining a consistent temperature around 100degC (212degF).
- Heat Transfer - Steam transfers heat efficiently, cooking vegetables evenly while preventing nutrient loss.
- Cooking Time - Vegetables typically steam within 5 to 15 minutes depending on size and type.
- Equipment - Requires a pot with a steaming basket or perforated insert to hold the vegetables above boiling water.
Traditional steaming offers simplicity and nutrient retention but lacks precise temperature control compared to sous vide steaming.
Understanding Sous Vide Steaming
Sous vide steaming involves sealing vegetables in vacuum bags and cooking them in a precisely controlled water bath, preserving nutrients and enhancing flavor retention. This method maintains consistent temperature, preventing overcooking and ensuring even texture throughout the vegetables.
Traditional steaming exposes vegetables to direct steam, which can cause nutrient loss and uneven cooking due to fluctuating temperatures. Understanding sous vide steaming highlights its ability to optimize vegetable texture and nutritional value compared to conventional steaming methods.
Key Equipment for Each Method
| Steaming | Essential equipment includes a steamer basket or a tiered steaming rack placed over a pot of boiling water; this setup allows vegetables to cook with moist heat while retaining nutrients and texture. A lid is crucial to trap steam and maintain consistent temperature. Simple stovetop setups are most common for traditional steaming. |
| Sous Vide Steaming | Requires an immersion circulator to precisely control water temperature and vacuum-sealed bags to enclose vegetables, ensuring even cooking and enhanced flavor infusion. The water bath maintains precise heat, preventing overcooking, while the sealed environment locks in moisture and nutrients. A vacuum sealer is also essential for effective sous vide steaming preparation. |
Temperature and Precision: Steaming vs Sous Vide
Steaming typically cooks vegetables at temperatures around 212degF (100degC), which can lead to slight nutrient loss due to high heat exposure. Sous vide steaming, however, uses precise temperature control often between 131degF to 185degF (55degC to 85degC), preserving more vitamins and maintaining optimal texture.
Sous vide offers unparalleled precision by immersing vegetables in vacuum-sealed bags, ensuring even cooking at targeted temperatures without overcooking. Traditional steaming exposes vegetables directly to steam heat, which is less precise and can result in uneven cooking or mushy textures. The controlled low-temperature environment of sous vide enhances flavor retention and nutrient preservation compared to standard steaming methods.
Nutrient Retention in Vegetables
Steaming vegetables preserves more vitamins and minerals compared to boiling, as it reduces nutrient loss by limiting water contact. Sous vide steaming, performed at precise, lower temperatures, further enhances nutrient retention by minimizing oxidation and leaching of water-soluble vitamins.
- Steaming retains water-soluble vitamins - Vitamins B and C are better preserved during steaming due to limited exposure to water.
- Sous vide offers temperature control - Precise heat regulation decreases nutrient degradation compared to traditional steaming.
- Sous vide minimizes nutrient leaching - Vacuum-sealed bags prevent vitamins from escaping into cooking water.
Flavor and Texture Differences
Steaming preserves the natural flavors and texture of vegetables by cooking them with moist heat, resulting in a tender yet slightly crisp bite. Sous vide steaming, by contrast, uses precise temperature control to enhance flavor infusion and maintain consistent, delicate textures without overcooking.
- Flavor retention in steaming - Traditional steaming keeps vegetables' natural sweetness intact by preventing nutrient and flavor loss.
- Enhanced flavor infusion in sous vide - Sous vide allows vegetables to absorb seasonings evenly, intensifying taste through sealed cooking bags.
- Texture control differences - Steaming may cause slight texture variation while sous vide ensures uniformly tender and perfectly cooked vegetables.
Cooking Time Comparison
Steaming vegetables typically takes 5 to 10 minutes, preserving nutrients while providing a crisp texture. Sous vide steaming requires longer cooking times, often 30 to 60 minutes, but ensures even heat distribution and enhanced flavor infusion. The precise temperature control in sous vide results in consistently tender vegetables compared to conventional steaming.
Best Vegetables for Each Method
Leafy greens such as spinach and kale retain more nutrients and vibrant color when steamed, making steaming ideal for delicate vegetables. Root vegetables like carrots, potatoes, and beets benefit from sous vide steaming, as the precise temperature control ensures even cooking and enhanced texture. Cruciferous vegetables including broccoli and cauliflower achieve optimal crisp-tender results with traditional steaming, while sous vide steaming preserves their subtle flavors and nutrients more effectively.
Related Important Terms
Precision Steam Cooking
Precision steam cooking enhances nutrient retention and texture in vegetables by carefully controlling temperature and humidity, unlike traditional steaming which may lead to uneven cooking. Sous vide steaming further refines this process by immersing vacuum-sealed vegetables in a precisely regulated water bath, ensuring consistent heat distribution and optimal flavor preservation.
Low-Temp Steam Infusion
Low-temp steam infusion preserves more nutrients and vibrant colors in vegetables compared to traditional sous vide steaming, as it operates at precisely controlled temperatures that prevent overcooking. This method enhances texture and flavor by allowing gentle steam penetration, maintaining freshness without water dilution or nutrient loss.
Active Steam Circulation
Active steam circulation in steaming ensures even heat distribution, preserving the natural texture and nutrients of vegetables more effectively than sous vide steaming. Unlike sous vide, this method rapidly cooks vegetables with uniform steam flow, enhancing flavor retention and reducing cooking time.
Sous Vide Steam Blending
Sous vide steam blending preserves maximum nutrients and enhances the natural flavors of vegetables by precisely controlling temperature and steam exposure during cooking. This method minimizes oxidation and texture loss compared to traditional steaming, resulting in vibrant, tender vegetables with superior taste and nutritional value.
Aroma Retention Steaming
Steaming preserves the natural aroma of vegetables by gently cooking them with hot steam, which minimizes flavor loss and enhances their fresh scent. Compared to sous vide steaming, traditional steaming allows more direct exposure to steam, resulting in better aroma retention and a more pronounced vegetable fragrance.
Vacuum-Assisted Steaming
Vacuum-assisted steaming enhances vegetable texture and nutrient retention by reducing cooking time and minimizing oxidation compared to traditional steaming and sous vide steaming. This method uses a vacuum to lower the boiling point of water, allowing for efficient heat transfer and preserving vibrant colors and natural flavors in vegetables.
Sous Vide Steam Compression
Sous vide steam compression preserves vegetable nutrients and texture by cooking at precise temperatures within sealed bags, preventing nutrient loss and overcooking common in traditional steaming. This method ensures enhanced flavor retention and consistent texture through controlled steam pressure and temperature regulation.
Steam Texture Enhancement
Steaming vegetables preserves their natural crunch by gently cooking them with moist heat, enhancing texture without sogginess, while sous vide steaming, using precise temperature control in vacuum-sealed bags, results in evenly tender but firmer textures. Steam texture enhancement through traditional steaming allows for quicker cooking times and better retention of vibrant colors and nutrients compared to sous vide methods.
Humidity-Controlled Steaming
Humidity-controlled steaming maintains optimal moisture levels for vegetables, preserving nutrients and texture better than traditional steaming methods. Unlike sous vide steaming, which relies on vacuum-sealed bags, humidity-controlled steaming provides more uniform heat distribution and prevents overcooking by precisely regulating steam saturation.
Steaming vs Sous Vide Steaming for vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com