Steaming preserves the natural aroma of ingredients by gently cooking them with moist heat, preventing flavor loss. Clay pot steaming enhances this effect by trapping steam within its porous surface, intensifying aroma retention and infusing a subtle earthy fragrance into the dish. This method allows for a richer sensory experience compared to conventional steaming techniques.
Table of Comparison
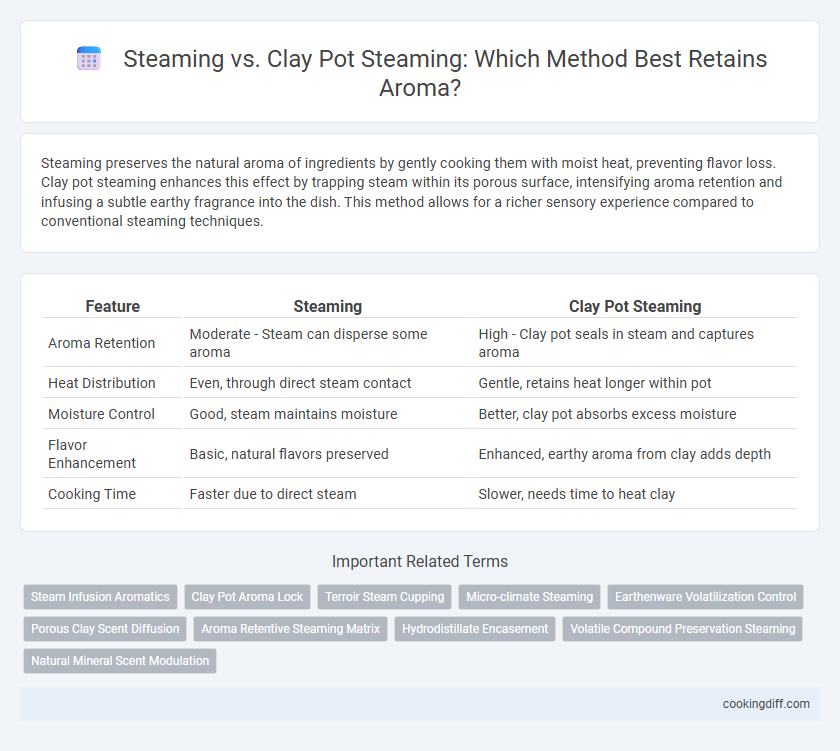
| Feature | Steaming | Clay Pot Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Aroma Retention | Moderate - Steam can disperse some aroma | High - Clay pot seals in steam and captures aroma |
| Heat Distribution | Even, through direct steam contact | Gentle, retains heat longer within pot |
| Moisture Control | Good, steam maintains moisture | Better, clay pot absorbs excess moisture |
| Flavor Enhancement | Basic, natural flavors preserved | Enhanced, earthy aroma from clay adds depth |
| Cooking Time | Faster due to direct steam | Slower, needs time to heat clay |
Introduction to Steaming and Clay Pot Steaming
Steaming is a popular cooking method that uses hot steam to cook food gently, preserving nutrients and natural flavors. Clay pot steaming enhances this process by using porous clay vessels that evenly distribute heat and moisture, intensifying aroma retention.
Traditional steaming involves placing food in a perforated container over boiling water, allowing steam to circulate freely. Clay pot steaming leverages the pot's unique material, which absorbs and releases moisture slowly, thus maintaining a richer scent profile. This method is especially effective for delicate ingredients like seafood and herbs, where aroma retention is crucial for flavor.
How Steaming Preserves Food Aromas
Steaming preserves food aromas by gently cooking ingredients with moist heat, which prevents the loss of volatile compounds responsible for fragrance. Unlike high-temperature methods, steaming maintains the integrity of natural oils and essences, resulting in enhanced flavor profiles.
Clay pot steaming traps steam and aromas within its porous surface, intensifying the scent and taste of food by allowing deeper absorption. The slow, even heat distribution in clay pots ensures that aroma compounds are effectively sealed inside, enhancing the overall sensory experience.
The Science Behind Clay Pot Steaming
Clay pot steaming utilizes porous ceramic material that traps steam and gradually releases heat, preserving volatile aromatic compounds better than traditional steaming. The slow, even heat distribution in clay pots minimizes aroma loss and enhances flavor concentration.
- Porosity of Clay - Clay's porous nature allows controlled moisture retention, maintaining essential oils and aromas within the food.
- Heat Distribution - Clay pots distribute heat evenly and slowly, preventing rapid evaporation that dilutes flavor intensity.
- Steam Circulation - The enclosed environment in clay pots reduces steam loss, capturing aromatic vapors and enhancing the sensory profile.
Aroma Retention: Steaming vs Clay Pot Methods
| Steaming Aroma Retention | Traditional steaming uses direct steam to cook food, which can dilute delicate aromas due to water vapor dispersion. |
| Clay Pot Steaming Aroma Retention | Clay pot steaming traps steam and essential oils within its porous walls, enhancing aroma concentration and preserving intense flavors. |
| Conclusion | Clay pot steaming offers superior aroma retention compared to standard steaming by maintaining moisture balance and capturing aromatic compounds effectively. |
Moisture and Flavor Sealing Mechanisms
How does steaming compare to clay pot steaming in terms of aroma retention? Steaming uses direct steam to cook food, which can sometimes allow aromatic compounds to escape with the moisture. Clay pot steaming traps steam and moisture within a sealed environment, enhancing flavor sealing by preserving essential oils and intensifying the food's natural aroma.
Ingredient Suitability for Each Method
Steaming preserves the natural aromas of delicate ingredients like fish and vegetables by using gentle, consistent heat. Clay pot steaming enhances aroma retention for rich, robust ingredients such as meats and dense root vegetables due to its moisture-trapping properties.
- Steaming suits delicate ingredients - It prevents overpowering flavors and maintains subtle aromas.
- Clay pot steaming excels with dense ingredients - The clay retains heat and moisture, intensifying aroma release.
- Ingredient moisture content impacts method choice - High-moisture foods benefit from traditional steaming while low-moisture foods achieve better aroma in clay pots.
Selecting the right steaming method optimizes aroma retention based on the ingredient's texture and moisture level.
Impact on Nutrient and Aroma Retention
Steaming preserves nutrients by using moist heat that minimizes nutrient loss, while clay pot steaming enhances aroma retention through its porous material that allows gradual flavor infusion. The gentle heat and moisture control in clay pots contribute to a richer, more sustained aroma experience compared to traditional steaming methods.
- Moist Heat Preservation - Steaming uses moist heat to retain water-soluble vitamins and minerals effectively during cooking.
- Porous Material Advantage - Clay pots' porous structure slowly absorbs and redistributes steam, enhancing aroma concentration in food.
- Flavor Infusion - The controlled environment in clay pot steaming enables deeper infusion of aromatic compounds, improving sensory quality.
Cultural Significance of Clay Pot Steaming
Clay pot steaming holds deep cultural significance in many Asian cuisines, enhancing aroma retention by allowing slow, even heat distribution that infuses food with earthy, natural flavors. Unlike conventional steaming methods, the porous surface of clay pots absorbs and gradually releases moisture, preserving the delicate spices and herbs essential to traditional recipes. This technique not only maintains the integrity of aromas but also embodies centuries of culinary heritage and regional identity.
Practical Tips for Maximizing Aroma with Each Method
Steaming food in a conventional steamer allows flavors to circulate evenly, preserving delicate aromas by using consistent steam temperature and avoiding direct water contact. To maximize aroma, use tightly covered lids and add aromatic herbs or spices in the steaming water.
Clay pot steaming enhances aroma retention due to its porous material that absorbs and gradually releases fragrance during cooking. For best results, preheat the clay pot and avoid overfilling with water, ensuring gentle steam infusion that intensifies natural flavors.
Related Important Terms
Steam Infusion Aromatics
Steam infusion aromatics in clay pot steaming enhance aroma retention by gently enveloping ingredients in concentrated steam infused with herbs and spices, preserving delicate flavors better than traditional steaming. The porous clay pot material absorbs and re-releases aromatic steam, intensifying the sensory experience through sustained, even heat distribution.
Clay Pot Aroma Lock
Clay pot steaming enhances aroma retention by creating a sealed environment that traps essential oils and flavors within the food, unlike standard steaming methods where steam disperses aromas quickly. The porous nature of the clay pot also absorbs and gradually releases fragrant compounds, intensifying the overall sensory experience.
Terroir Steam Cupping
Steaming preserves the natural aromas of ingredients by gently enveloping them in vapor, while clay pot steaming enhances aroma retention through porous earthenware that absorbs and intensifies flavors. Terroir Steam Cupping leverages this method to capture and highlight subtle regional nuances, maximizing the sensory experience of each terroir.
Micro-climate Steaming
Micro-climate steaming creates a sealed environment that traps moisture and heat, enhancing aroma retention by preventing the escape of volatile compounds during the cooking process. In comparison, clay pot steaming, while traditional, often allows more aroma diffusion, resulting in less concentrated flavor profiles.
Earthenware Volatilization Control
Clay pot steaming using earthenware significantly enhances aroma retention by minimizing volatilization through its porous structure, which traps steam and essential oils more effectively than conventional steaming methods. This controlled release of volatile compounds preserves the natural flavors and intensifies the sensory experience in steamed dishes.
Porous Clay Scent Diffusion
Porous clay pot steaming enhances aroma retention by allowing natural scent diffusion through its micro-pores, which absorb and gradually release essential flavors during cooking. This porous clay scent diffusion creates a more intense and authentic aroma compared to traditional steaming methods that use non-porous materials.
Aroma Retentive Steaming Matrix
Steaming preserves food aroma by using moist heat, which gently locks in volatile compounds, whereas clay pot steaming enhances aroma retention through its porous matrix that absorbs and gradually releases scents, creating a more intense and layered sensory experience. The Aroma Retentive Steaming Matrix in clay pot steaming facilitates optimal heat and vapor diffusion, maximizing the preservation and infusion of natural aromas during cooking.
Hydrodistillate Encasement
Steaming preserves aroma through hydrodistillate encasement by trapping volatile compounds within a moist, heated environment, while clay pot steaming enhances this effect by creating a sealed microclimate that intensifies fragrance retention. The porous nature of clay pots allows gradual vapor exchange, preventing aroma loss and promoting deeper infusion compared to conventional steaming methods.
Volatile Compound Preservation Steaming
Steaming preserves volatile compounds by using direct steam heat, which minimizes nutrient loss and retains the natural aroma of ingredients. Clay pot steaming, while slower, creates a sealed environment that traps steam and intensifies aroma retention by reducing the escape of volatile oils.
Steaming vs Clay Pot Steaming for aroma retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com