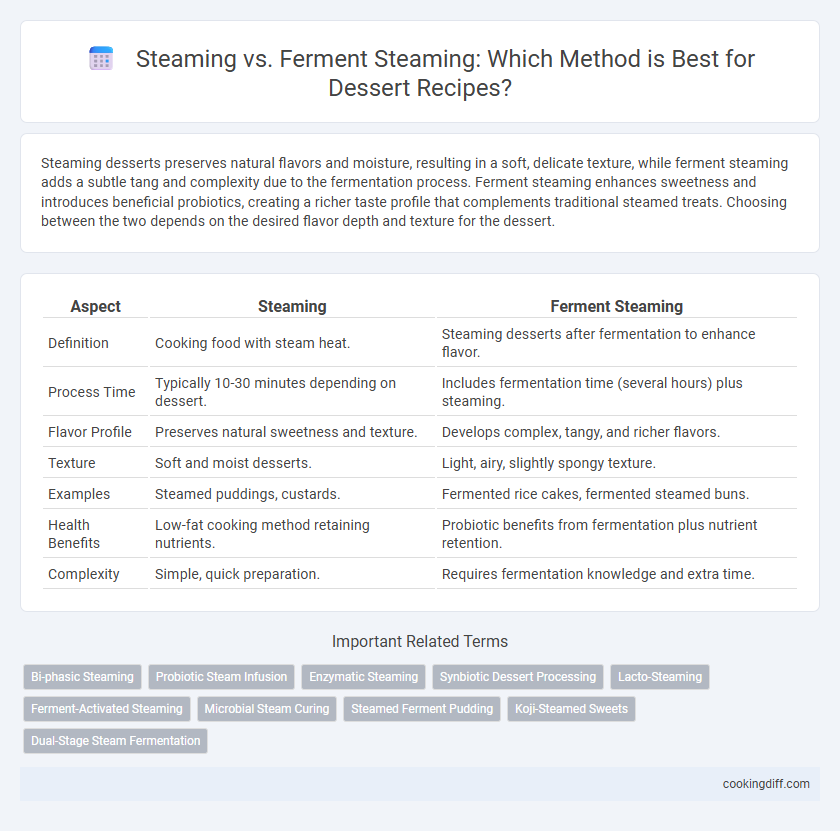
Steaming desserts preserves natural flavors and moisture, resulting in a soft, delicate texture, while ferment steaming adds a subtle tang and complexity due to the fermentation process. Ferment steaming enhances sweetness and introduces beneficial probiotics, creating a richer taste profile that complements traditional steamed treats. Choosing between the two depends on the desired flavor depth and texture for the dessert.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Steaming | Ferment Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food with steam heat. | Steaming desserts after fermentation to enhance flavor. |
| Process Time | Typically 10-30 minutes depending on dessert. | Includes fermentation time (several hours) plus steaming. |
| Flavor Profile | Preserves natural sweetness and texture. | Develops complex, tangy, and richer flavors. |
| Texture | Soft and moist desserts. | Light, airy, slightly spongy texture. |
| Examples | Steamed puddings, custards. | Fermented rice cakes, fermented steamed buns. |
| Health Benefits | Low-fat cooking method retaining nutrients. | Probiotic benefits from fermentation plus nutrient retention. |
| Complexity | Simple, quick preparation. | Requires fermentation knowledge and extra time. |
Introduction to Steaming and Ferment Steaming in Dessert Preparation
Steaming is a traditional cooking method that uses moist heat to cook desserts gently, preserving texture and flavor. Ferment steaming combines fermentation and steaming, adding unique tang and enhanced softness to desserts by allowing natural microbes to develop prior to cooking.
- Steaming - Utilizes direct exposure to steam for even, moisture-retentive cooking ideal for delicate sweets.
- Ferment Steaming - Involves fermenting batter or dough to develop flavor complexity and improved texture before steaming.
- Dessert Application - Both methods are widely used in Asian cuisine for cakes and puddings, with ferment steaming offering probiotics and deeper aroma.
How Traditional Steaming Works for Desserts
| Traditional steaming for desserts uses moist heat to cook ingredients evenly, preserving delicate textures and natural moisture. This method is ideal for custards, cakes, and puddings, as it prevents dryness and enhances softness in the final product. Temperature control between 90-100degC (194-212degF) ensures gentle cooking, allowing desserts to set without curdling or cracking. |
Understanding the Process of Ferment Steaming in Sweets
Ferment steaming involves allowing the batter or dough to undergo fermentation before the steaming process, which develops natural leavening through yeast or bacterial cultures. This creates a lighter texture and enhances the flavor profile in steamed desserts like mantou and fermented rice cakes.
In contrast, traditional steaming skips fermentation, resulting in denser and less complex-flavored sweets. Understanding the fermentation step is crucial for achieving the characteristic airy softness found in many Asian steamed desserts.
Key Differences Between Steaming and Ferment Steaming Methods
Steaming cooks desserts by using direct steam heat, preserving moisture and texture. Ferment steaming involves fermentation before steaming, enhancing flavor complexity and developing a slightly tangy taste.
- Cooking Process - Steaming applies immediate heat, while ferment steaming requires a prior fermentation period.
- Flavor Profile - Steamed desserts have a pure, subtle taste, whereas ferment steamed treats offer richer, fermented flavors.
- Texture Differences - Steaming yields smooth, soft textures, and ferment steaming produces denser, more aerated desserts.
Choosing between steaming and ferment steaming depends on desired flavor intensity and texture complexity for the dessert.
Flavor Impact: Steamed vs. Ferment Steamed Desserts
How does the flavor of steamed desserts compare to those that are ferment steamed? Steamed desserts offer a clean, delicate taste that highlights natural sweetness, while ferment steaming introduces complex tangy and umami notes due to microbial activity. This fermentation process deepens flavor profiles, resulting in richer and more nuanced dessert experiences.
Texture and Appearance: What Changes with Ferment Steaming?
Ferment steaming enhances dessert texture by introducing a light, airy crumb with subtle bubbles, contrasting with the denser, more uniform texture of traditional steaming. The fermentation process also deepens the color, creating a richer, golden hue that makes desserts visually more appealing. Overall, ferment steaming results in a fluffier texture and a more vibrant appearance, elevating the sensory experience of steamed desserts.
Nutritional Comparison: Steaming Versus Ferment Steaming
Steaming preserves most vitamins and minerals in desserts by using gentle heat, while ferment steaming enhances nutritional value by introducing probiotics and improving bioavailability of nutrients. Ferment steaming can increase the presence of beneficial enzymes and antioxidants compared to regular steaming, promoting better digestion and immune support.
- Steaming retains water-soluble vitamins - Gentle steaming minimizes nutrient loss, especially vitamin C and B-complex vitamins, keeping desserts nutritious.
- Ferment steaming boosts probiotics - The fermentation process fosters beneficial bacteria that improve gut health and nutrient absorption.
- Fermented desserts have enhanced antioxidants - Fermentation increases antioxidant levels, reducing oxidative stress more effectively than plain steaming.
Popular Steamed Desserts Around the World
Steaming preserves the delicate texture and natural flavors of desserts like Chinese baozi and Indian idli, which rely on heat and moisture. Ferment steaming enhances flavor complexity in desserts such as Korean tteok and Vietnamese banh beo by combining fermentation with steaming.
Popular steamed desserts around the world showcase unique cultural traditions. In Asia, steamed rice cakes, including Japanese mochi and Filipino puto, highlight the use of rice flour and natural fermentation. These desserts benefit from steaming methods that retain moisture and create soft, fluffy textures treasured by many.
Iconic Ferment Steamed Desserts to Try
Iconic ferment steamed desserts like Chinese red bean cake and Korean rice cake showcase unique textures and deep umami flavors developed through natural fermentation processes. Unlike traditional steaming, ferment steaming relies on microbial activity to enhance sweetness and create complex taste profiles, offering a distinctive culinary experience. Exploring these desserts reveals a rich cultural heritage and innovative techniques in Asian dessert preparation.
Related Important Terms
Bi-phasic Steaming
Bi-phasic steaming enhances dessert texture by combining an initial high-temperature steam phase to set the structure with a subsequent lower-temperature phase for gentle moisture retention, distinguishing it from traditional ferment steaming that relies primarily on fermentation for flavor and texture development; this method improves consistency and reduces fermentation time. Steaming desserts bi-phasically optimizes starch gelatinization and protein coagulation, achieving a more uniform crumb and preventing over-fermentation-related off-flavors typical in ferment steaming.
Probiotic Steam Infusion
Steaming coupled with probiotic steam infusion enhances desserts by preserving live beneficial bacteria, promoting gut health without compromising texture or flavor. Unlike traditional fermentation-steaming methods, probiotic steam infusion introduces targeted probiotics during the steaming process, ensuring a higher concentration of active cultures in the final dessert.
Enzymatic Steaming
Enzymatic steaming enhances dessert texture and flavor by activating natural enzymes that break down starches and proteins, unlike traditional steaming which relies solely on heat. This method promotes a tender crumb and intensified sweetness, offering a more complex sensory experience in delicacies such as steamed buns and puddings.
Synbiotic Dessert Processing
Steaming preserves the delicate texture and nutritional profile of desserts while enabling controlled heat transfer essential for synbiotic dessert processing, which combines probiotics and prebiotics for enhanced gut health benefits. Ferment steaming integrates microbial fermentation before steaming, enriching flavor complexity and bioactive compounds, thereby optimizing the synbiotic potential and improving digestive efficacy.
Lacto-Steaming
Lacto-steaming enhances desserts by combining steaming with lacto-fermentation, which introduces beneficial lactic acid bacteria that improve flavor complexity and texture. This method not only preserves the moisture and softness typical of traditional steaming but also adds natural probiotics, boosting the dessert's nutritional profile and digestibility.
Ferment-Activated Steaming
Ferment-Activated Steaming enhances dessert textures by utilizing microbial fermentation to produce natural gases that gently aerate batters, resulting in lighter, fluffier outcomes compared to traditional steaming. This method also improves flavor complexity and nutrient bioavailability by activating enzymes during fermentation, setting it apart from standard steaming techniques in dessert preparation.
Microbial Steam Curing
Microbial steam curing in steaming involves applying controlled heat to promote beneficial microbial activity, enhancing texture and flavor in desserts, unlike ferment steaming which relies primarily on microbial fermentation before steaming. This method optimizes microbial enzyme activation during steaming, leading to improved sweetness and softer crumb structures in traditional Asian pastries.
Steamed Ferment Pudding
Steamed ferment pudding combines the moist texture of traditional steaming with the complex flavors developed through fermentation, resulting in a richer taste and improved digestibility compared to standard steamed desserts. This method enhances the pudding's natural sweetness and creates a delicate, airy structure that distinguishes it from non-fermented steamed varieties.
Koji-Steamed Sweets
Koji-steamed sweets combine the natural enzymes of koji mold with steaming, enhancing sweetness and texture through enzymatic fermentation during cooking. This method contrasts traditional steaming by developing deeper umami flavors and improved digestibility, making desserts lighter and more complex in taste.
Steaming vs Ferment steaming for desserts Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com