Steaming preserves the natural texture and nutrients of food through moist heat, making it ideal for vegetables and delicate proteins. Sous-vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it at a precise, low temperature in a water bath, resulting in evenly cooked dishes with enhanced flavor and tenderness. While steaming offers simplicity and speed, sous-vide excels in precision and consistency for gourmet-level preparation.
Table of Comparison
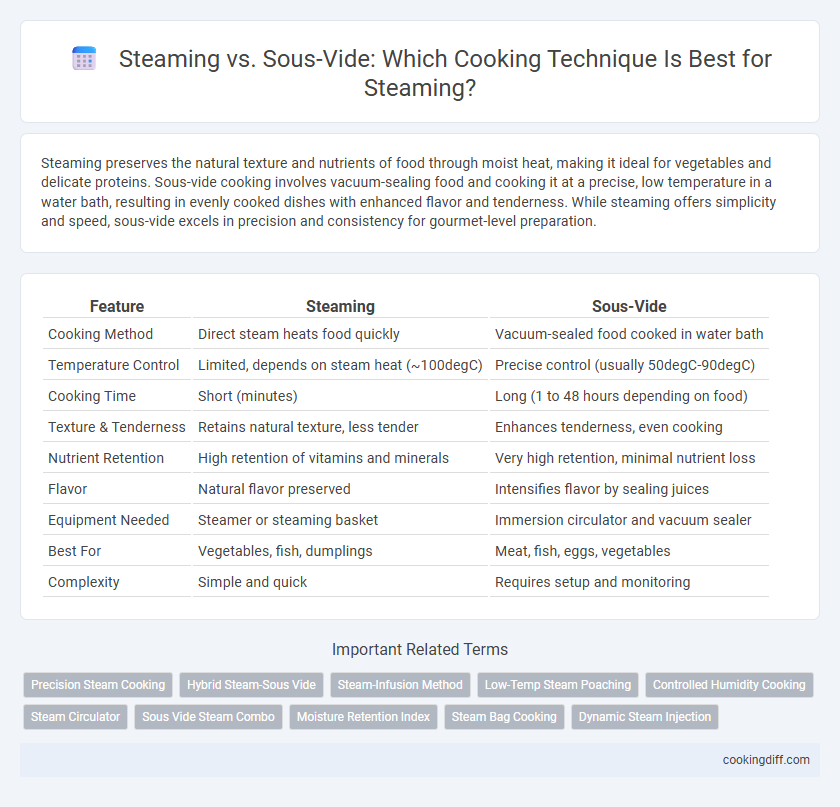
| Feature | Steaming | Sous-Vide |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Direct steam heats food quickly | Vacuum-sealed food cooked in water bath |
| Temperature Control | Limited, depends on steam heat (~100degC) | Precise control (usually 50degC-90degC) |
| Cooking Time | Short (minutes) | Long (1 to 48 hours depending on food) |
| Texture & Tenderness | Retains natural texture, less tender | Enhances tenderness, even cooking |
| Nutrient Retention | High retention of vitamins and minerals | Very high retention, minimal nutrient loss |
| Flavor | Natural flavor preserved | Intensifies flavor by sealing juices |
| Equipment Needed | Steamer or steaming basket | Immersion circulator and vacuum sealer |
| Best For | Vegetables, fish, dumplings | Meat, fish, eggs, vegetables |
| Complexity | Simple and quick | Requires setup and monitoring |
Introduction to Steaming and Sous-Vide Techniques
Steaming is a cooking method that uses hot vapor to gently cook food, preserving nutrients and texture. Sous-vide involves vacuum-sealing ingredients and cooking them in a temperature-controlled water bath for precise doneness. Both techniques emphasize moisture retention but differ in equipment and cooking time requirements.
How Steaming Works: Principles and Process
| Steaming operates by circulating hot steam around food, transferring heat through condensation to cook items evenly without direct contact with water. |
| The process preserves nutrients and natural flavors by using moist heat at temperatures typically between 100degC (212degF) and slightly above, depending on pressure. |
| Unlike sous-vide, which uses precise temperature control in sealed bags, steaming relies on steam's latent heat to rapidly cook and maintain food's texture and moisture. |
Sous-Vide Explained: Method and Equipment
What distinguishes sous-vide from traditional steaming techniques in cooking? Sous-vide involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a precisely temperature-controlled water bath, ensuring even doneness and retention of flavors. Essential equipment includes an immersion circulator and vacuum sealer, which maintain consistent heat and airtight conditions for optimal results.
Temperature and Precision: Comparing Control Levels
Steaming typically operates at 212degF (100degC), providing reliable heat but less precise control over cooking temperature compared to sous-vide techniques. Sous-vide cooking maintains exact temperatures, often ranging from 104degF to 195degF (40degC to 90degC), ensuring consistent doneness and texture.
The precision of sous-vide allows for slow, uniform cooking and reduces the risk of overcooking, which is harder to achieve with steaming due to its higher, less adjustable temperature. This temperature control makes sous-vide ideal for delicate proteins and complex recipes requiring exact timing.
Flavor Development: Steaming vs Sous-Vide
Steaming preserves the natural flavors of ingredients by gently cooking with moist heat, which prevents flavor loss. Sous-vide enhances flavor development by cooking food slowly in vacuum-sealed bags, allowing marinades and seasonings to infuse deeply.
- Steaming retains original taste - The steam's moisture locks in the food's intrinsic flavors without dilution.
- Sous-vide enhances infusion - Vacuum sealing allows seasonings to penetrate evenly and intensify flavor profiles.
- Texture impacts flavor perception - Sous-vide's low and slow cooking tenderizes food, enhancing flavor experience more than steaming's firmer results.
Nutrient Retention in Steamed and Sous-Vide Foods
Steaming preserves water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex by minimizing nutrient leaching during cooking. Sous-vide also retains nutrients effectively by sealing food in vacuum bags and cooking at precise, lower temperatures over extended periods.
- Higher retention of vitamin C in steaming - Steaming reduces nutrient loss caused by water contact compared to boiling.
- Enhanced nutrient preservation in sous-vide - Vacuum sealing prevents oxidation and nutrient degradation during cooking.
- Temperature control impact - Sous-vide's precise temperature maintains enzyme activity and nutrient integrity better than traditional steaming.
Choosing between steaming and sous-vide depends on the desired texture and cooking time alongside nutrient preservation.
Texture and Moisture: Outcomes in Both Methods
Steaming preserves the natural texture of food by gently cooking with moist heat, resulting in tender yet slightly firm vegetables and proteins. Sous-vide, however, utilizes precise temperature control to achieve uniformly soft and exceptionally moist textures without overcooking.
Both methods excel at retaining moisture, but sous-vide cooking seals food in vacuum bags, preventing moisture loss and intensifying flavor. Steaming allows for quicker cooking times but may lead to slight nutrient leaching into the steam. Choosing between them depends on whether desired texture favors the delicate bite of steaming or the melt-in-your-mouth sensation typical of sous-vide.
Suitability for Different Ingredients
Steaming is ideal for delicate vegetables and seafood that require gentle heat to retain texture and nutrients. Sous-vide excels with tougher cuts of meat and precise temperature control for even cooking throughout.
- Steaming suits delicate ingredients - It preserves color, nutrients, and moisture well in vegetables and fish.
- Sous-vide works best for meats - It tenderizes tougher proteins by cooking them slowly at consistent low temperatures.
- Ingredient texture impacts method choice - Soft ingredients benefit from steaming, while dense or fibrous items respond better to sous-vide.
Equipment, Cost, and Accessibility
Steaming requires minimal equipment, typically just a pot and a steaming basket, making it cost-effective and accessible for most home cooks. Sous-vide demands specialized devices such as immersion circulators and vacuum sealers, often resulting in higher initial investment costs. While steaming is widely available and easy to use, sous-vide offers precise temperature control but has limited accessibility due to equipment complexity and price.
Related Important Terms
Precision Steam Cooking
Precision steam cooking utilizes controlled steam temperature and humidity to evenly cook food while preserving texture and nutrients, offering faster results compared to sous-vide's long, low-temperature water bath. Unlike sous-vide, steaming requires no vacuum sealing and allows for immediate food transfer, enhancing convenience without sacrificing flavor or moisture retention.
Hybrid Steam-Sous Vide
Hybrid steam-sous vide cooking combines the precise temperature control of sous vide with the moisture-retaining benefits of steam, enhancing food texture and flavor while reducing cooking time. This method optimizes nutrient preservation and ensures even heat distribution, making it a superior choice for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Steam-Infusion Method
The steam-infusion method uses heated steam at precise temperatures to rapidly cook food while preserving nutrients and texture, unlike sous-vide, which relies on long, low-temperature water baths for even cooking. Steam-infusion offers faster cooking times, enhanced flavor retention, and reduced nutrient loss, making it ideal for delicate vegetables and seafood.
Low-Temp Steam Poaching
Low-temp steam poaching preserves delicate flavors and nutrients by cooking food gently at temperatures around 140degF to 160degF, preventing overcooking and moisture loss. Compared to sous-vide, this technique offers faster cooking times with less equipment required while maintaining tender textures and vibrant colors.
Controlled Humidity Cooking
Steaming utilizes high-humidity environments to cook food through moist heat, preserving nutrients and texture by maintaining consistent moisture levels. Sous-vide employs precise temperature control with vacuum-sealed bags, combining gentle heat and controlled humidity to ensure even cooking and enhanced flavor retention.
Steam Circulator
Steam circulators utilize precise temperature control to cook food evenly while preserving nutrients and texture, offering faster cooking times compared to sous-vide methods that rely on water immersion with longer heat transfer periods. Unlike sous-vide, steam circulation uses saturated steam to achieve higher temperatures quickly, ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables requiring rapid yet gentle cooking.
Sous Vide Steam Combo
The Sous Vide Steam Combo technique combines precise temperature control from sous-vide with the moisture retention benefits of steaming, resulting in evenly cooked, tender, and flavorful dishes. This hybrid method enhances texture and nutrient preservation compared to traditional steaming or sous-vide alone, making it ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Moisture Retention Index
Steaming preserves a high Moisture Retention Index by cooking food with direct steam heat, which minimizes water loss and maintains natural juiciness. Compared to sous-vide, steaming achieves faster moisture retention due to shorter cooking times without vacuum sealing, but sous-vide offers more precise temperature control for optimal texture and moisture preservation.
Steam Bag Cooking
Steam bag cooking preserves nutrients and enhances flavors by trapping steam and juices inside a sealed pouch, offering a quick and convenient alternative to sous-vide. Unlike sous-vide, steam bag cooking requires less time and specialized equipment while maintaining tender textures and vibrant colors in vegetables and proteins.
Steaming vs Sous-Vide for cooking technique. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com