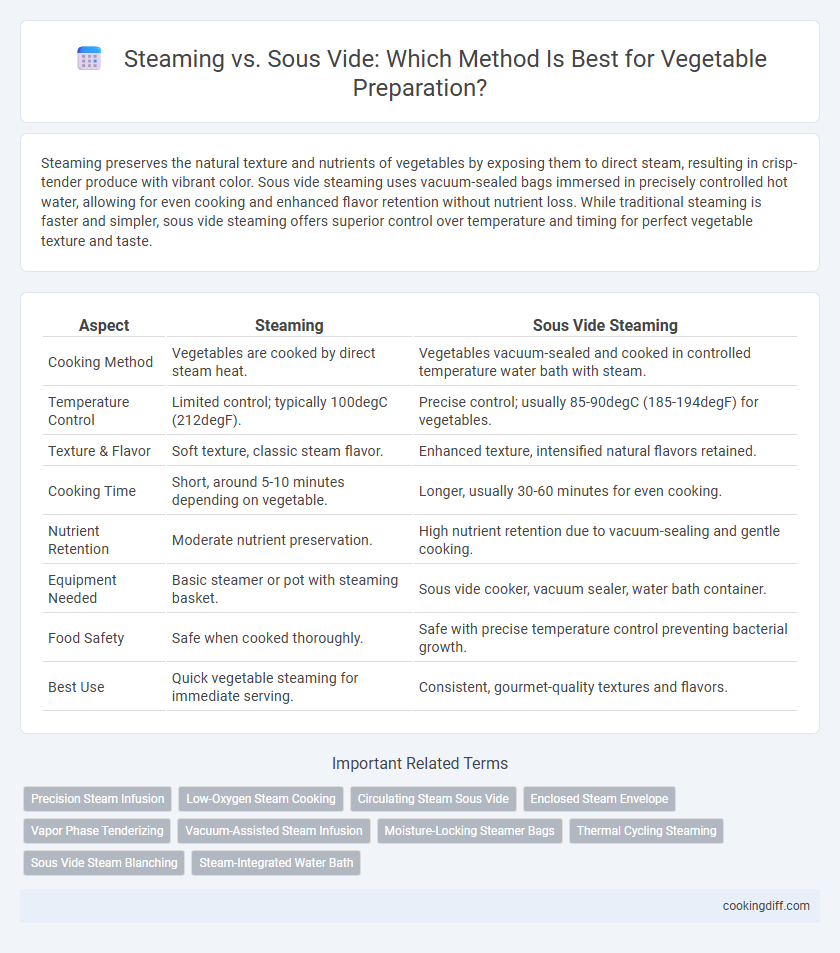
Steaming preserves the natural texture and nutrients of vegetables by exposing them to direct steam, resulting in crisp-tender produce with vibrant color. Sous vide steaming uses vacuum-sealed bags immersed in precisely controlled hot water, allowing for even cooking and enhanced flavor retention without nutrient loss. While traditional steaming is faster and simpler, sous vide steaming offers superior control over temperature and timing for perfect vegetable texture and taste.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Steaming | Sous Vide Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vegetables are cooked by direct steam heat. | Vegetables vacuum-sealed and cooked in controlled temperature water bath with steam. |
| Temperature Control | Limited control; typically 100degC (212degF). | Precise control; usually 85-90degC (185-194degF) for vegetables. |
| Texture & Flavor | Soft texture, classic steam flavor. | Enhanced texture, intensified natural flavors retained. |
| Cooking Time | Short, around 5-10 minutes depending on vegetable. | Longer, usually 30-60 minutes for even cooking. |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate nutrient preservation. | High nutrient retention due to vacuum-sealing and gentle cooking. |
| Equipment Needed | Basic steamer or pot with steaming basket. | Sous vide cooker, vacuum sealer, water bath container. |
| Food Safety | Safe when cooked thoroughly. | Safe with precise temperature control preventing bacterial growth. |
| Best Use | Quick vegetable steaming for immediate serving. | Consistent, gourmet-quality textures and flavors. |
Introduction: Steaming vs Sous Vide Steaming for Vegetables
Steaming and sous vide steaming are popular methods for cooking vegetables, each offering distinct benefits in texture and flavor preservation. Traditional steaming uses hot vapor to cook vegetables quickly, while sous vide steaming involves vacuum-sealing and precise temperature control.
Sous vide steaming enhances nutrient retention and produces uniformly cooked vegetables by maintaining consistent heat, which reduces overcooking and nutrient loss common in traditional steaming. This method also allows for infusing flavors by sealing herbs and spices with the vegetables. However, traditional steaming remains faster and requires less specialized equipment, making it accessible for everyday cooking.
How Traditional Steaming Works
Traditional steaming cooks vegetables by exposing them to hot steam generated from boiling water, which transfers heat quickly and preserves nutrients. The steam surrounds the vegetables, ensuring even cooking without direct contact with water, minimizing nutrient loss. This method maintains texture and vibrant color while softening vegetables efficiently within minutes.
The Science Behind Sous Vide Steaming
Sous vide steaming involves cooking vegetables in vacuum-sealed bags at precise, controlled temperatures, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than traditional steaming. This technique minimizes oxidation and nutrient loss by limiting exposure to oxygen and water.
The science behind sous vide steaming relies on stable low-temperature water baths that ensure even heat distribution, preventing overcooking and maintaining optimal cell structure in vegetables. This method enhances flavor retention and maximizes vitamin content, offering a superior cooking approach compared to conventional steaming.
Temperature Control: Precision Differences
Steaming typically uses boiling water at around 100degC, providing a consistent but less controllable temperature environment for cooking vegetables. Sous vide steaming offers precise temperature regulation, often within 0.1degC increments, allowing for exact texture and nutrient preservation in vegetables.
Temperature control in sous vide steaming prevents overcooking and maintains optimal vegetable firmness and flavor. Conventional steaming lacks this precision, which may result in uneven cooking and nutrient loss in sensitive vegetables.
Texture Comparison: Steamed vs Sous Vide Vegetables
Steamed vegetables often have a firmer texture due to direct exposure to high heat steam, which can sometimes cause uneven cooking. Sous vide steaming, however, allows precise temperature control, resulting in consistently tender and evenly cooked vegetables.
- Texture firmness - Steaming produces a slightly crisper bite by quickly cooking vegetables at high temperatures.
- Evenness - Sous vide steaming gently heats vegetables, ensuring uniform doneness throughout.
- Moisture retention - Sous vide steaming preserves natural moisture better than traditional steaming methods.
Sous vide steaming offers superior texture control, making vegetables tender yet retaining their natural structure more effectively than conventional steaming.
Flavor Retention in Steaming Methods
Steaming preserves more vitamins and minerals in vegetables compared to boiling, enhancing flavor retention by preventing nutrient loss. Sous vide steaming offers precise temperature control, resulting in even cooking and intensified natural flavors without overcooking.
- Traditional Steaming - Uses direct steam to cook vegetables quickly while maintaining moisture, but can result in slight nutrient leaching.
- Sous Vide Steaming - Utilizes vacuum-sealed bags and regulated low temperatures to lock in flavors and nutrients efficiently.
- Flavor Retention - Sous vide steaming outperforms traditional methods by minimizing flavor dilution and preserving vegetable texture.
Nutrient Preservation: Which Technique Wins?
| Technique | Nutrient Preservation |
|---|---|
| Steaming | Uses hot steam to cook vegetables, retaining more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C compared to boiling because it limits direct contact with water. Heat exposure is minimized, but rapid cooking may cause some nutrient loss. |
| Sous Vide Steaming | Vegetables are vacuum-sealed and cooked at precisely controlled low temperatures, significantly preserving heat-sensitive nutrients and antioxidants. Prolonged exposure to gentle heat reduces nutrient degradation better than traditional steaming. |
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Traditional steaming requires basic equipment such as a pot with a steaming basket or an electric steamer, which are widely available and easy to set up. Sous vide steaming, on the other hand, demands specialized sous vide devices that precisely control water temperature and often include vacuum sealers for airtight cooking.
- Traditional steamer - Uses simple pots or electric steamers with baskets for direct steam exposure.
- Sous vide setup - Requires immersion circulators to maintain exact temperatures and vacuum-sealed bags to cook vegetables evenly.
- Space and cost - Sous vide equipment is generally more expensive and takes up more kitchen space compared to conventional steamers.
Efficiency and Cooking Times
Steaming typically requires less time than sous vide steaming, often completing vegetable cooking in 5 to 10 minutes depending on the vegetable type and size. Sous vide steaming, while slower, offers precise temperature control that enhances texture and nutrient retention, making it ideal for delicate or nutrient-sensitive vegetables. Efficiency in steaming favors quick preparation, whereas sous vide prioritizes consistent, high-quality results through controlled cooking times ranging from 20 to 60 minutes.
Related Important Terms
Precision Steam Infusion
Precision Steam Infusion delivers targeted, controlled steam that preserves vegetable nutrients and texture more effectively than traditional steaming, enhancing flavor and color vibrancy. Sous vide steaming offers precise temperature control but lacks the rapid infusion and uniform heat distribution of Precision Steam Infusion, resulting in less efficient cooking and potentially uneven texture.
Low-Oxygen Steam Cooking
Low-oxygen steam cooking preserves vegetable nutrients and vibrant colors more effectively than traditional sous vide steaming by minimizing oxidation and nutrient loss. This method uses a controlled steam environment with reduced oxygen levels, enhancing flavor retention and texture while maintaining optimal moisture.
Circulating Steam Sous Vide
Circulating steam sous vide technology ensures precise temperature control and even heat distribution, preserving the nutrients and vibrant colors of vegetables better than traditional steaming methods. This technique enhances flavor retention and texture by maintaining a consistent steam flow, reducing the risk of overcooking or uneven softening.
Enclosed Steam Envelope
Enclosed steam envelopes in steaming create a high-humidity environment that preserves vegetable nutrients and texture by preventing moisture loss, while sous vide steaming uses vacuum-sealed bags to maintain precise temperature control and enhance flavor infusion. This controlled enclosure in sous vide steaming also minimizes nutrient degradation compared to traditional steaming methods, optimizing both taste and health benefits.
Vapor Phase Tenderizing
Vapor phase tenderizing in steaming preserves vegetable nutrients by using hot steam to gently penetrate and soften fibers without direct water contact, maintaining texture and flavor integrity. Sous vide steaming, while precise in temperature control, often relies on water immersion that can leach vitamins, making vapor phase steaming superior for nutrient retention and tenderness in vegetable preparation.
Vacuum-Assisted Steam Infusion
Vacuum-assisted steam infusion enhances vegetable preparation by rapidly infusing steam under reduced pressure, preserving nutrients and vibrant colors more effectively than traditional steaming or sous vide steaming methods. This technology ensures even heat distribution and faster cooking times while maintaining texture and maximizing flavor retention.
Moisture-Locking Steamer Bags
Moisture-locking steamer bags enhance steaming by retaining water vapor, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than traditional sous vide steaming for vegetables. These bags prevent nutrient loss and maintain optimal moisture levels, ensuring crisp yet tender vegetable results.
Thermal Cycling Steaming
Thermal cycling steaming enhances vegetable texture and nutrient retention by alternating precise temperature phases, unlike the consistent low temperature in sous vide steaming. This method prevents overcooking and preserves vibrant colors while maintaining the natural flavors and crispness of vegetables.
Sous Vide Steam Blanching
Sous vide steam blanching preserves vegetable nutrients and texture by cooking at precise low temperatures in a controlled steam environment, reducing nutrient loss compared to traditional steaming. This method enhances flavor retention and ensures even heat distribution, making it ideal for delicate vegetables and extended storage.
Steaming vs Sous Vide Steaming for vegetable preparation. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com