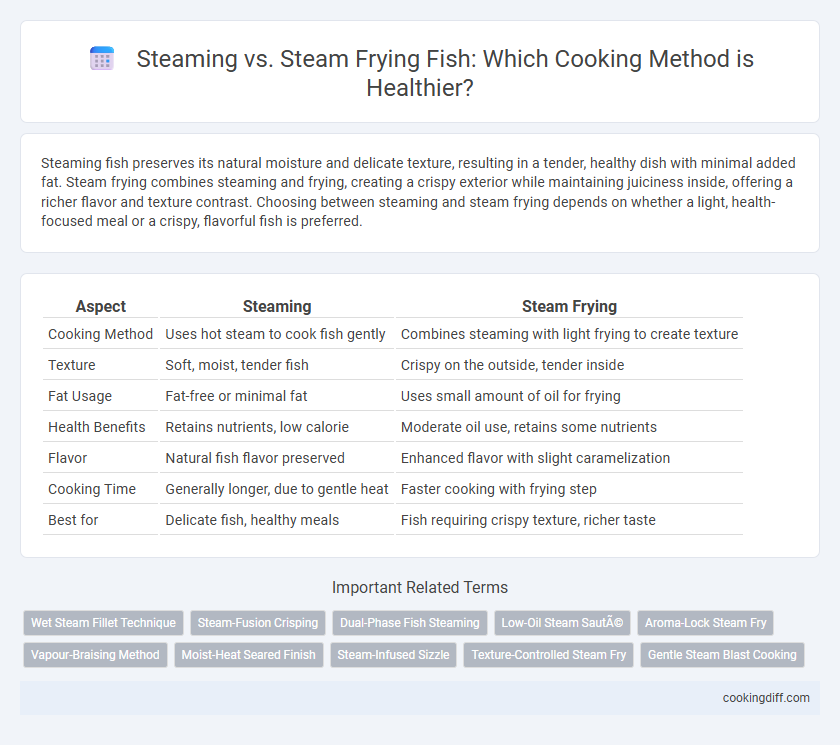
Steaming fish preserves its natural moisture and delicate texture, resulting in a tender, healthy dish with minimal added fat. Steam frying combines steaming and frying, creating a crispy exterior while maintaining juiciness inside, offering a richer flavor and texture contrast. Choosing between steaming and steam frying depends on whether a light, health-focused meal or a crispy, flavorful fish is preferred.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Steaming | Steam Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses hot steam to cook fish gently | Combines steaming with light frying to create texture |
| Texture | Soft, moist, tender fish | Crispy on the outside, tender inside |
| Fat Usage | Fat-free or minimal fat | Uses small amount of oil for frying |
| Health Benefits | Retains nutrients, low calorie | Moderate oil use, retains some nutrients |
| Flavor | Natural fish flavor preserved | Enhanced flavor with slight caramelization |
| Cooking Time | Generally longer, due to gentle heat | Faster cooking with frying step |
| Best for | Delicate fish, healthy meals | Fish requiring crispy texture, richer taste |
Introduction to Steaming and Steam Frying Fish
Steaming is a gentle cooking method that uses vaporized water to cook fish, preserving its moisture and delicate texture. Steam frying combines steaming and pan-frying techniques, offering a balance of tenderness and a crispy exterior.
- Steaming - Requires a closed environment where steam circulates, cooking fish evenly without added fats.
- Steam Frying - Involves initially steaming fish, then frying briefly to develop a golden crust.
- Flavor Profile - Steaming maintains a clean, subtle taste while steam frying adds texture and richer flavor.
How Steaming Works for Cooking Fish
Steaming cooks fish by surrounding it with hot steam, preserving moisture and enhancing natural flavors while retaining nutrients. The steam transfers heat evenly, ensuring the fish remains tender and flaky without drying out.
Steam frying combines steaming with a quick saute, using minimal oil to create a crispy exterior while maintaining the moist interior achieved by steam. This method speeds up cooking time and adds texture contrasts not found in traditional steaming. Steam frying requires precise temperature control to balance moisture retention and browning.
The Steam Frying Technique Explained
Steam frying combines the benefits of steaming and frying by cooking fish in a small amount of oil with steam, resulting in a crispy texture while retaining moisture. This technique allows fish to cook evenly without drying out, offering a flavorful alternative to traditional methods.
- Cooking Process - Steam frying involves sealing the fish in a pan with a bit of oil and adding water or broth to generate steam during cooking.
- Texture Outcome - The steam softens the fish's interior while the oil crisps the exterior, achieving a balanced texture.
- Nutritional Benefits - This method reduces oil absorption compared to deep frying, making it a healthier option for preparing fish.
Nutritional Differences: Steaming vs Steam Frying Fish
Steaming fish preserves more water-soluble vitamins such as B vitamins and antioxidants due to the gentle cooking method, which minimizes nutrient loss. This technique also retains omega-3 fatty acids crucial for heart health, as it avoids high temperatures and added fats.
Steam frying combines steaming with frying using a small amount of oil, slightly increasing calorie content and introducing healthy fats depending on the oil used. While steam frying enhances flavor and texture, it may reduce some heat-sensitive nutrients compared to pure steaming, impacting the overall nutritional profile.
Texture and Flavor: Comparing Both Methods
Steaming fish preserves its delicate texture by cooking it gently with moist heat, resulting in tender and flaky flesh. Steam frying combines the benefits of steaming and frying, producing a slightly crisp exterior while maintaining moisture inside. Flavor-wise, steaming highlights the natural taste of fish, whereas steam frying adds a subtle caramelized richness due to the Maillard reaction.
Time and Convenience: Which Method Is Faster?
Steaming fish typically takes 10 to 15 minutes, offering a hands-off cooking experience that requires minimal attention. Steam frying combines steaming and frying, cooking fish faster, usually within 7 to 10 minutes, while also delivering a crispy texture. For those prioritizing speed and convenience, steam frying is generally the quicker method without sacrificing flavor.
Equipment Needed for Steaming and Steam Frying Fish
| Steaming Equipment | Steaming fish requires a steamer basket or an electric steamer, often used with a pot or wok to hold boiling water. Bamboo steamers are preferred for retaining moisture and flavor, while stainless steel steamers provide durability and even heat distribution. A lid to trap steam and a heat source like a stove are essential components for efficient steaming. |
|---|---|
| Steam Frying Equipment | Steam frying fish utilizes a special steam fryer or a deep pan with a fitted lid to contain both steam and oil for frying. This equipment allows simultaneous steaming and shallow frying by maintaining a controlled temperature and moisture environment. Temperature control devices and oil with a high smoke point are critical for achieving the desired crispy texture without overcooking. |
Best Types of Fish for Each Cooking Method
Steaming is ideal for delicate fish such as cod, sole, and flounder, as it preserves moisture and enhances natural flavors without added fat. Steam frying suits firmer fish like salmon, tuna, and swordfish, enabling a crispy exterior while retaining a moist interior.
White fish like tilapia and haddock benefit from gentle steaming to avoid flaking, while oily fish such as mackerel and trout excel in steam frying due to their higher fat content. Choosing the right cooking method depends on the fish's texture and fat level to optimize taste and nutritional value.
Health Benefits: Steaming vs Steam Frying Fish
What are the health benefits of steaming fish compared to steam frying? Steaming fish preserves more nutrients and reduces fat intake as it uses only water vapor without added oils. Steam frying, while slightly higher in calories, enhances flavor and texture by combining steaming with a light oil saute, but may introduce more fats into the diet.
Related Important Terms
Wet Steam Fillet Technique
Wet steam fillet technique preserves the fish's natural moisture and delicate texture by cooking it gently with steam, ensuring even heat distribution without direct contact with water. Compared to steam frying, wet steaming reduces fat content and prevents the Maillard reaction, resulting in a tender, flaky fillet ideal for health-conscious recipes.
Steam-Fusion Crisping
Steam-Fusion Crisping combines the gentle moisture of steaming with a high-heat searing technique, creating fish that is tender inside with a perfectly crisped exterior. This method preserves delicate flavors while enhancing texture, offering a superior alternative to traditional steaming or steam frying alone.
Dual-Phase Fish Steaming
Dual-phase fish steaming combines traditional steaming with a brief steam frying phase, enhancing flavor and texture by locking in moisture while creating a slightly crispy exterior. This method optimizes nutrient retention and results in a tender, juicy interior with a delicate, savory crust, offering a superior alternative to conventional steaming or steam frying alone.
Low-Oil Steam Sauté
Low-oil steam saute combines the gentle heat of traditional steaming with the slight caramelization of steam frying, using minimal oil to preserve the fish's delicate texture and enhance natural flavors. This method reduces fat content while maintaining moisture, resulting in a healthier, tender, and flavorful fish compared to conventional frying techniques.
Aroma-Lock Steam Fry
Aroma-Lock Steam Fry preserves the natural flavor and nutrients of fish by combining the benefits of steaming with a light frying technique, resulting in a crispy texture without losing moisture. Unlike traditional steaming, this method enhances aroma retention and delivers a rich, savory taste while avoiding excess oil absorption.
Vapour-Braising Method
Vapour-braising combines the gentle heat of steaming with light sauteing, preserving the fish's moisture and enhancing its natural flavors through a slight caramelization. This method uses minimal oil and intense steam to create a tender texture while infusing the fish with savory, aromatic notes often lost in traditional steaming or steam frying.
Moist-Heat Seared Finish
Steaming preserves the delicate texture and moisture of fish by cooking it evenly with moist heat, while steam frying combines steaming with a high-heat sear to create a crisp, golden exterior. This hybrid technique enhances flavor through caramelization while maintaining the fish's tenderness and juiciness.
Steam-Infused Sizzle
Steam-infused sizzle in steam frying enhances fish by combining the gentle moisture of steaming with the crisp texture of frying, preserving delicate flavors and nutrients. This method creates a perfectly balanced dish where the fish remains tender inside with a golden, slightly crispy exterior, maximizing both taste and health benefits.
Texture-Controlled Steam Fry
Texture-controlled steam fry enhances fish by combining gentle steam cooking with a quick, high-heat searing that locks in moisture and creates a crispy exterior, unlike traditional steaming which yields a uniformly soft texture. This method balances tenderness and a golden crust, improving flavor complexity and visual appeal while preserving the fish's delicate structure.
Steaming vs Steam Frying for fish. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com