Steaming uses direct contact with steam to cook food evenly while preserving moisture and nutrients, making it ideal for vegetables and delicate proteins. Steam infusion combines vapor and liquid steam to enhance heat transfer, resulting in faster cooking times and more uniform temperature distribution. Choosing between steaming and steam infusion depends on the desired cooking speed and texture precision for different food types.
Table of Comparison
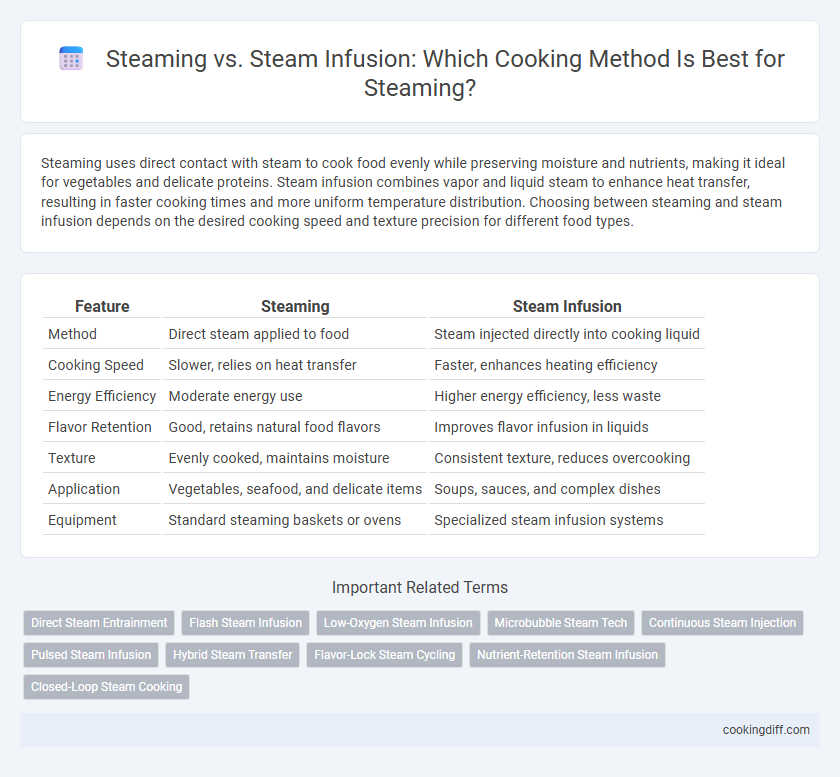
| Feature | Steaming | Steam Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Direct steam applied to food | Steam injected directly into cooking liquid |
| Cooking Speed | Slower, relies on heat transfer | Faster, enhances heating efficiency |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy use | Higher energy efficiency, less waste |
| Flavor Retention | Good, retains natural food flavors | Improves flavor infusion in liquids |
| Texture | Evenly cooked, maintains moisture | Consistent texture, reduces overcooking |
| Application | Vegetables, seafood, and delicate items | Soups, sauces, and complex dishes |
| Equipment | Standard steaming baskets or ovens | Specialized steam infusion systems |
Introduction to Steaming and Steam Infusion
Steaming is a traditional cooking method that uses hot steam to gently cook food, preserving nutrients and natural flavors. It involves surrounding ingredients with moist heat, making it ideal for vegetables, seafood, and delicate proteins.
Steam infusion is an advanced variation that introduces steam directly into food or liquid through specialized equipment, enhancing heat transfer and reducing cooking times. This technique improves flavor absorption and texture consistency while maintaining nutritional value. Steam infusion is often used in industrial food processing and high-end culinary applications for precise temperature control.
How Steaming Works: Traditional Method Explained
Steaming works by circulating hot vapor around food, allowing heat to cook it gently without direct contact with water. Traditional steaming uses a pot with boiling water beneath a perforated basket or rack where the food sits, ensuring even heat distribution. This method preserves nutrients and texture by cooking at lower temperatures compared to boiling or frying.
What Is Steam Infusion? An Overview
Steam infusion is a cooking technique where steam is directly injected into the food, enhancing heat transfer and reducing cooking time compared to traditional steaming. This method allows for more precise temperature control and improved flavor retention.
- Enhanced heat transfer - Steam infusion injects steam directly into the food, providing rapid and uniform cooking.
- Reduced cooking time - The direct contact with steam accelerates the heating process, significantly cutting down preparation time.
- Improved flavor retention - Steam infusion minimizes nutrient loss and preserves the food's natural taste better than conventional steaming.
Cooking Performance: Flavor and Texture Differences
How does steaming compare to steam infusion in terms of cooking performance regarding flavor and texture? Steaming preserves the natural flavors and nutrients by cooking food gently with hot steam, resulting in a tender texture without moisture loss. Steam infusion enhances flavor penetration and uniform cooking by injecting steam directly into the food, creating a more intense taste and consistent texture throughout.
Nutrient Retention: Comparing Both Techniques
Steaming preserves nutrients by cooking food with moist heat, minimizing vitamin loss and maintaining antioxidant levels. Steam infusion uses pressurized steam for faster cooking but may cause slightly higher nutrient degradation due to intense heat exposure.
- Steaming retains water-soluble vitamins - Gentle heat prevents leaching of vitamins like B and C during cooking.
- Steam infusion accelerates cooking - High-pressure steam shortens cooking time, which can reduce nutrient breakdown.
- Both methods reduce fat usage - Cooking without oil helps preserve nutrient density and overall food quality.
Steaming is generally superior for nutrient retention, while steam infusion offers speed with a modest trade-off in vitamin preservation.
Equipment Needed: Steaming vs Steam Infusion
Steaming typically requires basic equipment such as steamers, pots with lids, or bamboo steam baskets that generate steam through boiling water. These tools are affordable and easy to use in both home and professional kitchens.
Steam infusion systems demand specialized machinery that injects steam directly into the food or cooking medium, often involving advanced controls and stainless steel nozzles. This equipment is more expensive and commonly found in industrial or high-end culinary environments.
Versatility: Suitable Foods for Each Method
Steaming is highly versatile for cooking a wide range of foods including vegetables, fish, and dumplings, preserving nutrients and texture effectively. Steam infusion, on the other hand, is particularly suited for delicate items such as custards and sauces where gentle, evenly distributed heat is essential.
While steaming accommodates bulkier and firmer foods, steam infusion excels in culinary applications requiring precise temperature control and uniform cooking. Both methods enhance moisture retention but differ in suitability based on the food's texture and cooking requirements.
Energy Efficiency and Cooking Time
Steaming uses direct steam contact to cook food, resulting in moderate energy consumption and average cooking times. Steam infusion injects high-velocity steam into the cooking chamber, significantly reducing energy usage by up to 30% and cutting cooking time by nearly 50%. This method enhances heat transfer efficiency, making it ideal for energy-conscious kitchens aiming to speed up meal preparation.
Health Benefits: Which Method Is Healthier?
Steaming preserves nutrients by cooking food at lower temperatures using steam, minimizing nutrient loss. Steam infusion combines rapid steam injection with vacuum technology, which can further reduce cooking time and preserve vitamins and minerals more effectively.
- Steaming retains nutrients - This method uses gentle heat, which helps maintain water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex.
- Steam infusion accelerates cooking - Faster cooking times mean reduced exposure to heat, preserving delicate nutrients better than traditional steaming.
- Both methods reduce fat usage - They cook food without oil, supporting heart-healthy and low-calorie meal preparation.
Related Important Terms
Direct Steam Entrainment
Direct steam entrainment involves injecting steam directly into food, ensuring rapid heat transfer and uniform cooking, which enhances texture and flavor retention compared to traditional steaming methods. This technique contrasts with steam infusion, where steam is mixed with food in a controlled environment, resulting in gentler heating but slower cooking times.
Flash Steam Infusion
Flash Steam Infusion delivers rapid heat transfer by injecting steam directly into food, ensuring faster cooking times and enhanced flavor retention compared to traditional steaming methods. This technique reduces nutrient loss and improves texture by maintaining high moisture levels while minimizing exposure to prolonged heat.
Low-Oxygen Steam Infusion
Low-oxygen steam infusion significantly reduces oxidation during cooking, preserving flavor, color, and nutritional value compared to traditional steaming methods. This technique injects steam directly into the food under controlled low-oxygen conditions, enhancing heat transfer efficiency and reducing cooking times while maintaining superior food quality.
Microbubble Steam Tech
Microbubble steam technology enhances steaming by producing ultra-fine steam particles that penetrate food more efficiently than traditional steam infusion, resulting in faster cooking and improved nutrient retention. This method ensures uniform heat distribution and superior flavor preservation compared to conventional steaming techniques.
Continuous Steam Injection
Continuous steam injection delivers rapid, uniform heat transfer by directly infusing steam into the cooking medium, enhancing flavor retention and reducing cooking time compared to traditional steaming methods. Steam infusion technology ensures consistent temperature control and energy efficiency, offering superior texture and moisture preservation in various culinary applications.
Pulsed Steam Infusion
Pulsed Steam Infusion offers rapid, energy-efficient cooking by injecting high-velocity steam directly into food, reducing cooking time while preserving flavor and nutrients compared to traditional steaming methods. Unlike conventional steaming, this technique ensures uniform heat distribution and minimizes moisture loss, enhancing texture and taste in culinary applications.
Hybrid Steam Transfer
Hybrid Steam Transfer combines the benefits of traditional steaming and steam infusion, enhancing heat distribution and reducing cooking time while preserving food texture and nutrients. This method uses direct steam injection alongside gentle convection, optimizing energy efficiency and ensuring uniform cooking in commercial kitchens.
Flavor-Lock Steam Cycling
Flavor-Lock Steam Cycling enhances traditional steaming by repeatedly cycling steam to maintain optimal temperature and moisture, preserving the natural flavors and nutrients of food more effectively than continuous steam infusion. This method prevents overcooking and waterlogging, resulting in vibrant, flavorful dishes with superior texture and aroma.
Nutrient-Retention Steam Infusion
Steam infusion cooking enhances nutrient retention by rapidly circulating steam around food, reducing cooking time and minimizing nutrient leaching compared to traditional steaming methods. This technique preserves vitamins and minerals more effectively, making it ideal for maintaining the nutritional value of vegetables and delicate ingredients.
Steaming vs Steam Infusion for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com