Steaming preserves the natural texture and nutrients of vegetables by using direct steam heat, resulting in evenly cooked produce with a fresh taste. Steam infusion, by contrast, incorporates steam directly into the cooking medium, enhancing flavor and reducing cooking time while maintaining moisture and tenderness. Choosing between steaming and steam infusion depends on desired texture and cooking efficiency for vegetable preparation.
Table of Comparison
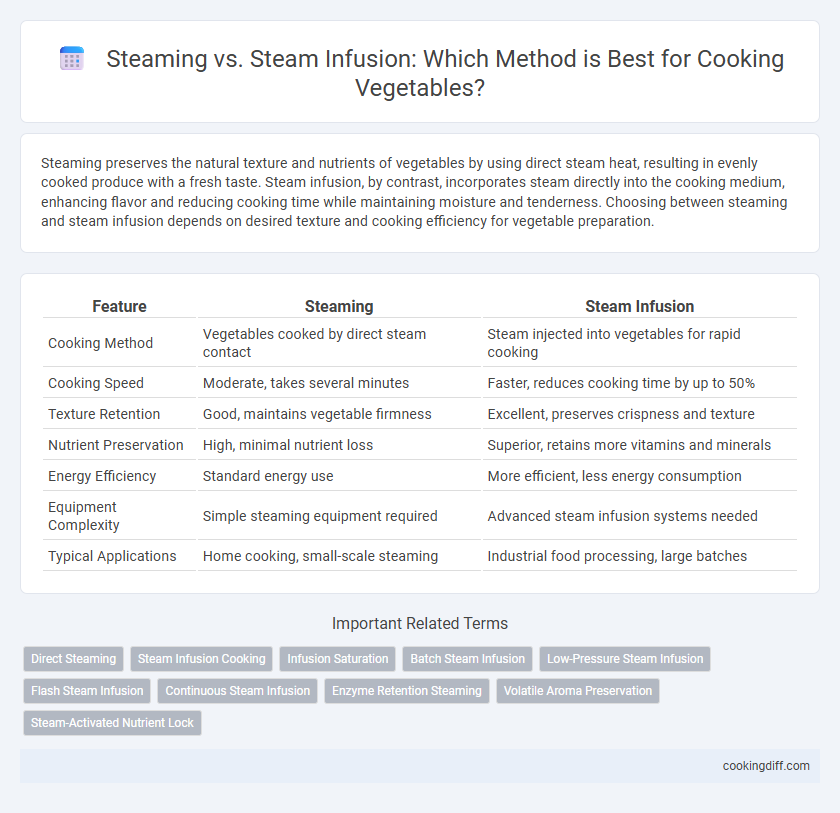
| Feature | Steaming | Steam Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vegetables cooked by direct steam contact | Steam injected into vegetables for rapid cooking |
| Cooking Speed | Moderate, takes several minutes | Faster, reduces cooking time by up to 50% |
| Texture Retention | Good, maintains vegetable firmness | Excellent, preserves crispness and texture |
| Nutrient Preservation | High, minimal nutrient loss | Superior, retains more vitamins and minerals |
| Energy Efficiency | Standard energy use | More efficient, less energy consumption |
| Equipment Complexity | Simple steaming equipment required | Advanced steam infusion systems needed |
| Typical Applications | Home cooking, small-scale steaming | Industrial food processing, large batches |
Introduction to Vegetable Steaming Methods
Vegetable steaming preserves nutrients and enhances natural flavors through the use of hot steam. Traditional steaming uses indirect steam to cook vegetables evenly without submerging them in water. Steam infusion combines steam with a mixing process, providing faster cooking times and more uniform heat distribution for improved texture and taste.
What is Traditional Steaming?
| Traditional steaming cooks vegetables by exposing them to hot steam from boiling water, preserving nutrients and texture without direct contact with water. The steam transfers heat efficiently, ensuring even cooking while retaining the vegetable's natural flavor. This method maintains crispness and color, making it a preferred choice for healthy vegetable preparation. |
What is Steam Infusion Cooking?
Steam infusion cooking involves directly injecting steam into food, enhancing heat transfer and preserving nutrients more efficiently than traditional steaming. This method reduces cooking time and maintains the vibrant colors and textures of vegetables by minimizing water contact.
Unlike conventional steaming, steam infusion uses pressurized steam to penetrate the food faster, ensuring even cooking and fewer nutrient losses. It is particularly effective for delicate vegetables, offering superior flavor retention and improved overall quality.
Key Differences: Steaming vs Steam Infusion
Steaming involves cooking vegetables by exposing them directly to steam, preserving nutrients and texture without submerging them in water. Steam infusion, however, uses a controlled injection of steam into a liquid or vacuum environment to rapidly cook and infuse flavors into vegetables.
Steaming typically results in evenly cooked, tender vegetables with minimal flavor alteration, ideal for maintaining natural taste and vitamins. Steam infusion enhances flavor penetration and reduces cooking time by combining steam with other ingredients or vacuum conditions for more complex dishes.
Nutritional Retention: Which Method Is Better?
Steaming preserves more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex compared to steam infusion, which may lead to some nutrient leaching. Steam infusion offers faster cooking times but can reduce overall nutritional retention due to higher exposure to steam pressure and temperature.
- Higher Vitamin Retention in Steaming - Steaming maintains more antioxidants and minerals by gently cooking vegetables without direct contact with water.
- Faster Cooking with Steam Infusion - Steam infusion reduces cooking time significantly but may compromise heat-sensitive nutrients.
- Better Texture and Color Preservation - Steaming helps retain the natural color and texture of vegetables, which correlates with nutrient preservation.
Texture and Flavor Impacts
Steaming preserves the natural texture and flavor of vegetables by using consistent steam heat, resulting in tender yet firm produce. Steam infusion enhances flavor absorption by circulating steam infused with herbs or spices, creating a more intense and aromatic taste profile.
- Steaming texture retention - Maintains crispness and prevents overcooking, preserving the vegetable's structural integrity.
- Steam infusion flavor enhancement - Infuses vegetables with targeted flavors, elevating the overall sensory experience.
- Moisture control - Steaming controls moisture levels to avoid sogginess, while steam infusion can introduce additional moisture and flavor compounds.
Choosing between steaming and steam infusion depends on desired flavor intensity and textural goals for vegetable preparation.
Cooking Times Compared
Steaming vegetables typically requires 5 to 10 minutes depending on the type and cut size, preserving nutrients and texture effectively. Steam infusion technology accelerates cooking times by delivering high-pressure steam directly into the vegetables, reducing cooking duration by up to 50%. This method also enhances uniform heat distribution, resulting in quicker, more consistent cooking compared to traditional steaming.
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Steaming vegetables typically requires a simple steam basket or an electric steamer that generates steam directly beneath the food. Steam infusion uses specialized equipment that injects steam at high velocity to cook vegetables more evenly and quickly.
- Basic Equipment - Steaming needs only a pot with a lid and a steam basket or an electric steamer, making it accessible and affordable.
- Advanced Machinery - Steam infusion requires a high-pressure steam generator and infusion chamber designed to accelerate cooking and retain nutrients.
- Space and Cost - Steam infusion systems tend to be larger and more expensive, often used in commercial kitchens, unlike the compact, budget-friendly steaming setups.
Best Vegetables for Steaming vs Steam Infusion
What are the best vegetables for steaming versus steam infusion? Root vegetables like carrots and potatoes retain their texture and nutrients best with traditional steaming, while leafy greens such as spinach and kale benefit more from steam infusion for a quicker, gentle cook. Steam infusion evenly distributes heat, making it ideal for delicate vegetables that require precise temperature control.
Related Important Terms
Direct Steaming
Direct steaming for vegetables involves exposing produce directly to steam, preserving nutrients and texture by avoiding water contact that can leach vitamins. This method ensures even cooking and enhanced flavor retention compared to steam infusion, where steam is mixed with liquids, potentially diluting taste and nutrients.
Steam Infusion Cooking
Steam infusion cooking uses high-velocity steam to rapidly penetrate vegetables, preserving nutrients, texture, and color more effectively than traditional steaming methods. This technique reduces cooking time and minimizes nutrient loss by delivering precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution.
Infusion Saturation
Steam infusion delivers higher infusion saturation by surrounding vegetables with superheated steam, enhancing nutrient retention and flavor absorption; traditional steaming often results in uneven heat distribution and moisture penetration. This increased saturation in steam infusion accelerates cooking while preserving texture and vibrant colors more effectively than conventional steaming.
Batch Steam Infusion
Batch Steam Infusion enhances vegetable cooking by evenly distributing steam, preserving texture and nutrients more effectively than conventional steaming. This method uses controlled bursts of steam that reduce cooking time and energy consumption, ensuring consistent quality in vegetable batches.
Low-Pressure Steam Infusion
Low-pressure steam infusion uses gentle steam at reduced pressure to quickly and evenly cook vegetables while preserving nutrients and texture compared to traditional steaming. This method enhances flavor retention and reduces cooking time by maximizing steam penetration without overcooking or leaching vitamins.
Flash Steam Infusion
Flash steam infusion rapidly cooks vegetables by exposing them to high-pressure steam in a short burst, preserving nutrients and vibrant colors more effectively than traditional steaming which relies on prolonged heat exposure. This method enhances texture and flavor retention by minimizing water contact and oxidation, making it ideal for delicate vegetables.
Continuous Steam Infusion
Continuous steam infusion maintains a consistent flow of saturated steam around vegetables, enhancing heat transfer and reducing cooking time compared to traditional steaming. This method ensures uniform cooking and better nutrient retention by preventing overexposure to water, which is common in conventional steam techniques.
Enzyme Retention Steaming
Steaming vegetables preserves enzymes more effectively than steam infusion, as direct exposure to steam at lower temperatures minimizes enzyme degradation. The gentle heat transfer in enzyme retention steaming maintains nutritional quality and enhances the vegetable's natural flavors, supporting healthier cooking outcomes.
Volatile Aroma Preservation
Steaming vegetables preserves volatile aromas by gently cooking with hot steam, minimizing aroma loss compared to higher-temperature methods. Steam infusion enhances flavor retention through rapid steam condensation directly onto the vegetable surface, locking in essential oils and aromatic compounds more effectively.
Steaming vs Steam Infusion for vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com