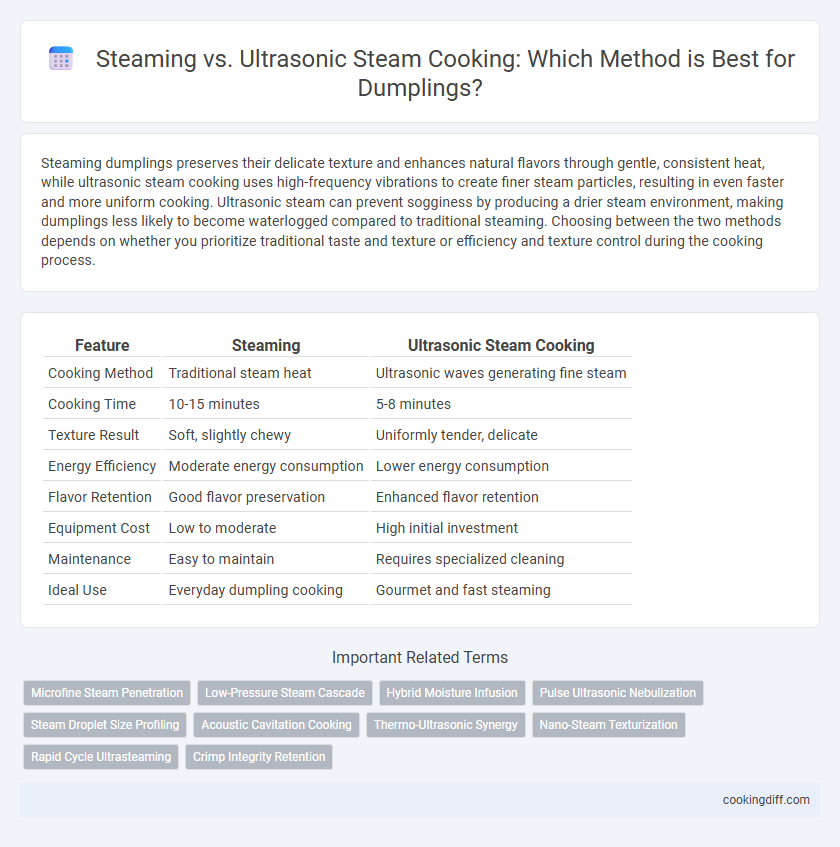
Steaming dumplings preserves their delicate texture and enhances natural flavors through gentle, consistent heat, while ultrasonic steam cooking uses high-frequency vibrations to create finer steam particles, resulting in even faster and more uniform cooking. Ultrasonic steam can prevent sogginess by producing a drier steam environment, making dumplings less likely to become waterlogged compared to traditional steaming. Choosing between the two methods depends on whether you prioritize traditional taste and texture or efficiency and texture control during the cooking process.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Steaming | Ultrasonic Steam Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Traditional steam heat | Ultrasonic waves generating fine steam |
| Cooking Time | 10-15 minutes | 5-8 minutes |
| Texture Result | Soft, slightly chewy | Uniformly tender, delicate |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy consumption | Lower energy consumption |
| Flavor Retention | Good flavor preservation | Enhanced flavor retention |
| Equipment Cost | Low to moderate | High initial investment |
| Maintenance | Easy to maintain | Requires specialized cleaning |
| Ideal Use | Everyday dumpling cooking | Gourmet and fast steaming |
Introduction to Steaming Methods for Dumplings
Steaming dumplings is a traditional cooking method that uses hot vapor to cook food evenly while preserving moisture and flavor. Ultrasonic steam cooking introduces high-frequency vibrations to produce finer steam particles, enhancing heat penetration and cooking efficiency.
- Traditional Steaming - Uses boiling water to generate steam that gently cooks dumplings without direct contact with water.
- Ultrasonic Steam Cooking - Employs ultrasonic waves to create superfine steam particles, promoting faster and more uniform cooking.
- Flavor & Texture Impact - Both methods maintain the dumplings' texture and flavor but ultrasonic steaming can yield a softer, more tender wrapper.
Choosing between steaming methods depends on equipment availability and desired cooking precision for dumplings.
What is Traditional Steaming?
Traditional steaming involves cooking food by surrounding it with hot vapor, usually generated from boiling water beneath a perforated tray or basket. This gentle cooking method preserves the natural moisture, texture, and nutrients of dumplings without direct contact with water.
Unlike ultrasonic steam cooking, traditional steaming relies on consistent steam heat rather than high-frequency vibrations to cook the dumplings evenly. This method has been used for centuries in Asian cuisine to produce tender and flavorful results.
How Ultrasonic Steam Cooking Works
Ultrasonic steam cooking uses high-frequency vibrations to generate a fine mist of steam that cooks dumplings evenly and quickly. This method preserves moisture and texture better than traditional steaming by creating micro-droplets that penetrate food more effectively.
- Ultrasonic transducer - Converts electrical energy into ultrasonic waves to produce high-frequency vibrations.
- Fine steam mist - Ultrasonic vibrations atomize water into tiny droplets, creating a fine steam mist for even heat distribution.
- Enhanced moisture retention - The micro-droplet steam penetrates dumplings quickly, maintaining juiciness and texture during cooking.
Comparing Cooking Times: Steaming vs Ultrasonic Steam
Steaming dumplings typically takes 10-15 minutes to cook thoroughly, preserving texture and flavor. Ultrasonic steam cooking reduces the time to approximately 5-7 minutes by generating fine steam particles that penetrate food faster.
- Traditional steaming - Uses boiling water to create steam that cooks food evenly but may require longer time.
- Ultrasonic steam cooking - Employs high-frequency vibrations to produce dense steam, accelerating heat transfer.
- Cooking efficiency - Ultrasonic steam cuts cooking time nearly in half compared to conventional steaming methods.
Retaining Dumpling Texture and Flavor
| Steaming | Provides gentle heat that preserves the dumpling's delicate texture and retains maximum moisture, enhancing natural flavors. |
| Ultrasonic Steam Cooking | Uses high-frequency vibrations to produce finer steam particles, allowing faster cooking but risking slight texture softening and flavor dilution. |
| Texture & Flavor Retention | Standard steaming is superior for maintaining the dumpling's firmness and rich taste, while ultrasonic steam cooking prioritizes speed over texture fidelity. |
Nutrient Preservation in Both Methods
Steaming preserves essential nutrients in dumplings by using gentle heat that minimizes nutrient loss, particularly water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Ultrasonic steam cooking creates finer steam particles that penetrate food more evenly, potentially enhancing nutrient retention compared to traditional steaming.
Studies show ultrasonic steam cooking can better maintain antioxidants and volatile compounds responsible for flavor and health benefits. Both methods avoid direct contact with water, reducing leaching of minerals and vitamins, thus making them superior to boiling for nutrient preservation in dumplings.
Energy Efficiency: Which Method Wins?
Ultrasonic steam cooking uses ultrasonic waves to generate fine steam particles, resulting in faster heat transfer and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional steaming. Traditional steaming relies on boiling water to produce steam, which typically requires more energy and longer cooking times for dumplings. Energy efficiency studies reveal ultrasonic steam cooking can save up to 30% more energy, making it a superior choice for eco-friendly dumpling preparation.
Dumpling Appearance: Visual Differences
Steaming dumplings results in a glossy, translucent skin that highlights the delicate folds and pleats. Ultrasonic steam cooking produces a smoother, more uniform surface with fewer visible textures or wrinkles. The visual appeal of steamed dumplings often emphasizes traditional craftsmanship, while ultrasonic steam cooking offers a modern, sleek presentation.
Ease of Use and Kitchen Requirements
Which method is easier to use for cooking dumplings, steaming or ultrasonic steam cooking? Traditional steaming requires minimal setup and uses common kitchen equipment such as a steamer basket and pot, making it straightforward for most home cooks. Ultrasonic steam cooking demands specialized devices that streamline temperature control but may require a learning curve and more counter space.
Related Important Terms
Microfine Steam Penetration
Ultrasonic steam cooking generates microfine steam particles that penetrate dumpling wrappers more effectively than traditional steaming, resulting in even cooking and enhanced moisture retention. This precise steam distribution preserves the dumplings' texture and flavor by preventing sogginess and overcooking.
Low-Pressure Steam Cascade
Low-pressure steam cascade in steaming provides consistent, gentle heat that preserves dumpling texture and flavor by preventing overcooking or sogginess. Ultrasonic steam cooking generates micro-droplets for rapid heat transfer but can unevenly distribute steam, making low-pressure steam cascade ideal for delicate dumpling steaming.
Hybrid Moisture Infusion
Hybrid Moisture Infusion combines the benefits of traditional steaming and ultrasonic steam cooking, delivering precise temperature control and uniform moisture distribution for perfectly cooked dumplings. This method enhances texture and flavor by infusing steam particles deeply into the dumpling dough, preventing sogginess while maintaining a tender bite.
Pulse Ultrasonic Nebulization
Pulse Ultrasonic Nebulization in steam cooking generates fine, uniform steam particles that penetrate dumplings more evenly than traditional steaming methods, preserving texture and enhancing flavor. This technique produces consistent moisture and temperature control, reducing cooking time and preventing sogginess compared to conventional ultrasonic steam cooking.
Steam Droplet Size Profiling
Steam droplet size profiling reveals that ultrasonic steam cooking produces finer and more uniform steam droplets compared to traditional steaming, enhancing heat penetration and texture consistency in dumplings. Smaller droplets facilitate quicker cooking by delivering concentrated moisture, resulting in tender dumplings with evenly cooked interiors.
Acoustic Cavitation Cooking
Steaming cooks dumplings by circulating hot vapor heat, preserving moisture and texture without chemical alteration, whereas ultrasonic steam cooking employs acoustic cavitation, generating microscopic bubbles that implode to produce localized high temperatures and pressure, enhancing flavor infusion and accelerating cooking time. Acoustic cavitation in ultrasonic steam cooking disrupts cell walls, improving ingredient absorption and yielding softer, more evenly cooked dumplings compared to traditional steaming.
Thermo-Ultrasonic Synergy
Thermo-Ultrasonic synergy in steaming dumplings combines precise temperature control with ultrasonic waves to enhance heat penetration and moisture retention, resulting in evenly cooked, tender dumplings with superior texture compared to traditional steaming. This method accelerates cooking time while preserving nutritional content and flavor, outperforming standard steam-only techniques.
Nano-Steam Texturization
Nano-Steam Texturization in steaming for dumplings enhances moisture retention and texture by using ultra-fine steam particles that penetrate dough more effectively than traditional ultrasonic steam cooking. This precise nano-scale steam delivery results in a tender yet firm dumpling skin, preserving flavor and preventing sogginess.
Rapid Cycle Ultrasteaming
Rapid Cycle Ultrasteaming uses ultrasonic technology to generate fine steam particles that penetrate dumpling wrappers more quickly and evenly than traditional steaming methods, ensuring faster cooking times and enhanced texture retention. This technique maintains moisture while preventing sogginess, offering superior flavor preservation compared to conventional steam cooking.
Steaming vs Ultrasonic Steam Cooking for dumplings Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com