Steaming preserves nutrients and moisture by cooking food gently with hot steam, making it ideal for healthy and quick meals. Steam frying combines steaming and frying techniques, using steam to cook food rapidly while achieving a crispy texture through minimal oil frying. This hybrid method offers a faster cooking time and enhanced flavors compared to steaming alone.
Table of Comparison
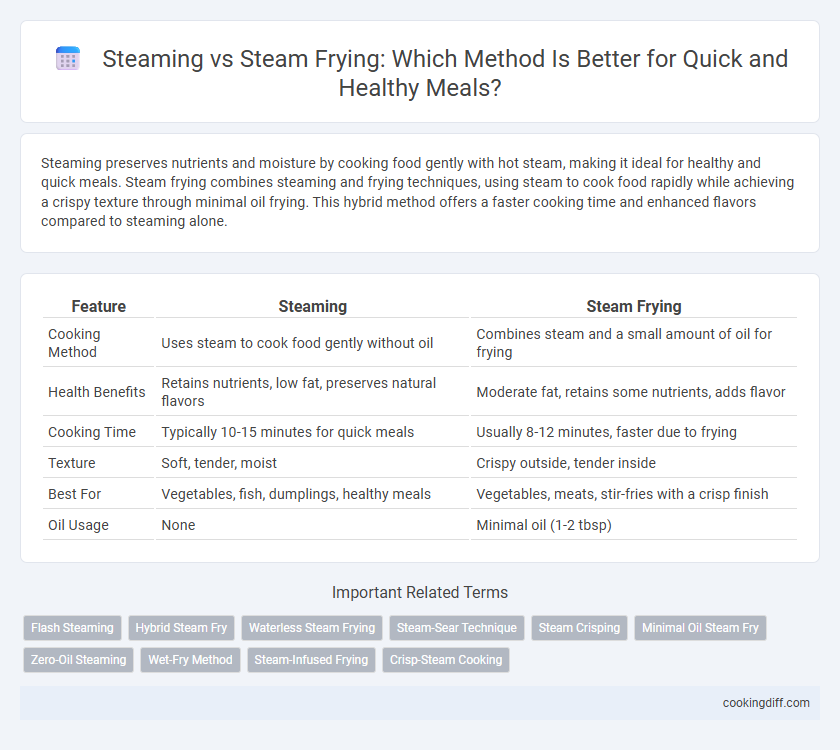
| Feature | Steaming | Steam Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses steam to cook food gently without oil | Combines steam and a small amount of oil for frying |
| Health Benefits | Retains nutrients, low fat, preserves natural flavors | Moderate fat, retains some nutrients, adds flavor |
| Cooking Time | Typically 10-15 minutes for quick meals | Usually 8-12 minutes, faster due to frying |
| Texture | Soft, tender, moist | Crispy outside, tender inside |
| Best For | Vegetables, fish, dumplings, healthy meals | Vegetables, meats, stir-fries with a crisp finish |
| Oil Usage | None | Minimal oil (1-2 tbsp) |
Understanding Steaming and Steam Frying: Key Differences
What distinguishes steaming from steam frying in meal preparation? Steaming cooks food by surrounding it with hot vapor, preserving nutrients and moisture without added fat. Steam frying combines high heat and steam, creating a crispy texture while maintaining the juiciness of quick meals.
Health Benefits: Steaming vs Steam Frying
Steaming preserves more nutrients in vegetables by cooking them gently with moist heat, reducing the loss of vitamins and minerals compared to high-heat methods. Steam frying combines steaming and light frying, which adds flavor and texture but may increase calorie content due to added oils. Choosing steaming over steam frying supports lower fat intake and better retention of antioxidants essential for a healthy diet.
Speed and Convenience: Which Method is Faster?
Steaming cooks food quickly using consistent heat and moisture, making it ideal for vegetables and delicate proteins. Steam frying combines steaming and frying, resulting in faster cooking times due to direct contact with hot oil after initial steaming.
For quick meals, steaming typically takes less active monitoring, thus offering convenience through simplicity. Steam frying speeds up the process slightly but requires more attention to avoid burning or overcooking.
Nutrient Retention: Steaming versus Steam Frying
Steaming preserves more water-soluble vitamins and antioxidants compared to steam frying, which introduces oil and higher heat that can degrade sensitive nutrients. Steam frying offers enhanced flavor and texture but may sacrifice some nutrient retention due to the cooking method.
- Higher Nutrient Preservation - Steaming retains up to 90% of vitamin C and B-complex vitamins by cooking food gently with moist heat.
- Oil Influence on Nutrients - Steam frying uses oil that can cause oxidation of certain nutrients, reducing levels of heat-sensitive vitamins.
- Cooking Time Impact - Faster cooking times in steam frying can partly preserve nutrients but typically less than pure steaming methods.
Texture and Taste: A Flavor Comparison
Steaming preserves the natural moisture of ingredients, resulting in tender and juicy textures, while steam frying adds a slight crispness and caramelization that enhances flavor depth. Both methods offer unique taste profiles ideal for quick meals, with steaming maintaining purity and steam frying providing a richer, more complex palate.
- Steaming retains nutrients - Ensures vegetables and proteins keep their vitamins and minerals intact without added fats.
- Steam frying enhances browning - Creates subtle Maillard reactions that develop a savory, crispy exterior.
- Texture differences - Steaming yields soft, moist dishes, whereas steam frying offers a balance between tenderness and crunch.
Choosing between steaming and steam frying depends on whether you prioritize natural flavor preservation or a more textured, flavorful bite.
Best Foods for Steaming vs Steam Frying
| Cooking Method | Best Foods | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Steaming | Vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and green beans; seafood like salmon and shrimp; dumplings and rice | Retains nutrients and natural flavors while preserving texture and moisture without added fats |
| Steam Frying | Chicken breasts, tofu, mixed stir-fry vegetables, and thin cuts of meat | Combines the moisture retention of steaming with a crispy texture, reducing oil usage for healthier quick meals |
Essential Tools for Steaming and Steam Frying
Essential tools for steaming include a bamboo steamer, heatproof steaming racks, and a pot with a tight-fitting lid to maintain consistent steam. For steam frying, a deep, heavy-bottomed skillet or wok and a steamer insert are necessary to combine frying and steaming techniques efficiently.
Steaming requires a reliable heat source and steamers made from materials like bamboo, stainless steel, or silicone, which preserve the food's nutrients and texture. Steam frying utilizes a versatile pan that can withstand both high heat and moisture, allowing quick cooking with less oil. Mastering the right tools enhances flavor and reduces cooking time in both steaming and steam frying methods.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Steam and Steam Fry
To steam, fill a pot with water, bring it to a boil, and place food in a steamer basket above the water to cook with the rising steam. Cover the pot and maintain the boiling temperature for even cooking while preserving nutrients and moisture.
For steam frying, heat a small amount of oil in a pan, add the ingredients, and pour a splash of water or broth to generate steam within the pan. Cover the pan and cook on medium heat, allowing the steam and oil to combine for a quick, flavorful sear and tenderness.
Quick Meal Recipes: Steamed and Steam-Fried Dishes
Steaming preserves nutrients and provides a moist texture ideal for vegetables and fish, making it perfect for quick, healthy meals. Steam frying combines the benefits of steaming and frying, offering a crispy exterior while retaining moisture inside for flavorful dishes.
- Steamed vegetables - Cooked quickly with minimal oil, maintaining vitamins and natural flavors.
- Steam-fried chicken - Delivers crispy skin with juicy meat inside through a fast cooking process.
- Quick meal versatility - Both methods enable preparation of diverse dishes in under 20 minutes for busy schedules.
Related Important Terms
Flash Steaming
Flash steaming preserves nutrients and texture by rapidly cooking food with high-pressure steam, making it ideal for quick meals without added fats. Unlike steam frying, which combines steam and oil for a crispy exterior, flash steaming ensures moist, tender results while significantly reducing cooking time.
Hybrid Steam Fry
Hybrid steam frying combines the health benefits of steaming with the crispy texture of frying by using controlled steam injection during high-heat cooking. This method reduces cooking time while preserving nutrients and enhancing flavor, making it ideal for quick, nutritious meals.
Waterless Steam Frying
Waterless steam frying combines high heat with minimal moisture, preserving nutrients while delivering a crispy texture ideal for quick meals. Unlike traditional steaming, this method uses hot steam and natural food oils, enhancing flavor without added fat or water.
Steam-Sear Technique
The steam-sear technique combines steaming's rapid, moisture-retentive cooking with a quick high-heat sear to create flavorful, tender meals in minutes. This method outperforms traditional steaming by adding caramelized texture without sacrificing the nutrient preservation and juiciness of steam cooking.
Steam Crisping
Steam crisping combines the gentle moisture infusion of steaming with high-heat air circulation to create quick meals that are both tender and crispy. This technique preserves nutrients like vitamins B and C while delivering a satisfying texture that steam frying often lacks due to its reliance on oil and direct heat.
Minimal Oil Steam Fry
Minimal oil steam frying combines the health benefits of steaming with enhanced flavor and texture from a slight amount of oil, speeding up cooking time while retaining nutrients. This method offers a quick meal solution by using just a teaspoon of oil, reducing fat intake compared to traditional frying while providing a crisp, savory finish.
Zero-Oil Steaming
Zero-oil steaming preserves maximum nutrients and natural flavors by cooking food with moist heat without adding fats, making it ideal for health-conscious quick meals. Steam frying combines steaming and light oil frying to enhance texture, but zero-oil steaming offers a cleaner, lower-calorie option perfect for retaining vitamins and minerals.
Wet-Fry Method
The wet-fry method combines steaming with light frying to retain moisture while adding a subtle crispness, making it ideal for quick meals that balance texture and flavor. Unlike traditional steaming, steam frying uses minimal oil and high heat to create a tender yet slightly caramelized finish, enhancing both taste and nutritional value.
Steam-Infused Frying
Steam-infused frying combines the benefits of steaming and frying by using steam to cook food quickly while retaining moisture and flavor, resulting in a crispy yet tender texture. This method reduces oil absorption compared to traditional frying, making it a healthier option for preparing quick meals without sacrificing taste.
Steaming vs Steam Frying for Quick Meals Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com