Dutch ovens offer superior heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for slow-cooked stews that require consistent temperatures. Clay pots provide a unique porous quality that allows moisture to circulate, enhancing the natural flavors and tenderness of the meat. Choosing between these depends on whether you prioritize durability and heat control or a more traditional, earthy taste profile in your stews.
Table of Comparison
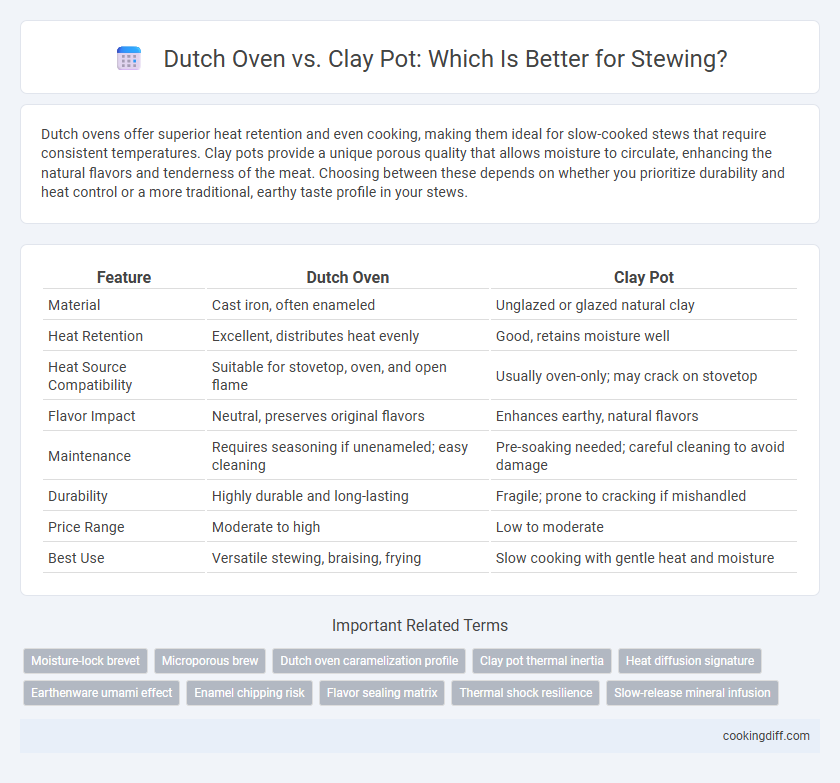
| Feature | Dutch Oven | Clay Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Cast iron, often enameled | Unglazed or glazed natural clay |
| Heat Retention | Excellent, distributes heat evenly | Good, retains moisture well |
| Heat Source Compatibility | Suitable for stovetop, oven, and open flame | Usually oven-only; may crack on stovetop |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral, preserves original flavors | Enhances earthy, natural flavors |
| Maintenance | Requires seasoning if unenameled; easy cleaning | Pre-soaking needed; careful cleaning to avoid damage |
| Durability | Highly durable and long-lasting | Fragile; prone to cracking if mishandled |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Best Use | Versatile stewing, braising, frying | Slow cooking with gentle heat and moisture |
Introduction: Dutch Oven vs Clay Pot for Stewing
Which cookware is better for stewing: a Dutch oven or a clay pot? A Dutch oven offers excellent heat retention and even cooking, ideal for long, slow stews. Clay pots provide natural moisture retention and enhanced flavor absorption, making them perfect for traditional, aromatic stews.
Material Composition: Cast Iron vs Clay
| Material Composition | Dutch Oven (Cast Iron) | Clay Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Excellent heat retention and even distribution due to dense cast iron structure | Moderate heat retention; porous clay allows gradual heat absorption and release |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to chipping and cracking with proper seasoning | Fragile and prone to cracking if exposed to sudden temperature changes |
| Flavor Impact | Neutral material that does not interact with food flavors | Porous composition can absorb and enhance flavors over time |
Heat Retention and Distribution
Dutch ovens excel in heat retention and even distribution due to their thick cast iron construction, making them ideal for slow stewing. Clay pots, while providing gentle and consistent heat, may have less uniform heat distribution, affecting the stew's cooking consistency.
- Heat Retention in Dutch Oven - Cast iron material retains heat longer, ensuring steady cooking temperatures.
- Heat Distribution in Dutch Oven - The heavy base and walls distribute heat evenly, preventing hot spots.
- Heat Retention in Clay Pot - Porous clay absorbs and radiates heat slowly, offering mild but steady cooking.
Moisture Retention and Flavor Infusion
Dutch ovens excel in moisture retention due to their heavy lids and thick metal walls, creating a sealed environment that prevents steam from escaping. Clay pots, made from porous material, allow slow evaporation which can enhance flavor infusion by concentrating the stew's natural taste.
- Dutch Oven Moisture Retention - Thick cast iron traps steam effectively, maintaining juiciness in stews.
- Clay Pot Flavor Infusion - Porous clay absorbs and redistributes moisture, deepening the stew's aroma and taste.
- Heat Distribution - Dutch ovens provide even heat, while clay pots offer gentle, radiant warmth that affects texture.
Choosing between a Dutch oven and clay pot depends on whether you prioritize moisture preservation or enhanced flavor complexity in your stewing process.
Versatility in Cooking Methods
The Dutch oven offers exceptional versatility, allowing for searing, slow cooking, braising, and even baking due to its thick cast iron construction and tight-fitting lid. The clay pot excels in maintaining steady, gentle heat that enhances flavors during slow stewing but is less suitable for high-heat methods like searing. Chefs often prefer the Dutch oven when switching between cooking techniques, while the clay pot is favored for traditional, slow-simmered dishes.
Stewing Performance: Results and Texture
The Dutch oven delivers consistent heat retention and even cooking temperatures, resulting in tender, evenly stewed meats and well-blended flavors. Its heavy cast iron construction promotes deep caramelization and a rich, full-bodied stew texture.
Clay pots provide a unique slow-cooking environment that preserves moisture and enhances natural food aromas, often resulting in a lighter, more delicate stew texture. The porous nature of clay allows steam to circulate gently, preventing overcooking. However, cooking times tend to be longer, and heat distribution can be less uniform compared to Dutch ovens.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Dutch ovens are made from cast iron coated with enamel, offering exceptional durability and resistance to chipping or cracking during regular use. Their non-porous surface simplifies cleaning and prevents odor absorption, reducing maintenance efforts significantly.
Clay pots, while excellent for slow cooking, are more fragile and prone to cracking under thermal shock or mishandling, requiring careful handling. They often need seasoning before use and must be thoroughly dried to avoid mold growth, increasing long-term maintenance requirements.
Ease of Use and Handling
Dutch ovens offer superior ease of use due to their heavy cast iron construction and ergonomic handles, making them simple to move safely, even when hot. Their tight-fitting lids help retain moisture, reducing the need for constant monitoring during stewing.
Clay pots, while excellent for heat distribution, require careful handling as they are more fragile and prone to cracking with sudden temperature changes. They often need soaking before use and delicate cleaning methods, which can complicate the stewing process for beginners.
Health and Safety Considerations
Dutch ovens, typically made from cast iron with an enamel coating, offer excellent heat retention and even cooking, reducing the risk of unevenly cooked stews that can harbor bacteria. Clay pots are naturally porous and may absorb liquids and flavors, but improper seasoning or cracks can lead to contamination or leaching of minerals. When choosing between them, consider that Dutch ovens are generally easier to sanitize and safer for high-temperature cooking, while clay pots require careful maintenance to ensure health safety during stewing.
Related Important Terms
Moisture-lock brevet
Dutch ovens excel in stewing due to their superior moisture-lock brevet, which traps steam and retains liquid for tender, flavorful dishes. Clay pots also maintain moisture but lack the advanced sealing technology of Dutch ovens, making them less efficient in preserving juices during long cooking times.
Microporous brew
A Dutch oven excels in stewing with its thick cast iron walls providing even heat distribution and excellent heat retention, while a clay pot's microporous structure allows gradual moisture evaporation and enhanced flavor infusion, resulting in a uniquely tender and aromatic stew. The microporous ceramic material of clay pots promotes superior breathability compared to the sealed cast iron environment of Dutch ovens, affecting the stew's texture and depth of flavor over long cooking periods.
Dutch oven caramelization profile
Dutch ovens excel in stewing due to their heavy cast iron construction, which provides even heat distribution and superior caramelization, enhancing complex flavors through Maillard reactions. Unlike clay pots, Dutch ovens maintain consistent high heat and develop a rich, deeply browned crust, intensifying the stew's savory profile.
Clay pot thermal inertia
Clay pots exhibit superior thermal inertia compared to Dutch ovens, allowing for consistent, even heat distribution during stewing. This slow, steady heat retention enhances flavor development and tenderness in slow-cooked dishes.
Heat diffusion signature
Dutch ovens offer superior heat diffusion due to their thick cast iron construction, ensuring even warmth distribution and consistent stewing results. Clay pots have porous walls that absorb and slowly release heat, creating a gentle, more uneven temperature profile ideal for delicate stews.
Earthenware umami effect
Dutch ovens provide excellent heat retention and even cooking, ideal for stewing meats and vegetables thoroughly, while clay pots enhance the umami effect by slowly releasing minerals and moisture that enrich flavors and deepen the savory profile of stews. The porous nature of earthenware subtly interacts with ingredients, promoting a natural, earthy taste that intensifies the complexity of traditional stews compared to the more uniform heat distribution of a Dutch oven.
Enamel chipping risk
Dutch ovens with enamel coating offer superior durability and resistance to chipping compared to traditional clay pots, which are more prone to enamel flaking under high heat or mechanical impact. Enamel chipping in clay pots can lead to contamination risks and diminished cooking performance, making Dutch ovens a safer and more reliable choice for stewing.
Flavor sealing matrix
Dutch ovens excel in creating a robust flavor-sealing matrix due to their thick cast iron construction and tight-fitting lids, which retain moisture and intensify the stew's flavors. Clay pots offer a porous quality that allows slow evaporation and subtle air exchange, enhancing natural flavors but resulting in a lighter sealing effect compared to the dense metal of Dutch ovens.
Thermal shock resilience
Dutch ovens exhibit superior thermal shock resilience due to their cast iron construction, allowing rapid temperature changes without cracking, whereas clay pots are more vulnerable to thermal shock and require gradual heating to prevent damage. This durability makes Dutch ovens ideal for stewing methods involving high heat transitions and consistent temperature control.
Dutch oven vs clay pot for stewing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com