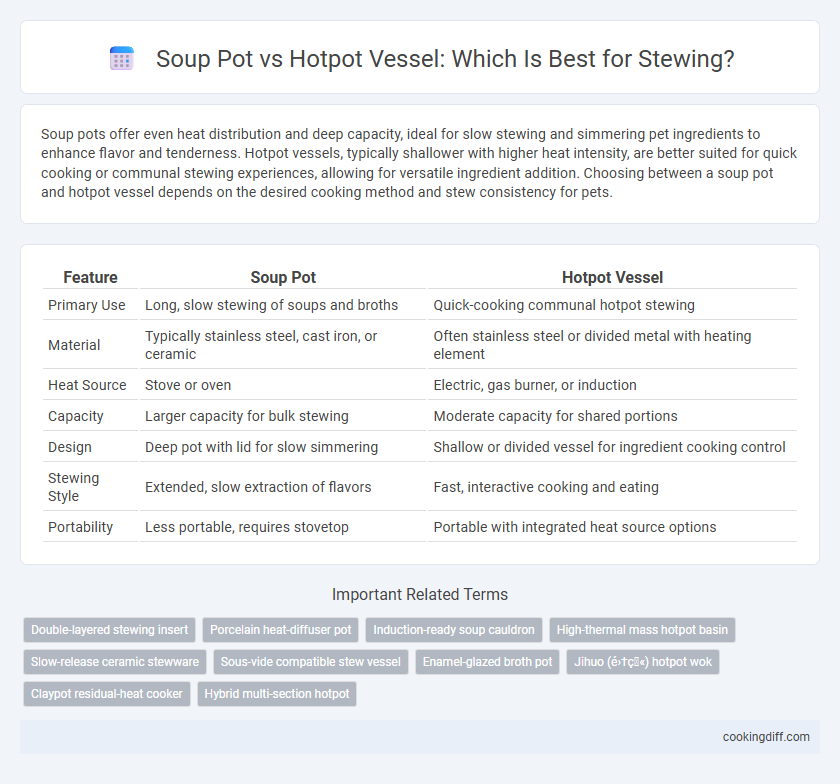
Soup pots offer even heat distribution and deep capacity, ideal for slow stewing and simmering pet ingredients to enhance flavor and tenderness. Hotpot vessels, typically shallower with higher heat intensity, are better suited for quick cooking or communal stewing experiences, allowing for versatile ingredient addition. Choosing between a soup pot and hotpot vessel depends on the desired cooking method and stew consistency for pets.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soup Pot | Hotpot Vessel |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Long, slow stewing of soups and broths | Quick-cooking communal hotpot stewing |
| Material | Typically stainless steel, cast iron, or ceramic | Often stainless steel or divided metal with heating element |
| Heat Source | Stove or oven | Electric, gas burner, or induction |
| Capacity | Larger capacity for bulk stewing | Moderate capacity for shared portions |
| Design | Deep pot with lid for slow simmering | Shallow or divided vessel for ingredient cooking control |
| Stewing Style | Extended, slow extraction of flavors | Fast, interactive cooking and eating |
| Portability | Less portable, requires stovetop | Portable with integrated heat source options |
Introduction: Understanding Stewing in Culinary Traditions
What distinguishes a soup pot from a hotpot vessel in traditional stewing methods? Soup pots, typically made from heavy-gauge materials like cast iron or stainless steel, ensure even heat distribution essential for slow cooking. Hotpot vessels, often ceramic or metal with multiple compartments, cater to communal dining and simultaneous cooking of diverse ingredients at varied temperatures.
Key Characteristics of Soup Pots
Soup pots are typically made from heavy-duty materials like stainless steel or cast iron, ensuring even heat distribution for slow and consistent stewing. Their deep, wide design allows for large quantities of ingredients to simmer gently without excessive evaporation. Equipped with tight-fitting lids, soup pots retain moisture and flavors, making them ideal for long, slow cooking processes.
Essential Features of Hotpot Vessels
Hotpot vessels are specifically designed to maintain consistent heat for prolonged stewing, ensuring deep flavor extraction. Unlike regular soup pots, these vessels often feature materials and shapes that optimize heat distribution and retention.
- Material Composition - Typically made from cast iron or thick stainless steel, hotpot vessels offer superior heat retention compared to standard soup pots.
- Shape and Size - Designed with a wider base and taller sides, hotpot vessels allow even cooking and accommodate various ingredients for extended stewing.
- Heat Source Compatibility - Many hotpot vessels are compatible with open flames and induction stoves, providing versatile cooking options for slow, steady heat.
Material Differences: Soup Pot vs Hotpot Vessel
Soup pots are typically made from heavy-gauge materials like stainless steel or enameled cast iron, offering even heat distribution essential for slow and consistent stewing. Hotpot vessels, often constructed from thinner metals such as aluminum or stainless steel with a built-in heating element, prioritize quick heating and temperature control for interactive cooking.
The material composition of soup pots ensures superior heat retention, making them ideal for long, slow cooking processes that develop rich flavors in stews. In contrast, hotpot vessels are designed with lighter materials and integrated heating, allowing precise temperature adjustments but less optimal heat retention. Choosing between the two depends on whether sustained slow cooking or rapid reheating and communal dining is the cooking priority.
Heat Distribution and Retention Compared
Soup pots are typically made from materials like stainless steel or aluminum, which provide even heat distribution essential for slow, consistent stewing. Hotpot vessels, often crafted from cast iron or ceramic, excel in heat retention, keeping the contents warm for extended periods after cooking.
The superior heat distribution of soup pots ensures ingredients cook uniformly without hotspots, ideal for long stewing processes. In contrast, hotpot vessels maintain a steady temperature, making them better suited for dishes that require continuous simmering and serving directly at the table.
Capacity and Size Suitability for Stewing
Soup pots typically offer larger capacities ranging from 6 to 12 quarts, making them ideal for preparing substantial quantities of stews for families or gatherings. Hotpot vessels usually have smaller sizes, around 2 to 4 quarts, suited for individual or small group servings where rapid cooking and sharing are emphasized. Choosing between these depends on the desired portion size and stewing duration, with soup pots favoring slow, large-batch cooking and hotpots enabling quick, communal meals.
Flavor Development: Which Vessel Performs Better?
Soup pots, typically made from heavy-gauge stainless steel or cast iron, provide even heat distribution essential for deep flavor extraction during stewing. Hotpot vessels, often designed for communal dining with thinner materials, offer less consistent heat, which can impact the depth of flavor development.
- Soup Pots Retain Heat Better - Their thick walls and lids trap moisture and heat, enhancing the melding of flavors over long cooking periods.
- Hotpot Vessels Heat Quickly - Rapid heating benefits quick cooking but may lead to uneven flavor integration in stewed dishes.
- Flavor Concentration - Soup pots enable gradual reduction and concentration of broth, resulting in richer, more complex taste profiles.
Safety and Ease of Use in Stewing
Choosing the right vessel for stewing is crucial for safety and ease of use, with soup pots and hotpot vessels offering distinct advantages. Soup pots typically provide better heat distribution and sturdier handles for safer handling during prolonged cooking.
- Soup Pot Stability - Heavy-bottomed soup pots minimize the risk of tipping and ensure even heat distribution throughout the stewing process.
- Hotpot Vessel Design - Hotpot vessels often feature open tops and side vents, allowing for easier monitoring but requiring careful handling to prevent spills.
- Handle Safety - Insulated and firmly attached handles on soup pots reduce burn risks compared to hotpots with more exposed or lightweight handles.
Selecting a vessel with secure handles and stable construction enhances safety and simplifies the stewing experience.
Cleaning and Maintenance Considerations
Soup pots typically feature smooth, non-porous surfaces such as stainless steel or enameled cast iron, making them easier to clean and more resistant to staining and odor retention compared to traditional hotpot vessels. Hotpot vessels, often made from clay or unglazed ceramic, require careful handwashing and thorough drying to prevent cracks and mold growth during stewing.
Regular maintenance for soup pots involves simple soaking and scrubbing with mild detergents, while hotpot vessels benefit from occasional seasoning to maintain their porous structure and enhance heat distribution. Proper storage of hotpot vessels in a dry, ventilated area is essential to extend their lifespan and preserve their stewing performance.
Related Important Terms
Double-layered stewing insert
A double-layered stewing insert in a soup pot enhances heat distribution and moisture retention, making it ideal for slow-cooking delicate ingredients without overcooking. Hotpot vessels typically lack this feature, resulting in less efficient stewing and a different texture profile in long-simmered dishes.
Porcelain heat-diffuser pot
Porcelain heat-diffuser pots offer superior heat retention and even distribution, making them ideal for delicate stewing processes compared to traditional soup pots or hotpot vessels. Their non-reactive surface preserves the natural flavors and nutrients of ingredients, enhancing the overall stewing experience.
Induction-ready soup cauldron
Induction-ready soup cauldrons, typically crafted from magnetic stainless steel or cast iron, provide even heat distribution and precise temperature control crucial for slow stewing processes. Unlike traditional hotpot vessels that prioritize quick boiling, soup pots designed for induction cooking ensure energy efficiency and maintain steady simmering essential for rich, flavorful stews.
High-thermal mass hotpot basin
A high-thermal mass hotpot basin retains and distributes heat more evenly than traditional soup pots, ensuring consistent temperature control critical for slow stewing processes. This thermal efficiency minimizes hot spots and energy consumption, enhancing flavor extraction and tenderizing ingredients effectively.
Slow-release ceramic stewware
Slow-release ceramic stewing vessels, whether in a soup pot or hotpot form, enhance flavor extraction by evenly distributing heat over extended cooking periods. Their porous structure maintains moisture and nutrients, making them superior for slow-cooked stews that require consistent temperature control and gradual simmering.
Sous-vide compatible stew vessel
A hotpot vessel designed for direct heat exposure often lacks the precise temperature control needed for sous-vide stewing, whereas a soup pot made from stainless steel or enameled cast iron offers superior heat retention and compatibility with immersion circulators for consistent, low-temperature cooking. Choosing a soup pot with tight-fitting lids and durable, non-reactive materials ensures optimal flavor infusion and prolonged simmering essential for sous-vide stew preparation.
Enamel-glazed broth pot
Enamel-glazed broth pots excel in stewing due to their non-reactive surface and even heat distribution, preserving flavor integrity and preventing metallic taste contamination. Unlike traditional hotpot vessels, these pots offer superior durability and easy cleaning, making them ideal for slow-cooked soups and stews that require prolonged simmering.
Jihuo (集火) hotpot wok
The Jihuo (Ji Huo ) hotpot wok excels in stewing by providing concentrated heat distribution that ensures even cooking and enhanced flavor extraction. Unlike traditional soup pots, its design supports precise temperature control and rapid heat retention, making it ideal for slow-cooked, rich stews.
Claypot residual-heat cooker
Claypot residual-heat cookers excel in stewing by retaining and evenly distributing heat, enhancing flavor concentration compared to typical soup pots or hotpot vessels. Their porous material absorbs and radiates warmth slowly, allowing ingredients to simmer gently for richer, more robust stews.
Soup Pot vs Hotpot Vessel for Stewing Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com